Shekhar Gulati
Writings on Software Engineering, Software Architecture, Generative AI and LLMs

7 Days with Java 8
I am maintaining this series on Github now https://github.com/shekhargulati/java8-the-missing-tutorial so please refer to it.
From last year or so I am learning Java 8 and trying to adapt to functional way of thinking. I have used Java 8 in few projects and given few talks. To take my learning to the next level, I decided to share my learning as a blog series with fellow developers, who want to learn Java 8 and remain relevant to the new paradigm shift — functional paradigm. In November 2013, I wrote a popular blog series 30 Technologies in 30 Days in which I blogged about a new technology everyday. The goal was to learn something new every day, build a small app with it, and finally publish a blog. It was a very good experience but I felt it would be more beneficial for the community if I focus on one topic and write about that. So, I decided to start a new initiative 7 Days with X in which I will learn a new technology in depth for a month and then blog about it continuously for 7 days.
Java 8 is not a new topic anymore. There are many good books published on it. Still I meet many Java developers unaware of the power of Java 8. The goal of this blog series is to cover some of the most important Java 8 features and how they can help developers in their day to day programming.
In 7 Days with Java 8 blog series, you will learn about following topics:
- 25th July 2015 — Day 1: Lambdas
- 26th July 2015 — Day 2: Streams
- 27th July 2015 — Day 3: Collector
- 28th July 2015 — Day 4: Optional
- 22nd August 2015 — Day 5: Interfaces
- 25th October 2015 — Day 6: Date-Time API
Share this:
8 thoughts on “7 days with java 8”.
- Pingback: Day 2 — Let’s learn about Streams | Shekhar Gulati
- Pingback: Day 4 — Let’s write Null free Java code | Shekhar Gulati
- Pingback: Java Annotated Monthly – August 2015 | JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA Blog
- Pingback: Day1 Building An Application From Scratch Using Rxjava And Java8 | Xebia Blog
java is a important language for development. thanks for sharing.
Thanks for sharing informative article with us: visit us: http://exltech.in/java-training.html
Thank you so much for sharing such a informative article !
this blog are very easy to understanding for beginners ! https://www.exltech.in/java-training.html
Short and Easy. A great practice to master Java 8 in beginning.
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
JavaScript disabled. A lot of the features of the site won't work. Find out how to turn on JavaScript HERE .
- Fundamentals
- Objects & Classes
- OO Concepts
- API Contents
- Input & Output
- Collections
- Concurrency
- Swing & RMI
- Certification
Assignment Operators J8 Home « Assignment Operators
- << Relational & Logical Operators
- Bitwise Logical Operators >>
Symbols used for mathematical and logical manipulation that are recognized by the compiler are commonly known as operators in Java. In the third of five lessons on operators we look at the assignment operators available in Java.
Assignment Operators Overview Top
The single equal sign = is used for assignment in Java and we have been using this throughout the lessons so far. This operator is fairly self explanatory and takes the form variable = expression; . A point to note here is that the type of variable must be compatible with the type of expression .
Shorthand Assignment Operators
The shorthand assignment operators allow us to write compact code that is implemented more efficiently.

Automatic Type Conversion, Assignment Rules Top
The following table shows which types can be assigned to which other types, of course we can assign to the same type so these boxes are greyed out.
When using the table use a row for the left assignment and a column for the right assignment. So in the highlighted permutations byte = int won't convert and int = byte will convert.
Casting Incompatible Types Top
The above table isn't the end of the story though as Java allows us to cast incompatible types. A cast instructs the compiler to convert one type to another enforcing an explicit type conversion.
A cast takes the form target = (target-type) expression .
There are a couple of things to consider when casting incompatible types:
- With narrowing conversions such as an int to a short there may be a loss of precision if the range of the int exceeds the range of a short as the high order bits will be removed.
- When casting a floating-point type to an integer type the fractional component is lost through truncation.
- The target-type can be the same type as the target or a narrowing conversion type.
- The boolean type is not only incompatible but also inconvertible with other types.
Lets look at some code to see how casting works and the affect it has on values:
Running the Casting class produces the following output:
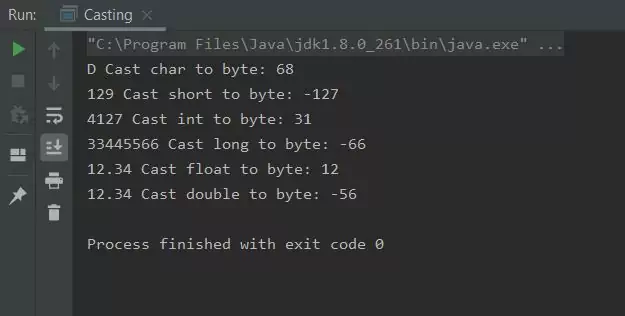
The first thing to note is we got a clean compile because of the casts, all the type conversions would fail otherwise. You might be suprised by some of the results shown in the screenshot above, for instance some of the values have become negative. Because we are truncating everything to a byte we are losing not only any fractional components and bits outside the range of a byte , but in some cases the signed bit as well. Casting can be very useful but just be aware of the implications to values when you enforce explicit type conversion.
Related Quiz
Fundamentals Quiz 8 - Assignment Operators Quiz
Lesson 9 Complete
In this lesson we looked at the assignment operators used in Java.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at the bitwise logical operators used in Java.
Getting Started
Code structure & syntax, java variables, primitives - boolean & char data types, primitives - numeric data types, method scope, arithmetic operators, relational & logical operators, assignment operators, assignment operators overview, automatic type conversion, casting incompatible types, bitwise logical operators, bitwise shift operators, if construct, switch construct, for construct, while construct.
Java 8 Tutorials

IMAGES
VIDEO