
PhD vs. DEng (Doctor of Engineering): What’s the Difference?
Choosing between a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Engineering and a Doctor of Engineering (DEng) is a crucial decision for many aspiring engineers, affecting their career trajectory and professional development. Both degrees offer distinct paths with their own set of benefits and challenges.
While a PhD is traditionally research-oriented, focusing on advancing knowledge and technology through rigorous study and experimentation, the Doctor of Engineering is designed to propel professionals into high-level problem-solving and management roles within the industry.
Understanding the key characteristics of each doctorate degree will help prospective students make an informed decision tailored to their career aspirations.
Table of Contents
PhD in Engineering vs. Doctor of Engineering: Definitions
Each of these programs offers a unique approach to engineering education, catering to different types of students and career goals.
What Is a PhD in Engineering?
A PhD in Engineering is considered the pinnacle of academic achievement in the engineering field. The degree has the following characteristics:
- Research-focused : The degree is aimed at generating new knowledge and technologies through extensive research.
- Academically oriented : Candidates are expected to contribute original findings to the broader engineering community through peer-reviewed publications.
- Long-term commitment : It typically requires four to six years of study, involving coursework and a significant original research project culminating in a dissertation.
What Is a Doctor of Engineering?
The Doctor of Engineering, on the other hand, is tailored for professionals aiming to deepen their technical expertise and lead engineering projects in the industry. The degree has the following characteristics:
- Application-driven : It focuses on applying research to practical problems in engineering.
- Professionally oriented : The degree is geared towards those who wish to excel in high-level industry positions rather than academic roles.
- Integration with industry : It often requires candidates to engage directly with engineering companies or projects, applying advanced concepts to real-world challenges.
Comparing PhD in Engineering and Doctor of Engineering
There are a number of similarities and differences between the two doctorate degrees .
Key Similarities
Although the PhD in Engineering and the DEng degrees cater to different career paths, they share several foundational elements:
- Advanced engineering knowledge : Both degrees require a deep understanding of advanced engineering principles.
- Critical thinking and problem-solving : Students must exhibit exceptional analytical skills to tackle complex engineering challenges.
- Commitment to ethics : Each program instills a strong commitment to ethical practices in both academic and professional settings.
Key Differences
The core distinctions between a PhD in Engineering and a DEng highlight their unique orientations and objectives:
- The PhD in Engineering emphasizes theoretical research and academic contributions.
- The DEng focuses on practical application and industry impact.
- PhD students complete a dissertation based on original research.
- DEng students typically undertake a project that solves a practical industry problem.
- PhD graduates often pursue careers in academia or research institutions.
- DEng holders typically seek leadership roles in engineering firms or technical consultancy positions.
PhD in Engineering vs. Doctor of Engineering: Education Structure and Curriculum
By exploring the structures and curriculums of the degrees, prospective students can gain a clearer understanding of what each degree entails and which might best suit their career goals.
PhD in Engineering Structure and Curriculum
The educational structure of a PhD in Engineering is designed to cultivate expert researchers and academics. Coursework focuses on advanced topics in engineering, mathematics, and related sciences to prepare students for independent research.
Significant time is dedicated to conducting original research , leading to new insights and technological advancements. The culmination of the PhD is a comprehensive dissertation that makes a novel contribution to the field of engineering.
Doctor of Engineering Structure and Curriculum
The curriculum of the Doctor of Engineering is structured to integrate advanced engineering theory with practical application. The advanced practice-oriented coursework is designed to enhance technical and management skills, preparing students for high-level industry roles.
Project work emphasizes solving real-world engineering problems, often in collaboration with engineering firms or through internships. The degree typically culminates in a substantial capstone project that demonstrates the application of engineering principles to industry challenges.
PhD in Engineering vs. Doctor of Engineering: Accreditation
Accreditation is an important aspect of all engineering degrees, and should be considered carefully by prospective students.
PhD in Engineering Accreditation
Accreditation for a PhD in Engineering ensures the quality and rigor of the academic program:
- Importance of accreditation : Accreditation verifies that the educational program meets specific standards of quality and rigor, essential for academic and professional recognition.
- Accrediting bodies : Major accrediting bodies for engineering programs include the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET) and regional accrediting organizations.
- Impact on career : Holding a degree from an accredited institution enhances a graduate’s prospects in academia and research fields, ensuring their qualifications are recognized and respected globally.
Doctor of Engineering Accreditation
Accreditation for the Doctor of Engineering focuses on both academic standards and industry relevance:
- Professional standards : Ensures that the program provides education that is relevant and up-to-date with industry standards.
- Accrediting organizations : Similar to the PhD, DEng programs are often accredited by ABET and may also seek accreditation from industry-specific bodies that recognize professional engineering qualifications.
- Professional recognition : Accreditation is crucial for DEng graduates to be recognized as qualified professionals in the engineering industry, potentially influencing hiring decisions and career advancement.
Career Options for PhD in Engineering and Doctor of Engineering
Both degrees prepare graduates for different professional paths. Students need to recognize the importance of choosing a degree that aligns with one’s engineering career aspirations and personal strengths.
PhD in Engineering Careers
A PhD in Engineering opens doors to a range of career opportunities, primarily in academia and research:
- Academic positions : Many PhD graduates become university professors, contributing to academic knowledge and educating the next generation of engineers.
- Research institutions : Some may hold positions in government or private research institutions where they can continue to develop new technologies and solutions.
- Specialist roles : Highly specialized industries such as biotechnology, nanotechnology, or renewable energy often seek PhD graduates for their advanced research capabilities.
Doctor of Engineering Careers
The career paths for Doctor of Engineering graduates are oriented toward industry and applied engineering solutions:
- Engineering management : Graduates may pursue leadership roles within engineering firms, overseeing projects and teams.
- Project management : Some may find jobs managing large-scale projects, ensuring they meet technical specifications, budgets, and timelines.
- Consultancy : Some graduates take positions providing expert advice in specific areas of engineering, often as an external consultant to various industries.
PhD in Engineering vs. Doctor of Engineering: Salary and Job Outlook
Examining the salary and career prospects related to the PhD in Engineering and DEng degrees can help prospective students gain insight into degree outcomes.
PhD in Engineering Salary
Graduates holding a PhD in Engineering are positioned for competitive salaries, especially in academia and specialized research roles:
- Average annual salary : According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for postsecondary engineering teachers was approximately $106,910 as of May 2023, though this can vary widely depending on the specific field and location.
- Salary range : Professor of engineering salaries can range from about $49,000 to over $182,000.
- Factors affecting salary : Industry, geographic location, and the specific engineering discipline significantly influence salary outcomes.
Doctor of Engineering Salary
The Doctor of Engineering degree typically leads to higher-paying positions in the industry due to its focus on applied engineering and management:
- Average annual salary : The median annual salary for architectural and engineering managers was approximately $165,370 as of May 2023, according to the BLS.
- Salary range : Starting salaries begin around $107,000, with potential to exceed $233,000 in senior management or consulting roles.
- Industry variance : Salaries can be particularly high in sectors such as aerospace, manufacturing, and systems engineering.
PhD in Engineering Job Outlook
The job outlook for PhD in Engineering graduates remains positive, reflecting the ongoing need for advanced expertise in research and development:
- Growth projection : The BLS projects that engineering teaching positions , commonly held by PhDs, will grow by 9% from 2022 to 2032.
- Emerging fields : Significant growth is expected in areas like renewable energy, robotics, and biomedical engineering, driving demand for research and development experts.
- Academic opportunities : The academic sector continues to offer opportunities, although competitive, for tenure-track positions.
Doctor of Engineering Job Outlook
Doctor of Engineering graduates have a strong job outlook in various industry sectors, especially those that value practical engineering leadership:
- Growth projection : Engineering management positions are expected to expand by about 4% over the decade, indicating stable demand for engineering leaders.
- Professional advancement : The degree is particularly valuable for professionals looking to ascend to executive-level positions in technical companies.
- Sector-specific demand : High demand in sectors such as construction, consulting services, and government projects.
This section highlights the salary expectations and job prospects for graduates of both PhD in Engineering and Doctor of Engineering programs, underscoring the potential financial and professional rewards of each path.
Tips for Choosing Between a PhD in Engineering and a Doctor of Engineering
Choosing between a PhD in Engineering and a Doctor of Engineering depends largely on individual career goals and personal interests. Here are some considerations to help prospective students make this important decision:
- Assess career goals : Consider whether your interest lies in academic research or practical industry applications. A PhD is ideal for those interested in research and teaching, while a DEng suits those aiming for senior engineering management roles.
- Consider industry requirements : Some industries may value the practical skills of a DEng more highly, whereas academia and research institutions typically require a PhD.
- Evaluate long-term objectives : Think about where you want to be in 10-15 years. Does one degree align better with your envisioned career path?
- Seek advice : Talk to current students and professionals in both tracks to understand the realities and demands of each path.
- Financial and time commitments : Be realistic about the time and financial investment each degree requires and what you can commit to.
What are the main differences between a PhD in Engineering and a Doctor of Engineering?
- Focus : PhD programs are research-oriented, ideal for those interested in academic careers or deep specialization in a field. DEng programs are application-oriented, designed for professionals aiming for high-level industry positions.
- Outcome : PhD graduates often pursue careers in academia or specialized research, while DEng graduates typically move into senior management or consultancy roles in engineering.
How long does it typically take to complete a PhD in Engineering versus a Doctor of Engineering?
- PhD in Engineering : Generally takes between four to six years, depending on the research project and dissertation requirements.
- Doctor of Engineering : Typically completed in three to five years, as it often integrates professional experience and may have a more structured curriculum.
Can a Doctor of Engineering degree lead to a teaching position in universities?
Yes, although less common than PhD holders, DEng graduates can teach, especially in universities that emphasize practical skills and applied engineering. However, tenure-track positions may prefer candidates with a PhD.
What kind of financial investment is involved in pursuing these degrees?
The cost can vary widely depending on the institution and the country. Generally, PhD programs may offer more funding opportunities, such as scholarships and stipends, due to their research focus. DEng programs may have less funding available but are often shorter in duration.
Is it possible to switch from a DEng to a PhD program or vice versa?
Switching between the programs is possible but may require fulfilling additional prerequisites or adjustments in one’s research focus. It’s important to consult academic advisors to understand the implications and requirements.
Are there online options available for either degree?
Yes, many universities now offer online or hybrid versions of both PhD and DEng programs. These options provide flexibility but require self-discipline and may have different networking opportunities compared to traditional on-campus programs.
Explore the PhD in Engineering vs. Doctor of Engineering Differences
Both the PhD in Engineering and the Doctor of Engineering offer valuable pathways to fulfilling and lucrative careers in their respective fields. The choice between a research-oriented PhD and a practice-oriented DEng should be guided by personal career aspirations, industry demands, and lifestyle considerations.
By carefully evaluating these factors and utilizing the resources available, prospective students can make an informed decision that best suits their professional goals and personal preferences. This careful deliberation will ensure that they embark on a path that not only meets their academic and professional needs but also enriches their personal growth and career satisfaction.
For further exploration and to aid in decision-making, the following resources can be helpful:
- Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology : ABET provides a list of accredited engineering programs, which is crucial for ensuring the quality of your education.
- Professional associations : Organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) offer resources for engineering students and professionals.
- Career planning tools : Organizations like Payscale and the BLS offer valuable tools for researching potential careers and salary data.
- University career services : Most universities offer career services to their students, which can help in understanding the prospects and requirements of both degrees.
What Is the Benefit of an EngD Degree vs. a Traditional PhD Degree?

Krystle Dodge
Managing Editor
Share this on:
Ready to start your journey?
In this article, we will be covering…
Going to school to earn a doctoral degree is a huge endeavor. Engineering doctoral students must also make a huge decision about which type of doctorate degree they will pursue. There is the traditional Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree to consider, but there is also the Doctor of Engineering degree, also called the EngD or DEng degree.
As you may expect, there are several similarities between the EngD and PhD paths. Both of these degrees are considered terminal degrees, which means that they are the highest level of academic study available. Either the Ph.D. or the D.Eng. can help you advance your engineering career, but the differences between these two doctoral degree programs are significant. If you choose the Doctor of Engineering degree over the Ph.D. program, some of the benefits you will receive include a stronger focus on practical application in professional engineering practice, more extensive preparation for industry job opportunities and differences in when in their careers students undertake doctoral study and how long it takes to earn their degrees.
What Is a Doctor of Engineering Degree?
Just about everyone has heard of the PhD, the type of doctoral degree that is, to most people, more recognizable than any other doctorate besides the ones granted to physicians by medical schools. The PhD is a type of doctorate that is awarded in all kinds of fields, from science and math to history, English and education. A PhD is traditionally a research-focused degree, although not all PhD holders go on to work in academic research.
The Doctor of Engineering degree is less well-known than the PhD, but it’s still a good option to consider for many engineers. EngD degrees are professional-focused, rather than research-focused, areas of doctoral-level study. As such, they emphasize applied engineering knowledge and research over basic research meant primarily to advance knowledge of the field. Generally, Doctor of Engineering degree programs are intended for engineering practitioners who want to advance their skills in industry work rather than preparing for opportunities in academia.
All in all, 10,476 students earned some sort of doctorate in an engineering discipline in 2020, according to the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics .
Doctor of Engineering vs. PhD Degree Programs
When pursuing either a Doctor of Engineering or a PhD in engineering degree, you will undertake challenging coursework that delves deep into an engineering discipline and develop your skills in conducting engineering research. However, there’s no question that these degrees have major differences, particularly in their areas of focus, the job opportunities for which they prepare graduates and the time it takes to earn the doctorate degree.
Professional vs. Research Focus
The most critical difference between the Doctor of Engineering and Doctor of Philosophy degrees is that the EngD is a professional degree, while the PhD is a research degree. A traditional Doctor of Philosophy focuses on engineering theory and scholarship, heavily emphasizing original research work that can take years. A professional doctorate, sometimes called an applied doctorate , focuses on developing specialized skills for practical application in the engineering workforce.
EngD degree programs are sometimes offered in different areas of specialization. For example, if you want to move up into a leadership position, you might choose to earn a Doctor of Engineering degree in engineering management. A Doctor of Engineering in manufacturing can be beneficial if you are one of the more than 578,000 engineers working in the manufacturing industry, which is the top employer of engineers, the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported. You could also seek a Doctor of Engineering degree in an engineering discipline such as biomedical, civil, electrical, chemical or mechanical engineering, just as you would typically pursue a PhD in a particular branch of engineering.
Any professional doctorate in engineering degree will focus on analyzing and applying research and theory to solve real-world industry problems. That isn’t to say that students in a Doctor of Engineering program get out of doing research. In fact, depending on your engineering school, you might need to submit a dissertation that presents original research for your EngD degree just as you would for a traditional PhD degree. However, the outcome of earning an EngD degree isn’t preparation for a career in theoretical research and academia but rather the cultivation of technical leadership skills.
Some Doctor of Engineering programs culminate in a portfolio that consists of the students’ plans, prototypes, user manuals, computer simulations and patent applications. This engineering portfolio can be used to demonstrate your skills and vision to potential employers or, if you aspire to launch your own startup, to investors.
Job Opportunities Outside of Academia
Historically, Ph.D. degrees in engineering were meant for engineers who were seeking tenure-track academic or industrial research careers. Engineers working in private industry and the corporate sector were the ones who would pursue a Doctor of Engineering degree. This terminal degree could potentially allow engineers to teach at the college level, but more typically, it prepared them for advancement to highly technical engineering practice roles or leadership opportunities.
Now, though, the differences between a professional doctorate and a Ph.D. in terms of career outcomes are not as clear-cut. Some PhD graduates work in the private sector, and some colleges and universities hire candidates with an EngD degree for academic research and teaching roles. This overlap in career opportunities shows that both doctoral degree paths in engineering are decently versatile. It also makes it easier for prospective doctoral students to decide whether they want to pursue a PhD or an EngD without having to worry that choosing the “wrong” educational path could limit their career options too much.
Generally, though, if conducting new research is what most appeals to you, the Ph.D. is the more appropriate career path, while students eager to move up in industry roles find the Doctor of Engineering degree to be more beneficial. The EngD degree is a good choice when you want to develop advanced technical skills and knowledge in a specialized area that would put you in a senior-level role. You can also use this education to cultivate the leadership skills necessary for high-ranking managerial positions in engineering, such as engineering director or engineering program manager.
Another distinction between the two degree paths is the source of research funding. Ph.D. projects are often funded by grants, while an industry or public sector organization might provide the funding for research done by Doctor of Engineering students.
Differences in Timing and Duration of Degree
The time it takes a student to earn a degree, and the time when an engineer begins his or her doctoral studies, also differentiate the EngD from the PhD degree. Generally, a professional doctorate degree in engineering takes at least three years of study—but still significantly less time than a PhD program takes.
While PhD programs are often structured to take three to five years to complete, they can also take longer. In fact, CBS News reported that the average doctoral student takes more than eight years to complete their PhD degree, and just 57 percent of PhD students will complete their doctoral studies within 10 years. Those who don’t manage to finish their PhD degree during this timeframe frequently drop out of school without receiving their degree, often with nothing to show for their many years of study and effort.
A shorter timeline to earning a degree does more than improve your odds of actually finishing the program as planned. Getting your degree in fewer semesters can save you the costs of additional tuition and fees, which can quickly add up to thousands—and potentially, tens of thousands—of dollars. It also allows you to start putting your doctoral education to work sooner, which means you start recouping on your investment in an advanced education earlier. Aside from the costs of actually going to school, there is an opportunity cost from being out of the workforce, especially if you plan to work in industry rather than academia. Shortening the time you’re in school can decrease this opportunity cost.
The time it takes to get your degree isn’t the only difference pertaining to the timing involved in earning a doctorate in engineering. There are also distinctions in the age and career level at which students typically begin working toward their EngD vs. their PhD. Generally, students pursuing a traditional Ph.D. degree often start their graduate coursework early in their careers. This typically means pushing back their entry into the workforce by several years. Students in a Doctor of Engineering program are often mid-career industry practitioners. As such, these doctoral students have a good deal of work experience under their belts already. Often, students pursuing a professional Doctor of Engineering degree are using graduate school to help them advance to senior-level roles.
On average, PhD students who start their degrees by age 25 are 33 by the time they graduate, and they typically have comparably little work experience outside of school. On the other hand, EngD students are often significantly older when they start working toward their doctorate, but as mid-career professionals, they bring plenty of work experience with them. Thus, a newly enrolled EngD student might be older than PhD graduates in their field, but they are still likely to spend less time in school overall and have more work experience.
The length of time it takes to earn your doctoral degree matters in part because so many students who begin pursuing a doctorate degree in engineering never complete their studies, according to U.S. News & World Report .
What to Expect From Doctorate of Engineering Curricula
As a doctoral student in engineering, you will take some of the most challenging upper-level classes available at a university. The exact curriculum you complete will vary depending on the school you enroll in and the discipline of engineering you choose to study at the doctoral level. Since doctoral program curricula often allow for considerable specialization and customization, the exact blend of classes you take may be unique to you.
A student pursuing a Doctor of Engineering Management degree , for example, might take classes in entrepreneurship and technology, logistics planning, research formulation for engineering management, technology commercialization, data analysis in engineering, applied optimization modeling and uncertainty analysis in engineering and cost engineering. Students pursuing a Doctor of Engineering in Systems Engineering might study the foundations of systems engineering, systems engineering processes, leadership and innovation in systems engineering, engineering project and program management and engineering risk analysis. Beyond their mandatory core coursework, though, these students may choose technical electives and depth or concentration courses that match their interests in areas ranging from cybersecurity to the grid integration of wind power systems.
Lessons that take place in a classroom or laboratory only make up part of the work that constitutes a Doctor of Engineering curriculum. Generally, students in these programs will have some opportunity to practice applying what they have learned in areas of praxis research or in the form of a professional internship experience. The student typically chooses the research area of their praxis, working in conjunction with an advisor, and then devotes considerable time and effort—though usually not on the same level as you might encounter in a PhD program—to conducting this research. Among Doctor of Engineering degree programs that require an internship instead of praxis research, the internship may be lengthy, often taking up to a year to complete. Naturally, the coursework you complete in the classroom and the lab and the work you do in research or a professional internship should fit together neatly for you to gain the full benefit of the Doctor of Engineering education and experience.
Whether you need a master’s degree or can jump straight to doctoral studies from your bachelor’s degree depends on different institutions, not only EngD vs. PhD programs. Some schools offer programs that follow both structures. Generally, a Doctor of Engineering degree program that accepts master’s degree students expects these applicants to have already completed graduate-level technical elective coursework, while programs that pick up where bachelor’s degrees leave off include this coursework. Keep this difference in mind when comparing the credit requirements and target graduation time between different Doctor of Engineering programs. A shorter EngD degree program is likely to require students to already hold a master’s degree, which means that you may be looking at another one to two years of study—and potentially even more, if you pursue a master’s degree part-time—than what the Doctor of Engineering program itself entails.
Where a PhD student must write and defend a dissertation, a student pursuing the EngD degree might instead work on a project or praxis research.
Related Resources:
Top 10 Highest Paying Engineering Careers
How Advanced Does My Degree in Engineering Need to Be to Get a Good Job?
What Is the Demand for a Graduate Degree in Engineering?
What Is the Fastest School for a Doctoral Degree in Engineering?
What Degree Do You Need to Be a Biomedical Engineer?
What Civil Engineering Courses Will I Have to Take for a Degree in Civil Engineering?
For Further Reading:
Which Degree Is Best for a Software Engineer?
What Are the 5 Best Careers in Environmental Science?
Want to continue learning?
Top 15 master’s in social work degree programs.
In the field of social work, you can do a lot with a bachelor’s degree, like attaining an entry-level job as a mental health […]
What Can I Do With a Fashion Degree?
“What you wear is how you present yourself to the world, especially today, when human contacts are so quick. Fashion is instant language.” —Miuccia […]
The 10 Best Online Masters in Chemical Engineering Degrees
Chemical engineering is at the heart of almost all great scientific and engineering advancements. From concrete used for skyscrapers that’s more resistant to torsion […]
© Copyright 2024 DegreeQuery.com | Advertiser Disclaimer
- The Doctor of Engineering (EngD) – A Guide
Written by Sarah Hastings-Woodhouse
Studying a Doctor of Engineering (EngD) is an opportunity to collaborate with an industrial partner on ground-breaking Engineering research.
You'll work on addressing industrial challenges with companies ranging from small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to multinational corporations. And the best part is, they'll sponsor you to do it!
This guide explains what the EngD is, what the costs are and how to apply (including entry requirements). We also cover the differences between the EngD and a traditional PhD.
If you already know that an EngD is the right choice for you, you can browse EngD programmes here on the website.
On this page
What is an engd.
The Doctor of Engineering is a specialised, industry-focused, professional doctorate in Engineering. Unlike a PhD, the EngD contains a significant taught component. This equips you with the technical and management skills needed to excel in your future career.
EngD candidates are known as research engineers. Together with a collaborating company and an academic supervisor, research engineers work to complete an independent research project addressing a live industrial challenge.
The EngD is a doctoral qualification, meaning that it is the highest qualification someone can achieve in the field of Engineering and of equal academic status to a PhD. However, there are some important differences between the two.
How much does it cost to do an EngD?
Annual tuition fees for EngD programmes in the UK are similar to PhD fees, ranging from £4,410-4,600 on average. Fees for international students will be considerably higher and can be up to £24,600 .
Most EngD programmes have funding attached, which is provided by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPRSC), usually with a contribution from your industry sponsor. Research engineers will normally receive an annual, tax-free stipend to cover living costs and tuition fees, with sponsors often providing a ‘top-up’ of around £3,000.
For some EngD programmes, studentships are only available to UK students. This means international applicants will have to self-fund. There are many options available for students taking this route, which we cover in our guide to international PhD funding .
Who should apply for an EngD?
An EngD is a good option for anyone seeking the blend of technical and commercial skills needed for a senior position within the Engineering industry, whilst conducting original research at the doctoral level.
Unlike many other professional doctorates, which are designed for professionals with several years’ workplace experience, the EngD can also be a suitable qualification for those at the beginning of their career. It is not uncommon for students to progress straight onto an EngD after finishing their Masters or even undergraduate degree (that’s right, you might be able to skip the Masters entirely ).
That said, many EngD applicants are Engineering professionals who are returning to higher education as a means of career development. You may even be a current employee of an industry sponsor looking to part-fund doctoral research that will serve the interests of the company – meaning you’ll be able to complete your EngD in collaboration with your employer!
If you’re not sure whether an EngD is the right qualification for you, it's a good idea to discuss your research interests and career aspirations with a programme tutor or administrator, who will be able to advise you.
Does an EngD lead to Chartered Engineer Status?
There are no qualifications that automatically lead to Charted Engineer (CEng) status. But, those who hold an EngD with an accredited Bachelors in Engineering or Technology qualify for interim registration with the UK Engineering Council. This can fast-track you to eventual CEng status.
What is the difference between an EngD and a PhD?
The EngD and the PhD are of equal academic status but differ in terms of content and delivery. An EngD is a more practical degree focusing on tangible industry outcomes whereas a PhD involves contributing to academic scholarly literature and research.
Here are a few key points of comparison:
Research environment
A PhD is an academic research degree that will largely take place on your university’s campus. Since an EngD is a collaboration between Research Engineer and industry sponsor, you’ll be expected to spend around 75% of your time working on the premises of your collaborating company.
Programme content
Whereas the PhD is a pure research degree, an EngD has a significant taught component. During the first one to two years of your EngD, you’ll take taught modules focusing on key technical, business, and personal competencies.
Supervisors
PhD candidates will have a single academic supervisor (or supervisory team) based at their university. Research engineers will be supported by an industry supervisor and an academic supervisor.
Subject areas
EngD courses are only available in Engineering subjects, while PhDs are available in all subjects where academic research is carried out.
EngD students will often receive a more generous stipend than PhD candidates, due to contributions from their industry sponsor.
What are the entry requirements for an EngD?
Unlike many other professional doctorates, EngD programmes tend not to have specific work experience requirements. This means you can apply straight after graduating.
The minimum entry requirement for EngD programmes is usually a 2:1 Bachelors degree in Engineering or related subject. Some programmes require a first-class undergraduate degree, but will consider applicants with 2:1 if they also have a relevant Masters and substantial work experience.
What is the application process for an EngD?
The exact process of applying for an EngD can vary between institutions – but the below should give you a rough idea of what to expect.
Finding a sponsor
All EngD students are paired with an industry sponsor. You may already have a sponsor at the time you submit your application (if they are your employer, for example), or you may be applying to a specific project that already has a sponsor listed.
If you do not have a sponsor, you can usually view a list of current opportunities on your university’s website and indicate your preference in your application. Alternatively, your university might pair you with a sponsor based on your research interests.
Submitting your application
You’ll submit your application directly to your chosen university, usually through an online portal. Every programme will have different specifications, but you’ll usually need to provide a combination of the following:
- An academic CV
- A personal statement
- A cover letter
- The details of two referees
Some programmes may also require you to submit a research proposal. If you already have an industry sponsor, this will be a document you have produced in collaboration with the company. If you are applying for a specific vacancy, then your research proposal will usually outline your planned approach to the project.

What's it like to study an EngD?
The vocationally orientated nature of the EngD means that you’ll spend at least half your time (and often much more than this) working directly with the company sponsoring your project. Research engineers are supported by an industrial supervisor, as well as an academic supervisory team within their university.
EngD programmes are usually split into two distinct phases:
- The first phase of your EngD (usually lasting one or two years) will have the strongest taught element. Modules cover technical aspects of Engineering relating to your research and provide commercial and management training. Teaching methods include lectures, seminars, group work, lab-based practical exercises, and case studies.
- The second phase will have a stronger focus on applied research. You’ll likely spend the bulk of your time working towards your final project on the premises of your sponsoring company and getting hands-on industrial experience.
How will I be assessed?
In the initial stage of your EngD, you will take taught modules, which are usually assessed through examinations and coursework. You’ll need to pass all compulsory modules (and the required number of optional ones) to be awarded your EngD.
On an annual basis, you may submit progress reports reflecting on the work you have done so far and outlining the next stages of your research plan. This will ensure you are continuing to meet the standards set by your sponsor and academic department year-on-year.
You'll usually submit your final research project in the form of either a portfolio or thesis . You’ll defend your work and explain its industrial applications in a viva voce exam .
Find an EngD programme
Ready to start applying? Browse EngD programmes here on FindAPhD
Want More Updates & Advice?

Looking for the best universities for PhDs in Electrical Engineering in the USA? Compare ranking tables from top sources here, along with their methodologies.

Looking for the best universities for PhDs in Electrical Engineering in Canada? Compare ranking tables from top sources here, along with their methodologies.

Looking for the best universities for PhDs in Engineering in the USA? Compare ranking tables from top sources here, along with their methodologies.

The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) provides generous PhD funding for UK Engineering and Physics subjects. Find out what an EPSRC studentship involves and how to apply.

Considering an innovative modern PhD in Science, Engineering and related fields? Or looking to tackle cutting edge Artificial Intelligence research? We've taken a closer look at funded PhD opportunities at new specialised Centres for Doctoral Training.
Sarah Hastings-Woodhouse
Sarah joined FindAPhD as a Content Writer in 2021 and produces polished and thoroughly researched pages to inspire and inform prospective postgraduate students. In her time at FindAPhD, she has gained a comprehensive understanding of the postgraduate journey and has engaged with hundreds of prospective postgraduates while manning the advice stand at our popular study fairs.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

Difference between EngD and PhD
The EngD programme ‘Design for AgriFood and Ecological Systems’ is focused on practice and on the needs of the industry and society, and less on gaining new scientific knowledge, such as for a PhD.
The objective of the programme for the Engineering Doctorate is to obtain knowledge about scientific ideas and methods and then apply this in a design. The study programme is therefore not focused on learning to develop new fundamental scientific knowledge (i.e. curiosity-driven research such as for a PhD), but on combining new and existing scientific knowledge from a variety of knowledge domains, with a focus on applying it in innovative designs and prototypes through the use of design methodologies.
The three most noticeable differences between a PhD and an EngD are:
- A PhD candidate focuses on research at the university, whereas an EngD candidate focuses on technological designs in industry and society
- A PhD programme has a duration of four years whereas the EngD takes two years to complete
- A PhD leads to the title “Doctor” (Dr., equivalent to PhD). The designer programme leads to an “Engineering Doctorate” (EngD).
- Menu Close
- Search
About the Program
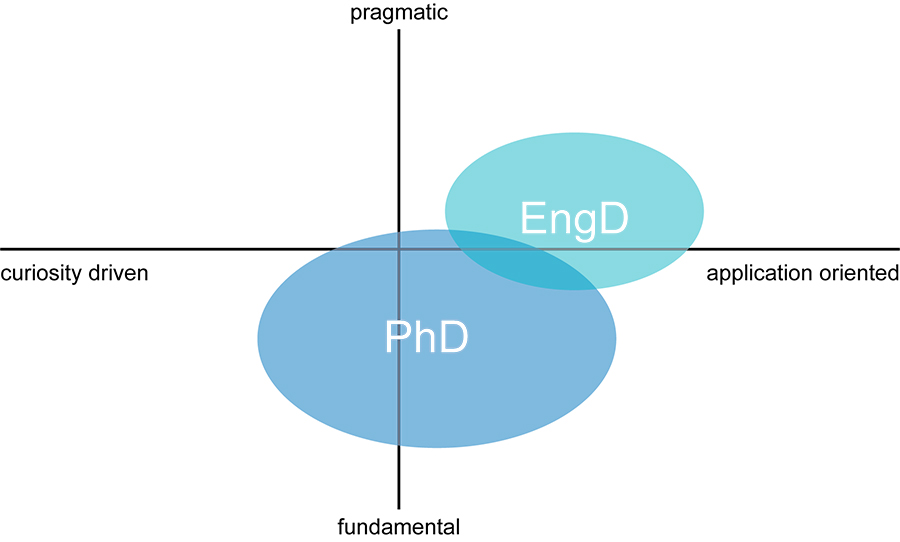
- DEng graduates are more knowledgeable, innovative, and creative problem solvers, and are better prepared for technical leadership roles in industry and the public sector.
Johns Hopkins University’s Doctor of Engineering program provides professional engineers with the advanced technical expertise they need to succeed in industry and the public sector by emphasizing creative problem solving and the innovative application of technical knowledge.
- The DEng program is a doctoral-level graduate degree program designed for working engineers and scientists.
- It is a full-time program that is pursued non-residentially.
- The program takes the form of a research collaboration between a student’s employer and the Whiting School of Engineering. Students are actively mentored by a primary advisor in the Whiting School as well as a co-advisor at their place of employment.
- Students customize their program to meet their professional goals, and immediately contribute to their current job responsibilities.
To learn more, please review the admission requirements or contact our office .
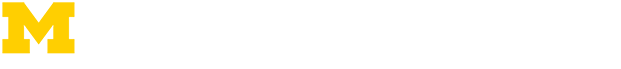
In this section
- Rackham Predoctoral Fellowship Program
- Master's Programs
- Certificates
- Admitted CECS Graduate Students
- Advising, Registration, and Forms
- Tuition, Scholarships, and Funding
- CECS Graduate and Professional Student Appreciation Week
- Graduate Recognition and Doctoral Pinning Ceremony
- Path to Degree
- Academic Policies & Code of Conduct
Ph.D. and D.Eng. Programs
The dearborn difference.
The College of Engineering and Computer Science (CECS) offers 6 doctoral programs: 4 full-time Ph.D. programs and 2 Doctor of Engineering (D. Eng.) programs. In CECS, we are committed to excellence. Our doctoral programs are administered and taught by tenure-track faculty with active theoretical and translational research interests. Students and faculty work collaboratively and develop strong mentor relationships.
Located in the automotive industry's global epicenter in Metro Detroit, the university has developed strategic partnerships with major automobile companies and suppliers. Faculty and students have a variety of opportunities and regularly collaborate on innovative research with industry partners.
CECS Ph.D. Alumni Stories
Program options.
We offer both the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) and the Doctor of Engineering (D. Eng.)
- Ph.D. in Computer and Information Science
- Ph.D. in Electrical, Electronics, and Computer Engineering
- Ph.D. in Industrial and Systems Engineering
- Ph.D. in Mechanical Sciences and Engineering
- D.Eng. in Automotive Systems and Mobility
- D.Eng. in Electrical and Computer Engineering
Rackham Graduate School Ph.D. Programs
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) : Full-time five-year research-based programs. The programs are designed to train and develop students to become academic and research scholars. The four Ph.D. programs of the Rackham Graduate School of the University of Michigan-Ann Arbor are located, administered, and offered by UM-Dearborn. These programs observe the standards for admissions, registration, degree requirements, awarding of degrees, and other administrative policies and regulations established by the Executive Board of the Rackham Graduate School.
Funding Support for Ph.D. Programs: Our programs are fully-funded. We understand the financial commitment of continuing your education, and we want to help. Students admitted receiving full-funding in the form of an appointment as Graduate Student Instructor (GSI), Research Assistant (GSRA), or a combination of both. This covers a competitive monthly stipend, health insurance, and tuition waiver.
Programs for Working Professionals
Doctor of Engineering (D.Eng.) : Full-time or part-time program geared toward working professionals with prior professional experience in mobility and the automotive industry. This professional degree centers on engineering practice and application, problem-solving skills, and innovation to prepare graduates for technical leadership roles in industry.
CECS Graduate Education Office
PhD or EngD?
Engineering doctorate: a practice-based alternative to a phd.
Do you want a more design-oriented approach? Check out our Engineering Doctorate programmes (EngD) . This design-traineeship offers you an application-focused alternative to a PhD position, and provides you with a solid basis for an accelerated start of your industrial career.
Difference between PhD and EngD
Although PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) and EngD (Engineering Doctorate) are both recognised as postgraduate degrees, they are not the same. A PhD is focused on scientific research, and an EngD is a design-oriented engineering doctorate which is best suited to the direct needs for product, process and system innovation of industry and society. Which one suits you best?
PhD | EngD |
|---|---|
Four years | Two years |
You are shifting the boundaries of knowledge by fundamental research | You are creating innovative designs for industry and society by applying scientific knowledge |
You focus on a contribution to scientific knowledge that may help solve societal challenges | You focus on the creation of (technological) designs and innovations |
You mainly work at the TU Delft campus | You work both at the TU Delft campus and the (mostly) industrial partner’s location |
You aim at a career in science or scientific leadership roles in industry | You aim at a career in technological design and innovation and technological leadership roles in industry |
Read more about the EngD programmes offered by TU Delft
Related subjects

PhD Programme
Doctoral Education Programme

Doctor of Engineering (D.Eng.) vs Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
Paresh asks :
"After reading so much helpful contents on this blog now I started the process for admission for PhD. At certain universities, I found PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) and Doctor of Engineering. What’s the exact difference between these two?"
D.Eng. vs Ph.D.
A Doctor of Engineering (D.Eng.) program prepares women and men to work at the highest levels of the engineering profession. This program emphasizes solving problems that arise from using technologies beneficial to mankind.
However, those problems and their solutions also frequently affect society at large in nontechnical ways.
Therefore, technological advances implemented through business and industry require direction by persons possessing both high technical competence and professional understanding of the social, political and institutional factors involved.
Graduates of the D.Eng. program are uniquely qualified to fulfill that important role.
This program prepares individuals for professional engineering careers in business, industry and the public sector.
It is not intended as a research degree nor as preparation for a faculty position at a research university. That is the province of the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) program.
The D.Eng. program emphasizes engineering practice, public service and the development of leadership potential, not basic research.
D.Eng. graduates are prepared to move quickly into positions of responsibility and authority. Therefore, students are required to take courses in business and communications, supplemented by elective graduate courses.
With this background, professional activities can and often do encompass both technical and nontechnical fields.
Positions of leadership call for interaction between technology and society; communication is required not only with other engineers but also with other professionals, laymen, and workers.
The ability to think and express oneself clearly is essential. [Via TAMU ]
Related: Yes or No: Is PhD Right for Me?
Similar Posts
7 questions to ask when your grad school applications are rejected.
I have been reading your blogs pretty much regularly, and I think you are the expert who can help me with my problem. Please I’m desperate and anxious and hope you would help me. GRE score : Verbal 150, Quant 161, Writing 3.0 Degree CGPA : 8.65 BE in Electronics from Punjab Engineering College, India…
Insider’s Guide to College Admission – Video
I had alraedy posted about the College Admission Process – Flowchart in this blog. But still, there are many questions to be answered with respect to college essay (or statement of purpose), recommendation letter, resumé, GPA, GRE scores, etc. Good thing I came across this 23 minute video, which will likely answer all your questions…
Myth 8 – It is Only Possible to be Enrolled at One University at a Time
This is the final myth. Have you considered studying at two universities at the same time? You might wonder why anyone would want to do that? Or is it even possible to do that? I have seen motivated students and high performers take this approach. Universities will allow you to transfer credits. Right? If there’s…
Graduate School Admission : Applied-6, Rejected-6
Students who had applied for the Fall 2009 semester are starting to know about their admission status. In line with this, I encountered one interesting comment from our reader. This comment seems to say that the reader had applied for 6 universities in the U.S. and unfortunately got rejection letters from all 6 universities! After…
When to Take GRE to Attend Fall Semester
In the previous article When to Take GRE , I gave an introduction about the factors that must be considered before deciding to take a GRE test. After you have made the decision to attend Fall semester, the following will be the typical timeline when taking a GRE Exam and applying for Fall semester. However,…
FAQ’s – Round 3 : Universities, GRE, TOEFL and Jobs
Round 3 of Q&A is continued here. Questions listed here from Newsletter subscriber’s reply to email titled “Week 2 : do you have any questions?” Round 1 [10 Questions] Round 2 [ 7 Questions] 1) Ratri If i want to do a PhD in USA, what are the requirements that i should full fill. My…
consider revising TAMU link to: https://engineering.tamu.edu/mtde/academics/degrees/graduate/deng/index.html
Does any Indian University offer Doctor of Engineering (D.Eng) ?
Many schools in China offer doctor of engineering, such as Fudan University and Tongji University.
Real time examples would help me to know what exactly u r talking abt.. pls do it for me..
waiting eagerly sir/madam..
Brilliant work you guys are doing here! I want to know if a PhD applicant requires to have work experience. What if I am applying for a PhD in Management- would I need to have prior work ex?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
EngD and the differences with a PhD
Engineering doctorate .
An EngD (Engineering Doctorate) programme is a 2-year post-master design programme focussing on the direct needs of the industry.

All EngD programmes are tailor-made in close cooperation with an industry partner. You will learn to design high-level, creative and innovative designs for complex issues, within a multidisciplinary team.
The University of Twente offers a diversity of Post-Master EngD programmes:
- Business & IT
- Civil Engineering
- Energy & Process Technology
- Maintenance
What can I expect from an EngD programme?
By combining an educational part at the University (~60 EC) and a practical design part at an organization (~60 EC), the programme offers academic research in a professional context.
- The courses in the educational part help you to further your professional development by providing the necessary (non)technological background to evaluate the effects of technology in the industrial context.
- During the practical part of the programme, you will spend time working in the industry on a challenging and innovative technological design project – a real problem that needs to be solved. You will be supervised by both engineers from the industry as well as by university staff. This ensures support in the areas of scientific knowledge, practical design experience and project management expertise.
EngD is open for a wide range of technically educated Master graduates, even if you're not graduated in one of the aforementioned specific fields. What matters is a perfect match between the specific design project and your MSc programme, your affinity with technological designs and your intrinsic motivation.
Difference between EngD and PhD
EngD is a practical-oriented professional doctorate in engineering which is better suited to the direct needs of industry, whereas a PhD track focuses on scientific research. The three most noticeable differences between a PhD and an EngD programme are:
- A PhD programme has a duration of 4 years, whereas an EngD programme takes 2 years to complete
- A PhD candidate focuses on research at the University, whereas an EngD trainee focuses on technological designs in the industry
- A PhD can be done in any research area represented by a full professor at the University and leads to the title “Doctor” (Dr., equivalent to a PhD). An EngD leads to an “Engineering Doctorate” (EngD) and can be taken at the University of Twente in 5 areas of expertise:

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- Master’s vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Published on November 27, 2020 by Lauren Thomas . Revised on May 10, 2024.
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master’s and doctoral degrees:
- A master’s is a 1–2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers.
- A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3–7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research.
A master’s is also the necessary first step to a PhD. In the US, the master’s is built into PhD programs, while in most other countries, a separate master’s degree is required before applying for PhDs.
Master’s are far more common than PhDs. In the US, 24 million people have master’s or professional degrees, whereas only 4.5 million have doctorates.
Table of contents
Master’s vs phd at a glance, which is right for you, length of time required, career prospects, costs and salaries, application process, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about master's and phd degrees.
The table below shows the key differences between the two.
| Master’s | PhD | |
|---|---|---|
| Career prospects | Usually intended for a career outside of academia. | Prepares for a research career, ideally as a university professor. |
| Length of time | 1–2 years | 5–7 in the US (master’s degree included); 3–5 outside the US (after a separate master’s degree) |
| Structure | Mostly coursework, often with a semester-long or capstone project at the end. | 2 years of coursework (in the US), followed by 3–5 years of preparing a dissertation, which should make a significant original contribution to current knowledge. |
| Cost | Varies by country, university and program; usually higher upfront cost with limited financial aid available. | Tuition fees are usually waived and a living stipend provided in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. |
| Graduate salaries | Wage premium (compared to earnings with a high school education) is 23% on average. | Wage premium is 26% on average. |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A PhD is right for you if:
- Your goal is to become a professor at a university or some other type of professional researcher.
- You love research and are passionate about discovering the answer to a particular question.
- You are willing to spend years pursuing your research even if you have to put up with a lot of dead ends and roadblocks.
A master’s degree is the better choice if any of the following apply:
- You want to continue studies in your field, but you’re not committed to a career as a professional researcher.
- You want to develop professional skills for a specific career.
- You are willing to pay a higher upfront cost if it means finishing with your degree (and thus being able to work) much faster.
- You want the option to study part-time while working.
The length of time required to complete a PhD or master’s degree varies. Unsurprisingly, PhDs take much longer, usually between 3–7 years. Master’s degrees are usually only 1–2 years.
Length of a master’s
Master’s degrees are usually 2 years, although 1-year master’s degrees also exist, mainly in the UK.
Most of the degree consists of classes and coursework, although many master’s programs include an intensive, semester-long master’s thesis or capstone project in which students bring together all they’ve learned to produce an original piece of work.
Length of a PhD
In the US, a PhD usually takes between 5 and 7 years to complete. The first 2 years are spent on coursework. Students, even those who choose to leave without finishing the program, usually receive a master’s degree at this point.
The next 3–5 years are spent preparing a dissertation —a lengthy piece of writing based on independent research, which aims to make a significant original contribution to one’s field.
Master’s degrees tend to prepare you for a career outside of academia, while PhDs are designed to lead to a career in research.
Careers for master’s graduates
There are two types of master’s degrees: terminal and research-intensive. The career prospects are different for each.
Terminal master’s degrees are intended to prepare students for careers outside of academia. Some degrees, known as professional degrees, specifically prepare students for particular professions; these include the Master of Public Policy (MPP), Master of Business Administration (MBA), Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT), Master of Fine Arts (MFA), and Master of Public Health (MPH) degrees.
Other master’s degrees, usually Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Sciences (MS or MSc) degrees, do not necessarily lead to a specific career, but are intended to be a final degree. Examples include an MS in Communications or MS in Data Analytics.
In research-intensive master’s programs, students take coursework intended to prepare them for writing an original piece of research known as the master’s thesis . Such programs are usually intended to prepare for further study in a doctoral program.
Careers for PhD graduates
As research degrees, PhDs are usually intended to lead to an academic career. A PhD can be thought of like an apprenticeship, where students learn from professional researchers (academics) how to produce their own research.
Most students aspire to become a university professor upon the completion of their degree. However, careers in academia are highly competitive, and the skills learned in a doctoral program often lend themselves well to other types of careers.
Some graduates who find they prefer teaching to producing research go on to be teachers at liberal arts colleges or even secondary schools. Others work in research-intensive careers in the government, private sector, or at think tanks.
Below are a few examples of specific fields and non-academic careers that are common destinations of graduates of those fields.
- Computer Science
- Lab Sciences
Many government jobs, including economists at a country’s central bank, are research-intensive and require a PhD. Think tanks also hire economists to carry out independent research.
In the private sector, economic consulting and technology firms frequently hire PhDs to solve real-world problems that require complex mathematical modeling.
Graduate students from the humanities are sometimes hired by museums, who can make use of their research and writing skills to curate exhibits and run public outreach.
Humanities PhDs are often well-suited to research and grant-writing roles at nonprofits. Since so much of research is funded by grants, PhD students often gain a lot of experience applying for them, which is a useful skill in the nonprofit sector.
There are a wide range of non-academic research jobs for lab scientists with doctorates in subjects like chemistry, biology, ecology and physics.
Many PhD graduates are hired by pharmaceutical companies that need to perform research to create and test their products. Government agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), also hire lab scientists to work on research projects.
Job prospects after graduation vary widely based on the field. In fields like management, computer science, statistics, and economics, there’s little underemployment—even graduates from less well-known programs can easily find jobs that pay well and use the skills they’ve gained from the PhD.
However, in other fields, particularly in the humanities, many PhD graduates have difficulty in the job market. Unfortunately, there are far more PhD graduates than assistant professor roles, so many instead take on part-time and low-paid roles as adjunct instructors. Even non-academic careers can sometimes be difficult for PhDs to move into, as they may be seen as “overqualified” or as lacking in relevant professional experience.
Because career options post-PhD vary so much, you should take the time to figure out what the career prospects are in your field. Doctoral programs often have detailed “placement” records online in which they list the career outcomes of their graduates immediately upon leaving the program. If you can’t find these records, contact the program and ask for them—placement information should play an important role in your choice of PhD program.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Although PhDs take far longer to complete, students often receive a living stipend in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. Master’s degrees are shorter but less likely to be funded.
Both master’s degrees and PhDs lead to increased salaries upon graduation. While PhDs usually earn a bit more than those with a master’s degree, in some fields, the wages are identical, meaning that no financial benefit is gained from going on to a PhD.
Cost of a master’s
The upfront cost of a master’s degree is usually higher than a doctoral degree due to the lower amount of financial aid available. However, increased salaries also arrive faster than with a doctoral degree, because people graduate much earlier from a master’s program.
Some master’s students do receive stipends for their degrees, usually as compensation for being a teaching or research assistant. In addition, many people complete master’s degrees part time while working full-time, which allows them to fund their living costs as well as tuition.
The cost varies significantly by school and program. Public schools are usually cheaper than private ones. Some master’s degrees, such as MBAs, are notoriously expensive, but also result in much higher wages afterwards that make up for the high cost.
The master’s wage premium , or the extra amount that someone with a master’s degree makes than someone with just a high school diploma, is 23% on average. Many universities provide detailed statistics on the career and salary outcomes of their students. If they do not have this online, you should feel free to contact an administrator of the program and ask.
Cost of a PhD
PhDs, particularly outside the humanities, are usually (though not always) funded, meaning that tuition fees are fully waived and students receive a small living stipend. During the last 3–5 years of a PhD, after finishing their coursework (and sometimes before), students are usually expected to work as graduate instructors or research assistants in exchange for the stipend.
Sometimes students can apply for a fellowship (such as the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Program in the United States) that relieves them of any obligations to be a teaching or research assistant. Doctoral programs in the US tend to be better funded than in the rest of the world.
Sometimes, PhD degrees can be completed part-time, but this is rare. Students are usually expected to devote at least 40 hours a week to their research and work as teaching or research assistants.
The main cost of doctoral programs comes in the form of opportunity cost—all the years that students could be working a regular, full-time job, which usually pays much better than a graduate school stipend.
The average wage premium for PhDs is 26%, which is not much higher than the master’s degree premium.
In the US, the application process is similar for master’s and PhD programs. Both will generally ask for:
- At least one application essay, often called a personal statement or statement of purpose .
- Letters of recommendation .
- A resume or CV .
- Transcripts.
- Writing samples.
Applications for both types of programs also often require a standardized test. PhDs usually require the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), which tries to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative, critical thinking , and analytical writing skills. Many master’s programs require this test as well.
Applying for a master’s
Master’s degrees programs will often ask you to respond to specific essay prompts that may ask you to reflect upon not just your academic background, but also your personal character and future career ambitions.
Northwestern University’s Kellogg Business School requires Master’s of Business Administration (MBA) applicants write two essays, one about a recent time they demonstrated leadership and the second about their personal values.
Who you should ask for your letters of recommendation varies by program. If you are applying to a research-intensive master’s program, then you should choose former professors or research supervisors. For other programs, particularly business school, current work supervisors may be a better choice.
Some professional master’s programs require a specific test. For example, to apply to law school, you must take the Law School Admissions Test, or LSAT. For business school, you must take either the GRE or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT).
Applying for a PhD
When applying for a PhD, your resume should focus more on your research background—you should especially emphasize any publications you’ve authored or presentations that you’ve given.
Similarly, your statement of purpose should discuss research that you’ve participated in, whether as an assistant or the lead author. You should detail what exactly you did in projects you’ve contributed to, whether that’s conducting a literature review, coding regressions, or writing an entire article.
Your letters of recommendations should be from former professors or supervisors who can speak to your abilities and potential as a researcher. A good rule of thumb is to avoid asking for recommendations from anyone who does not themselves have a PhD.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Thomas, L. (2024, May 09). Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/masters-vs-phd/
Is this article helpful?

Lauren Thomas
Other students also liked, when to apply for graduate school | month-by-month timeline, how to write a statement of purpose | example, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How can one differentiate between Dr. (PhD) and Dr. (MD or DO)?
Reading the question posted here left me with a more general question:
Given the professional title and name: Dr. (First Name)(Last Name), is there some way to differentiate between the holder of a philosophical doctorate and a medical doctor? Wouldn't it be more appropriate for a PhD holder to have the title (First Name)(Last Name), PhD?
14 Answers 14
You can't immediately tell from the title, but then titles are not typically used by an individual to broadcast their occupation - we don't have variants of "Mr" for plumbers, bank managers, or rock stars - despite their very different occupations. Rather, the title is to be used by others when addressing that individual, in order to signify a degree of respect, typically for a particular level of training, qualification and responsibility, or else for a particularly respected position in society. Even the term "mister" is a meaningful sign of respect that historically would not have been as widely applied as it is today - the ratchet of etiquette has gradually eliminated everything below it.
The actual title "Doctor" means "teacher" (from Latin "doceo", "I teach"). This title is more often more relevant to PhDs than MDs, so you probably have your suggested solution backwards. That said, the solution is really neither necessary nor appropriate. Much like "Master" (from Latin "magister", in this case "teacher"), "Doctor" signifies that an individual has not only gained enough competency to practice in a particular field, but has developed enough expertise to instruct others. An individual who is sufficiently qualified to practice but not teach would historically have been known as a "journeyman", roughly equivalent to "professional".
In short "doctor" refers not to a field of expertise, but rather to a level of expertise.
Incidentally, most UK surgeons drop their title of "Dr" and revert to "Mr" after joining the Royal College of Surgeons. I've heard through a friend of at least one surgeon who reacted quite angrily at being addressed as a mere "Dr", which in such circles, due to a collision between traditional titles and modern medical training, could be unkindly translated as "trainee".
- 2 I think the Mr should be spelled out after joining the Royal College of Surgeons ie. Mr.Smith -> Dr.Smith -> Mister Smith – user288447 Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 16:34
- 7 @user288447, do you have reference? I can't find anything on that. – DeveloperInDevelopment Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 16:46
- 2 Unfortunately not, it may just have been convention in one hospital that I was in several years ago. – user288447 Commented Oct 30, 2014 at 10:31
You can't. That's why there are numerous jokes in English-speaking culture about whether someone addressed as "doctor" is a "real" doctor or not. Medical doctors are supposed to be the "real" ones in the jokes.
- 30 Regarding the jokes, I recently heard introducing a speaker (MD) in a conference "and then he became a real doctor when he did his PhD in...". – Davidmh Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 12:25
- 8 Also: 'not that kind of doctor' – Cape Code Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 12:53
- 18 According to peoplefinders.com/search/… , there are 2 people named "Doctor Smith" in the US. Do they have PhDs or MDs? I don't know. Their first name is Doctor. – emory Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 13:46
- 16 @Emory: Following the example of Major Major , they should enroll in a university and see if a computer error will summarily grant them a doctorate. – Nate Eldredge Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 14:53
- 6 Ironically, it is neither MD's, nor PhD's that are the true, original " Doctors ", but rather DD's. Though try convincing anyone of that today ... – RBarryYoung Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 19:15
In the United States, in spoken address, both are called "doctor."
For personal correspondence, both are addressed as "Dr." as with an invitation addressed to "Dr. and Mrs. Smith." (Or maybe "Dr. and Mr. Smith." If they both hold doctorates, it is "Drs. Smith." For a couple with different family names, use "Dr. Smith and Mr. Brown.")
For professional correspondence, both are addressed by name and degree, as "James Smith, M.D." or "Bob Brown, Ph.D."
Since the distinction is only relevant in professional interactions, there really isn't any ambiguity.
If you are speaking to a medical doctor professionally, you will know it by the setting, and you still say "doctor." If you ask for medical advice at a cocktail party because someone was introduced as "doctor" you deserve anything you get! I've been known to say, "I'm a college teacher type doctor, not a take-off-your-clothes doctor." That usually sends the message and often gets a laugh.
- 2 I am not a medical doctor, but I often work in hospital settings interacting with both patients and medical doctors so the setting is not always informative. – StrongBad Commented Oct 31, 2014 at 11:36
- 3 I know a microbiologist and a physicist who work in a hospital. Their degrees appear on their ID badges, as do those of medical doctors. – Bob Brown Commented Oct 31, 2014 at 11:46
- This was edited by "Anonymous" to introduce irrelevant commentary about women taking husbands' names. The commentary on the edit also incorrectly stated that more women than men earn doctorates. In the United States, at least, that is incorrect. From the 2014 SED: "Overall, women earned 46% of all doctorates in 2014." – Bob Brown Commented Nov 29, 2016 at 14:24
I have seen the difference in the written form of their name;
One is Name Family, PhD. and other one is Name Family MD.
The same applies to the people holding Engineering doctorates such as Name Family, EngD. or holding doctorate in business such as DBA. Also, in different countries there are usually different doctorate titles ( link ) awarded.
But all of these people are called doctors .
- 1 I've seen it for dentists too. Name Family D.D.S – jonescb Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 16:53
- @jonescb just look at the link provided in the answer, you can see more than twenty doctorate titles for different countries and different majors... – enthu Commented Oct 29, 2014 at 16:56
A medical practitioner usually holds a MBBS or MD degree or similar and - at a reasonable level of proficiency - membership of a professional body such as the AMA ( American Medical Association) or the RCP ( Royal College of Physicians) or whatever applies in their part of the world.
A holder of an academic doctorate ( PhD, DrPh, EngD etc) has researched a topic or problem within their specific subject in sufficient depth to have generated fresh insights or made a breakthrough or contributed significant new knowledge to the existing corpus.
Both have earned the right to be addressed as 'Dr'.
However, it would appear to me that one or two posters have been watching a few too many episodes of 'The Big Bang Theory' as I think the need to differentiate between the two very rarely applies except in a medical emergency.
- 1 In hospital settings where patients may be interacting with both medical doctors and academics, there is a need to differentiate. – StrongBad Commented Oct 31, 2014 at 11:37
While both have the title of "doctor," that is identifying the fact that they both have the same education level, a doctorate.
The meaningful difference here is occupation : one might be a professor, the other a physician.
To differentiate between the two you can use the actual doctorate type or the job title:
- My professor is Dr. Jones. (or) Dr. Jones teaches my class.
- My physician is Dr. Smith.
- Indiana Jones, Ph.D.
- Joe Smith, M.D.
Of course a physician could also be a professor (who teaches in medical school?), or an M.D. might be a researcher who does not treat patients as their primary means of income (i.e. they only deal with patients during the course of medical studies). I do not think you can do much about those cases.
In Germany, it is common to denote the subject area the doctor was obtained in, such as Dr. med. for medical doctors, Dr.-Ing. for engineers, or Dr.-rer-nat. (rerum naturalium) for sciences like chemistry.
The usual practical solution is "ask them."
Doctor means you have a doctorate. Simple as that, a medic can have a doctorate in medicine and thus be a doctor, but if you do not have the degree then you are not a doctor, you can be a surgeon or a licensee of medicine but you are just referred to as doctor out of colloquial use of the title based on historical rots and customs.
There is no difference in spoken address ('Doctor'), but one is a Ph.D. and the other is an M.D.
You can tell from the context, but without the context, you can't. If the context is obviously far removed from anything clinical, such as "Dr. xyz has written a book on archaeology of early Los Angeles", then it's obviously the PhD sense. If it's a clinical setting, including emergencies and simply asking for health advice, basically when someone's health is at stake, then it's obviously the MD sense.
Things can get more ambiguous in biomedical research, because I personally know some MDs (without PhD) doing research instead of practicing medicine, including some molecular biology professors. When a research paper that uses clinical samples says something like, "Samples were obtained after resection from Dr. xyz", then it really can be either MD or PhD or both. Some people in our field have both.
Anyway, I don't make too big a deal out of it because we in California are typically on first name basis outside the clinical setting (this includes medical doctors). When we PhDs and candidates (at least in CA) say "doctor", we also usually mean medical doctors, like in, "Our postdoc health insurance is so bad that I'm terrified of seeing a doctor", where "doctor" obviously doesn't refer to ourselves. Some states, including California, have laws forbidding anyone who is not a medical doctor to advertise themselves as Dr. something in order not to confuse patients.
The confusing aspect is that doctor connotes medical treatment to most people, not a doctoral degree. Anyone smart enough to have a PhD knows the difference. I would not want a PhD doing my surgery, nor an MD teaching me philosophy.
It's not an easy question to answer. Ph.D's who are professors are just called "professor," and research assistants with a Ph.D are called "doctor" by secretaries and students. Titles are never mentioned in academic papers.
It's different with doctors: Patients and nurses call them "doctor;" if they are also professors, which they often are, the are called "professor" since professors have a higher status than mere M.D.s, and when they write papers in medical journals they put M.D. after their names. When practitioners without an M.D. refer to themselves as "doctor" they are just called "frauds."
Things are much more interesting in Germany. I was treated there by a woman doctor in a University Hospital who was also a professor of medicine. Her title was Frau Dr. Med, Dr. Professor Mueller. Some Professors have three degrees, meaning that are called Herr (or Frau) Dr. Dr. Dr. Professor.
- I have never heard medical school Professors introduce themselves to patients as Professor. In the UK holders of a Bachelors in Medical Science (BMedSci) call themselves doctor and it is not fraud. – StrongBad Commented Oct 31, 2014 at 11:41
- Titles are never mentioned in academic papers — ...in some disciplines. In others, they are mentioned quite prominently. – JeffE Commented Apr 25, 2015 at 3:43
In French (maybe other latin countries too), but I don't know about English, you can make a small difference by adding ès : Albert Einstein, Docteur ès Physique.
Then twice in a row you have specified that he was a scientific doctor (not a medical one) and his field of research.
- 2 Hi Rucikir, welcome to Academia.SE. Your answer does not really answer the question. Basically you are explaining how to say Albert Einstein, PhD in French, which is not what the OP is asking. – earthling Commented Oct 30, 2014 at 10:47
- Well, I just didn't know if it could be used in English, apparently not, so it was irrelevant. Thanks for pointing it out. Sorry. But I'm not the only one to have done that, other answer about the German way. – Antonin Décimo Commented Oct 31, 2014 at 23:53
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd titles medicine ..
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
Hot Network Questions
- Will a recent B2 travel to the same location as my F1 college application affect the decision
- How to normalise note lengths when analysing music
- Are these colored sets closed under multiplication?
- Can All Truths Be Scientifically Verified?
- Is it true that before European modernity, there were no "nations"?
- Seeking a Text-Based Version of Paul Dirac's 1926 Paper on Quantum Mechanics
- Rocky Mountains Elevation Cutout
- Doesn't nonlocality follow from nonrealism in the EPR thought experiment and Bell tests?
- Convert base-10 to base-0.1
- Why is steaming food faster than boiling it?
- How would you address the premises of Schellenberg's non-resistant divine hiddenness argument?
- If one is arrested, but has a baby/pet in their house, what are they supposed to do?
- Positivity for the mild solution of a heat equation on the torus
- Building rear track wheel from road wheel
- What's the strongest material known to humanity that we could use to make Powered Armor Plates?
- What properties of the fundamental group functor are needed to uniquely determine it upto natural isomorphism?
- View undo history of Windows Explorer on Win11
- Recursive relation for power series coefficients
- Solaris 11 cbe: no more updates?
- Stuck as a solo dev
- C++ std::function-like queue
- Whom did Jesus' followers accompany -- a soldier or a civilian?
- Python script to renumber slide ids inside a pptx presentation
- Would a scientific theory of everything be falsifiable?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A PhD is ideal for those interested in research and teaching, while a DEng suits those aiming for senior engineering management roles. Consider industry requirements: Some industries may value the practical skills of a DEng more highly, whereas academia and research institutions typically require a PhD.
DEng vs. PhD. At Johns Hopkins University, both the Doctor of Engineering and the Doctor of Philosophy involve mentored research and in-depth investigation. There are a few key differences, though (although these are not hard and fast rules). DEng. PhD. Guiding Philosophy. Engineering practice and application. Engineering theory and scholarship.
The Doctor of Engineering (D.Eng [1] or EngD [2]) is a research doctorate in engineering and applied science.An EngD is a terminal degree similar to a PhD in engineering but applicable more in industry rather than in academia. The degree is usually aimed toward working professionals. The DEng/EngD along with the PhD represents the highest academic qualification in engineering, and the ...
Engineering Ph.D.s provide even more specialization than master's degrees, and a higher earning potential, but they also come with significant risks, experts say. Research jobs within government ...
A PhD is traditionally a research-focused degree, although not all PhD holders go on to work in academic research. The Doctor of Engineering degree is less well-known than the PhD, but it's still a good option to consider for many engineers. EngD degrees are professional-focused, rather than research-focused, areas of doctoral-level study.
The next Doctor of Engineering application deadline is January 1, 2025 The advanced technical expertise to succeed Designed for working engineers and scientists, the Doctor of Engineering takes the form of a research collaboration between a student's employer and the Whiting School of Engineering.
Specialization. Earning a master's degree in engineering typically allows you to get involved in many different types of engineering projects and roles after graduation. Conversely, Ph.D. programs are often much more specialized. The work you do while in a Ph.D. program usually prepares you for a specific role or niche within engineering.
The Doctor of Engineering is a specialised, industry-focused, professional doctorate in Engineering. Unlike a PhD, the EngD contains a significant taught component. This equips you with the technical and management skills needed to excel in your future career. EngD candidates are known as research engineers.
Graduates of PhD in Engineering programs can work as professors at research universities, dedicate their expertise to industrial or government research labs, or create a business around their own innovation. Consider building your career as the developer of a green energy trend, discovering a life-saving biomedical process, or taking the world ...
The three most noticeable differences between a PhD and an EngD are: A PhD candidate focuses on research at the university, whereas an EngD candidate focuses on technological designs in industry and society. A PhD programme has a duration of four years whereas the EngD takes two years to complete. A PhD leads to the title "Doctor" (Dr ...
The DEng program is a doctoral-level graduate degree program designed for working engineers and scientists. It is a full-time program that is pursued non-residentially. The program takes the form of a research collaboration between a student's employer and the Whiting School of Engineering. Students are actively mentored by a primary advisor ...
The Dearborn Difference. The College of Engineering and Computer Science (CECS) offers 6 doctoral programs: 4 full-time Ph.D. programs and 2 Doctor of Engineering (D. Eng.) programs. In CECS, we are committed to excellence. Our doctoral programs are administered and taught by tenure-track faculty with active theoretical and translational ...
Doctorate, or doctoral, is an umbrella term for many degrees — PhD among them — at the height of the academic ladder. Doctorate degrees fall under two categories, and here is where the confusion often lies. The first category, Research (also referred to as Academic) includes, among others: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)**.
Difference between PhD and EngD. Although PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) and EngD (Engineering Doctorate) are both recognised as postgraduate degrees, they are not the same. A PhD is focused on scientific research, and an EngD is a design-oriented engineering doctorate which is best suited to the direct needs for product, process and system ...
The Doctor of Engineering in Engineering Management is designed for practitioners who wish to apply the knowledge they gain in a technical management environment. Unlike a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), wherein research is focused on foundational work that is published, the D.Eng. requires solving a real-world problem using the latest ...
That is the province of the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) program. The D.Eng. program emphasizes engineering practice, public service and the development of leadership potential, not basic research. D.Eng. graduates are prepared to move quickly into positions of responsibility and authority. Therefore, students are required to take courses in ...
Often, when you have something like Doctor of Field vs PhD in Field, they are designed as a more applied degree vs a research/theory degree. If your goal is to be an academic, some places will have a bias and think that your research training will be lesser. ... (PhD is ballpark 60h of graduate-level credit plus a dissertation, original ...
EngD is a practical-oriented professional doctorate in engineering which is better suited to the direct needs of industry, whereas a PhD track focuses on scientific research. The three most noticeable differences between a PhD and an EngD programme are: A PhD programme has a duration of 4 years, whereas an EngD programme takes 2 years to complete.
EngDs are therefore good preparation for those seeking an engineering career in industry. EngD stipends also tend to be slightly more generous than those for PhD, although I am not sure if this difference extends to the US. this thread might also help. I'm a bit surprised that no one has mentioned the advisor.
I'm in the business field and a PhD in "field" is generally a 4-6 year degree from a R1 that is aimed at working in academia or, to a much lesser extent, doing consulting after. a DBA (doctorate of business administration) is a completely non-academic path aimed at people who will definitely go back to industry and will usually come from non-R1 ...
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master's and doctoral degrees: A master's is a 1-2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers. A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3-7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research. A master's is also the necessary first ...
Some say since Doctor of Engineering is project based it is somewhat less prestigious as getting a PhD with a thesis. Go for the PhD. The Doctor of Engineering or EdD or things like that are more for like folks who are deep in their careeer and just need the label for pension increases or promotions or something, but you probably wont be able ...
3. While both have the title of "doctor," that is identifying the fact that they both have the same education level, a doctorate. The meaningful difference here is occupation: one might be a professor, the other a physician. To differentiate between the two you can use the actual doctorate type or the job title: