- Assignment to property of function parameter no-param-reassign
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024 Reading time · 3 min


# Table of Contents
- Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for a single line
- Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for an entire file
- Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule globally
# Assignment to property of function parameter no-param-reassign
The ESLint error "Assignment to property of function parameter 'X' eslint no-param-reassign" occurs when you try to assign a property to a function parameter.
To solve the error, disable the ESLint rule or create a new object based on the parameter to which you can assign properties.
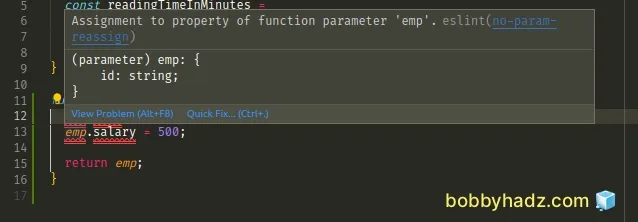
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
The ESLint rule forbids assignment to function parameters because modifying a function's parameters also mutates the arguments object and can lead to confusing behavior.
One way to resolve the issue is to create a new object to which you can assign properties.
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the properties of the function parameter into a new object to which we can assign properties.
If you need to unpack an array, use the following syntax instead.
The same approach can be used if you simply need to assign the function parameter to a variable so you can mutate it.
We declared the bar variable using the let keyword and set it to the value of the foo parameter.
We are then able to reassign the bar variable without any issues.
# Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for a single line
You can use a comment if you want to disable the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for a single line.
Make sure to add the comment directly above the assignment that causes the error.
# Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for an entire file
You can also use a comment to disable the no-param-reassign ESLint rule for an entire file.
Make sure to add the comment at the top of the file or at least above the function in which you reassign parameters.
The same approach can be used to disable the rule only for a single function.
The first comment disables the no-param-reassign rule and the second comment enables it.
If you try to reassign a parameter after the second comment, you will get an ESLint error.
# Disabling the no-param-reassign ESLint rule globally
If you need to disable the no-param-reassign rule globally, you have to edit your .eslintrc.js file.
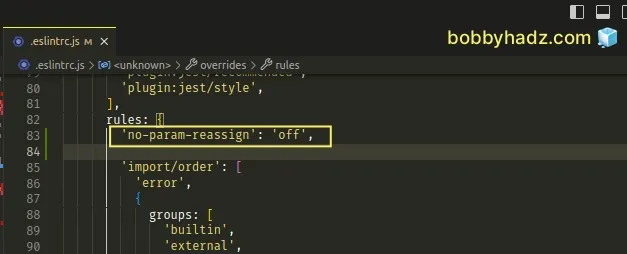
If you only want to be able to assign properties to an object parameter, set props to false instead of disabling the rule completely.
The following code is valid after making the change.
If you use a .eslintrc or .eslintrc.json file, make sure to double-quote the properties and values.
If you want to only allow assignment to object parameters, use the following line instead.
Make sure all properties are double-quoted and there are no trailing commas if your config is written in JSON.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- eslint is not recognized as an internal or external command
- Plugin "react" was conflicted between package.json » eslint-config-react-app
- React: Unexpected use of 'X' no-restricted-globals in ESLint
- TypeScript ESLint: Unsafe assignment of an any value [Fix]
- ESLint error Unary operator '++' used no-plusplus [Solved]
- ESLint Prefer default export import/prefer-default-export
- Arrow function should not return assignment. eslint no-return-assign
- TypeError: Cannot redefine property: X in JavaScript [Fixed]
- ESLint: disable multiple rules or a rule for multiple lines
- Expected linebreaks to be 'LF' but found 'CRLF' linebreak-style
- Missing return type on function TypeScript ESLint error

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Remember language
- Português (do Brasil)
The arguments object
Baseline widely available.
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015 .
- See full compatibility
- Report feedback
arguments is an array-like object accessible inside functions that contains the values of the arguments passed to that function.
Description
Note: In modern code, rest parameters should be preferred.
The arguments object is a local variable available within all non- arrow functions. You can refer to a function's arguments inside that function by using its arguments object. It has entries for each argument the function was called with, with the first entry's index at 0 .
For example, if a function is passed 3 arguments, you can access them as follows:
The arguments object is useful for functions called with more arguments than they are formally declared to accept, called variadic functions , such as Math.min() . This example function accepts any number of string arguments and returns the longest one:
You can use arguments.length to count how many arguments the function was called with. If you instead want to count how many parameters a function is declared to accept, inspect that function's length property.

Assigning to indices
Each argument index can also be set or reassigned:
Non-strict functions that only have simple parameters (that is, no rest, default, or destructured parameters) will sync the new value of parameters with the arguments object, and vice versa:
Non-strict functions that are passed rest , default , or destructured parameters will not sync new values assigned to parameters in the function body with the arguments object. Instead, the arguments object in non-strict functions with complex parameters will always reflect the values passed to the function when the function was called.
This is the same behavior exhibited by all strict-mode functions , regardless of the type of parameters they are passed. That is, assigning new values to parameters in the body of the function never affects the arguments object, nor will assigning new values to the arguments indices affect the value of parameters, even when the function only has simple parameters.
Note: You cannot write a "use strict"; directive in the body of a function definition that accepts rest, default, or destructured parameters. Doing so will throw a syntax error .
arguments is an array-like object
arguments is an array-like object, which means that arguments has a length property and properties indexed from zero, but it doesn't have Array 's built-in methods like forEach() or map() . However, it can be converted to a real Array , using one of slice() , Array.from() , or spread syntax .
For common use cases, using it as an array-like object is sufficient, since it both is iterable and has length and number indices. For example, Function.prototype.apply() accepts array-like objects.
Reference to the currently executing function that the arguments belong to. Forbidden in strict mode.
The number of arguments that were passed to the function.
Returns a new array iterator object that contains the values for each index in arguments .
Defining a function that concatenates several strings
This example defines a function that concatenates several strings. The function's only formal argument is a string containing the characters that separate the items to concatenate.
You can pass as many arguments as you like to this function. It returns a string list using each argument in the list:
Defining a function that creates HTML lists
This example defines a function that creates a string containing HTML for a list. The only formal argument for the function is a string that is "u" if the list is to be unordered (bulleted) , or "o" if the list is to be ordered (numbered) . The function is defined as follows:
You can pass any number of arguments to this function, and it adds each argument as a list item to a list of the type indicated. For example:
Using typeof with arguments
The typeof operator returns 'object' when used with arguments
The type of individual arguments can be determined by indexing arguments :
Specifications
Browser compatibility.
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
- Functions guide
- Rest parameters
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
Passing a function as a parameter in JavaScript
In this article, we will pass a function as a parameter in JavaScript . Passing a function as an argument to the function is quite similar to passing a variable as an argument to the function. So variables can be returned from a function.
The below examples describe passing a function as a parameter to another function.
Example 1: This example passes a function geeks_inner to the function geeks_outer as an argument.
Example 2: This example passes a function geeks_inner along with an argument ‘Geeks!’ to the function geeks_outer as an argument.
Example 3: Here in this example, a smaller function is passed as an argument in the sayHello function. So here we are passing a smaller function address to the function sayHello.
Similar Reads
- Web Technologies
- javascript-functions
- JavaScript-Questions
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO