
How to write an effective case study: A comprehensive guide
Case studies are powerful tools for analyzing real-life situations, making informed decisions, and applying theoretical knowledge to practical problems.
Whether used in business, education, healthcare, or other fields, case studies require a deep understanding of the context, key players, and the complex dynamics at play.
This guide will walk you through the essential steps for developing a comprehensive and effective case study, from defining the objective to presenting a well-supported resolution.
Table of Contents
What is a case study?
A case study is a written summary or synthesis of a real-life situation, typically based on data and research.
Unlike hypothetical scenarios, case studies deal with actual events and decisions that need to be analyzed against both theoretical frameworks and the broader comparative environment.
The goal of a case study is to isolate key issues, evaluate potential strategies for resolving these issues, and recommend the best course of action with a solid rationale.
Considering this, case studies often involve:
- Isolating Key Issues : Identifying the most critical challenges or problems in the case.
- Evaluating Strategies : Weighing the pros and cons of various remedial options or strategies.
- Making Recommendations : Presenting a well-reasoned solution that addresses the key issues effectively.
10 steps to develop a case study
Creating a comprehensive case study involves a systematic process of investigation, analysis, and presentation.
Below are the key steps to follow when developing a case study:
1. Define the objective
The first step in developing a case study is to clearly define its objective.
What are you trying to achieve with this case study?
Are you aiming to solve a specific problem, understand the impact of certain decisions, or explore the dynamics within an organization?
Defining the objective will guide the direction of your analysis and help you focus on the most relevant issues.
2. Identify key players and stakeholders
Next, identify the important players within the organization or scenario you are studying. These could include:
- Internal Stakeholders : Such as management, employees, and decision-makers who have a direct impact on the situation.
- External Stakeholders : Such as clients, suppliers, and partners who are affected by the organization’s decisions.
Understanding who the stakeholders are and what their interests are is crucial for analyzing the situation accurately.
Additionally, scale the importance of these stakeholders based on their influence in decision-making and the consequences they may face.
3. Explore the organizational context
Studies have shown that organizations with clearly defined and well-communicated missions are more likely to experience alignment among stakeholders.
So guess what?
To fully grasp the situation in your case study, it’s crucial to dive into the organizational context.
This involves examining the official mission of the organization — what it publicly aims to achieve — as well as its historical mission, which can shed light on how its goals and strategies have evolved over time.
It’s also important to understand how different stakeholders perceive the organization’s mission.
These varied perspectives often influence decisions and outcomes, revealing potential areas of conflict or alignment within the organization.
What’s more, considering the competitive landscape will help you see where the organization stands in its industry and what external pressures it faces.
4. Map out the decision-making process
Understanding how decisions are made within the organization is key to analyzing the case.
Start by mapping out the formal decision-making processes, such as structured meetings, documented procedures, and official protocols.
However, don’t overlook the informal processes that often play a significant role, such as personal relationships, unwritten rules, and back-channel communications.
These informal elements can heavily influence outcomes, often in ways that aren’t immediately apparent.
Recognizing both formal and informal processes will give you a clearer picture of how decisions are truly made and the factors that impact them.
5. Analyze production and service delivery
The next step is to delve into the nuts and bolts of how the organization operates by examining its production or service delivery processes.
In general, this includes looking at the resources, technologies, and methods the organization uses to create its products or deliver its services.
Ideally, you should identify any challenges or inefficiencies that might be hindering performance, as well as the support mechanisms in place — like training programs, technology, or workflow systems — that help maintain or improve operations.
6. Pinpoint and investigate problems
Did you know that conducting a thorough root cause analysis is crucial for long-term problem resolution?
That’s why you should clearly articulate the primary problem or set of problems that the case presents.
Go beyond surface issues to explore underlying causes and subsequent challenges that arise from the main problem.
For example, a decline in customer satisfaction might lead to secondary issues like increased return rates or damaged brand reputation.
Investigating these interconnected problems helps to build a comprehensive understanding of the situation, allowing you to trace the ripple effects of the core issue and anticipate future complications.
7. Assess strategic issues and risks
Identify the strategic issues at the heart of the case, which require thoughtful decision-making.
These might include questions of resource allocation, market strategy, or operational changes.
Once these issues are identified, assess the associated risks—be they financial, reputational, or operational.
Evaluating both the strategic implications and the potential risks is crucial for understanding the stakes involved in any decision and for proposing solutions that are both effective and feasible.
8. Weigh remedial options
After identifying the strategic issues, it’s time to consider the different remedial options available.
For each option, assess the advantages and disadvantages, taking into account how each aligns with theoretical frameworks, the potential risks, and the practicalities of implementation.
Comparing these options helps you determine which course of action is most likely to succeed given the specific context and constraints of the case.
This comparative analysis forms the basis for your final recommendation.
9. Make a well-supported recommendation
Finally, based on your comprehensive analysis, make a clear and actionable recommendation.
Your recommendation should directly address the identified issues and be backed by a strong rationale.
It’s important to justify why this solution is the best, referencing the analysis you’ve conducted, the pros and cons of other options, and the potential risks.
This well-supported recommendation not only solves the problem at hand but also stands up to scrutiny from others who may review your case study.
10. Craft an executive summary
Now, the only thing you’ve left to do is to wrap up your case study with an executive summary that highlights the key elements of your analysis.
The executive summary should be concise, providing a quick overview of the major issues, the solutions considered, and the recommended course of action.
This section is designed to give readers a snapshot of your findings and conclusions, enabling them to grasp the essence of your case study without delving into the full report.
Writing an effective case study requires a systematic approach to identifying key issues, analyzing potential solutions, and making well-supported recommendations.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can develop a comprehensive and insightful case study that not only addresses the problems at hand but also provides valuable lessons for future situations.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or a researcher, mastering the art of case study writing will enhance your ability to think critically, solve problems, and communicate your findings effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CONTACT INFORMATION
1209 MOUNTAIN ROAD PL NE, STE N, ALBUQUERQUE, NM 87110 (505) 317-7468
STAY CONNECTED
Copyright @2024 Studygs.net - a Study GS LLC Company. All Rights Reserved.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
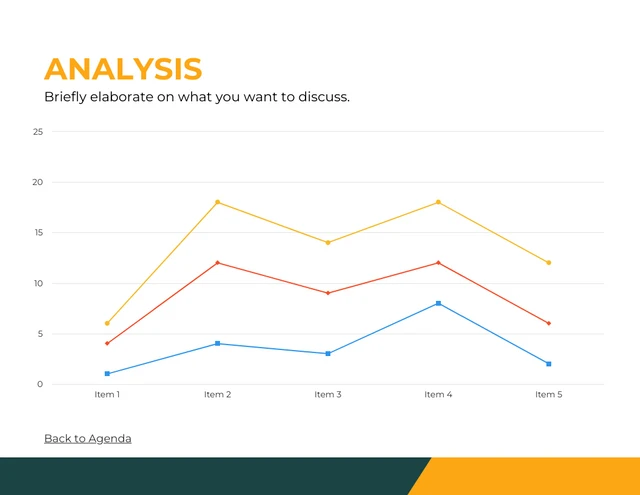
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
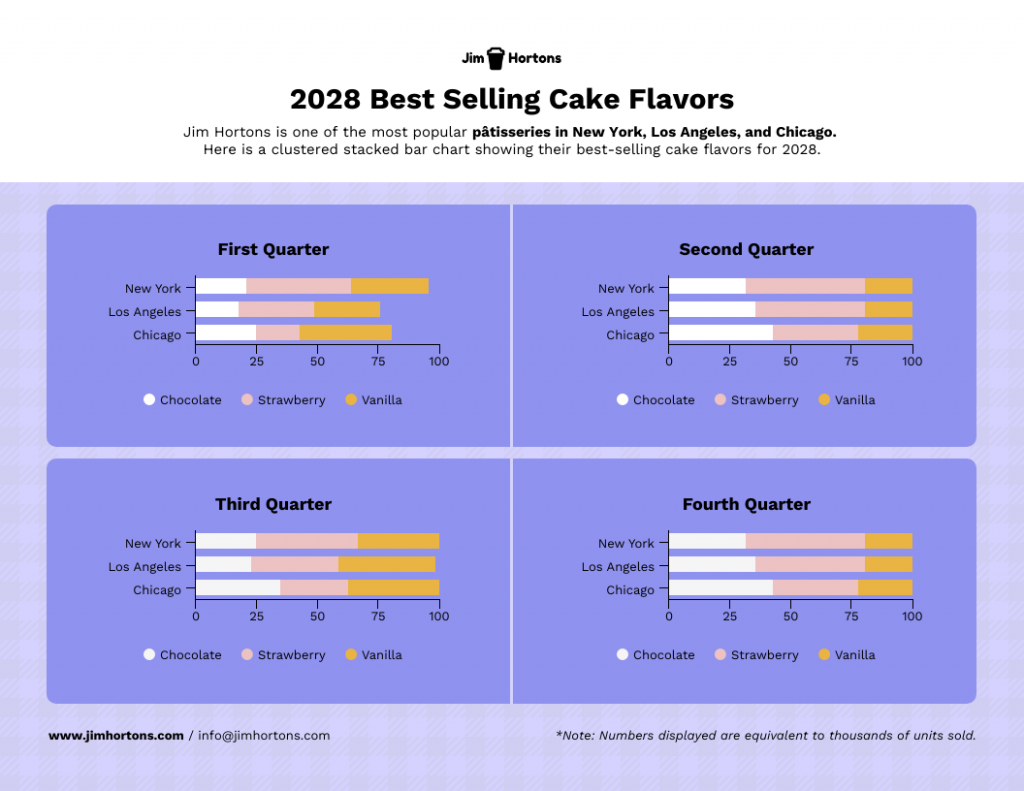
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Analyse a Case Study
Last Updated: April 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Sarah Evans . Sarah Evans is a Public Relations & Social Media Expert based in Las Vegas, Nevada. With over 14 years of industry experience, Sarah is the Founder & CEO of Sevans PR. Her team offers strategic communications services to help clients across industries including tech, finance, medical, real estate, law, and startups. The agency is renowned for its development of the "reputation+" methodology, a data-driven and AI-powered approach designed to elevate brand credibility, trust, awareness, and authority in a competitive marketplace. Sarah’s thought leadership has led to regular appearances on The Doctors TV show, CBS Las Vegas Now, and as an Adobe influencer. She is a respected contributor at Entrepreneur magazine, Hackernoon, Grit Daily, and KLAS Las Vegas. Sarah has been featured in PR Daily and PR Newswire and is a member of the Forbes Agency Council. She received her B.A. in Communications and Public Relations from Millikin University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 413,975 times.
Case studies are used in many professional education programs, primarily in business school, to present real-world situations to students and to assess their ability to parse out the important aspects of a given dilemma. In general, a case study should include, in order: background on the business environment, description of the given business, identification of a key problem or issue, steps taken to address the issue, your assessment of that response, and suggestions for better business strategy. The steps below will guide you through the process of analyzing a business case study in this way.

- Describe the nature of the organization under consideration and its competitors. Provide general information about the market and customer base. Indicate any significant changes in the business environment or any new endeavors upon which the business is embarking.

- Analyze its management structure, employee base, and financial history. Describe annual revenues and profit. Provide figures on employment. Include details about private ownership, public ownership, and investment holdings. Provide a brief overview of the business's leaders and command chain.

- In all likelihood, there will be several different factors at play. Decide which is the main concern of the case study by examining what most of the data talks about, the main problems facing the business, and the conclusions at the end of the study. Examples might include expansion into a new market, response to a competitor's marketing campaign, or a changing customer base. [3] X Research source

- Draw on the information you gathered and trace a chronological progression of steps taken (or not taken). Cite data included in the case study, such as increased marketing spending, purchasing of new property, changed revenue streams, etc.

- Indicate whether or not each aspect of the response met its goal and whether the response overall was well-crafted. Use numerical benchmarks, like a desired customer share, to show whether goals were met; analyze broader issues, like employee management policies, to talk about the response as a whole. [4] X Research source

- Suggest alternative or improved measures that could have been taken by the business, using specific examples and backing up your suggestions with data and calculations.

Community Q&A
- Always read a case study several times. At first, you should read just for the basic details. On each subsequent reading, look for details about a specific topic: competitors, business strategy, management structure, financial loss. Highlight phrases and sections relating to these topics and take notes. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In the preliminary stages of analyzing a case study, no detail is insignificant. The biggest numbers can often be misleading, and the point of an analysis is often to dig deeper and find otherwise unnoticed variables that drive a situation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you are analyzing a case study for a consulting company interview, be sure to direct your comments towards the matters handled by the company. For example, if the company deals with marketing strategy, focus on the business's successes and failures in marketing; if you are interviewing for a financial consulting job, analyze how well the business keeps their books and their investment strategy. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not use impassioned or emphatic language in your analysis. Business case studies are a tool for gauging your business acumen, not your personal beliefs. When assigning blame or identifying flaws in strategy, use a detached, disinterested tone. Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 4
Things You'll Need
You might also like.

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about business writing, check out our in-depth interview with Sarah Evans .
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/cms4/asset/CC3BFEEB-C364-E1A1-A5390F221AC0FD2D/business_case_analysis_gg_final.pdf
- ↑ https://bizfluent.com/12741914/how-to-analyze-a-business-case-study
- ↑ http://www.business-fundas.com/2009/how-to-analyze-business-case-studies/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-case-study-analysis
- http://college.cengage.com/business/resources/casestudies/students/analyzing.htm
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lisa Upshur
Jun 15, 2019
Did this article help you?
Tejiri Aren
Jul 21, 2016
Jul 15, 2017
Jenn M.T. Tseka
Jul 3, 2016
Devanand Sbuurayan
Dec 6, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved August 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
What is case study research?
Last updated
8 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Suppose a company receives a spike in the number of customer complaints, or medical experts discover an outbreak of illness affecting children but are not quite sure of the reason. In both cases, carrying out a case study could be the best way to get answers.
Organization
Case studies can be carried out across different disciplines, including education, medicine, sociology, and business.
Most case studies employ qualitative methods, but quantitative methods can also be used. Researchers can then describe, compare, evaluate, and identify patterns or cause-and-effect relationships between the various variables under study. They can then use this knowledge to decide what action to take.
Another thing to note is that case studies are generally singular in their focus. This means they narrow focus to a particular area, making them highly subjective. You cannot always generalize the results of a case study and apply them to a larger population. However, they are valuable tools to illustrate a principle or develop a thesis.
Analyze case study research
Dovetail streamlines case study research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What are the different types of case study designs?
Researchers can choose from a variety of case study designs. The design they choose is dependent on what questions they need to answer, the context of the research environment, how much data they already have, and what resources are available.
Here are the common types of case study design:
Explanatory
An explanatory case study is an initial explanation of the how or why that is behind something. This design is commonly used when studying a real-life phenomenon or event. Once the organization understands the reasons behind a phenomenon, it can then make changes to enhance or eliminate the variables causing it.
Here is an example: How is co-teaching implemented in elementary schools? The title for a case study of this subject could be “Case Study of the Implementation of Co-Teaching in Elementary Schools.”
Descriptive
An illustrative or descriptive case study helps researchers shed light on an unfamiliar object or subject after a period of time. The case study provides an in-depth review of the issue at hand and adds real-world examples in the area the researcher wants the audience to understand.
The researcher makes no inferences or causal statements about the object or subject under review. This type of design is often used to understand cultural shifts.
Here is an example: How did people cope with the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami? This case study could be titled "A Case Study of the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami and its Effect on the Indonesian Population."
Exploratory
Exploratory research is also called a pilot case study. It is usually the first step within a larger research project, often relying on questionnaires and surveys . Researchers use exploratory research to help narrow down their focus, define parameters, draft a specific research question , and/or identify variables in a larger study. This research design usually covers a wider area than others, and focuses on the ‘what’ and ‘who’ of a topic.
Here is an example: How do nutrition and socialization in early childhood affect learning in children? The title of the exploratory study may be “Case Study of the Effects of Nutrition and Socialization on Learning in Early Childhood.”
An intrinsic case study is specifically designed to look at a unique and special phenomenon. At the start of the study, the researcher defines the phenomenon and the uniqueness that differentiates it from others.
In this case, researchers do not attempt to generalize, compare, or challenge the existing assumptions. Instead, they explore the unique variables to enhance understanding. Here is an example: “Case Study of Volcanic Lightning.”
This design can also be identified as a cumulative case study. It uses information from past studies or observations of groups of people in certain settings as the foundation of the new study. Given that it takes multiple areas into account, it allows for greater generalization than a single case study.
The researchers also get an in-depth look at a particular subject from different viewpoints. Here is an example: “Case Study of how PTSD affected Vietnam and Gulf War Veterans Differently Due to Advances in Military Technology.”
Critical instance
A critical case study incorporates both explanatory and intrinsic study designs. It does not have predetermined purposes beyond an investigation of the said subject. It can be used for a deeper explanation of the cause-and-effect relationship. It can also be used to question a common assumption or myth.
The findings can then be used further to generalize whether they would also apply in a different environment. Here is an example: “What Effect Does Prolonged Use of Social Media Have on the Mind of American Youth?”
Instrumental
Instrumental research attempts to achieve goals beyond understanding the object at hand. Researchers explore a larger subject through different, separate studies and use the findings to understand its relationship to another subject. This type of design also provides insight into an issue or helps refine a theory.
For example, you may want to determine if violent behavior in children predisposes them to crime later in life. The focus is on the relationship between children and violent behavior, and why certain children do become violent. Here is an example: “Violence Breeds Violence: Childhood Exposure and Participation in Adult Crime.”
Evaluation case study design is employed to research the effects of a program, policy, or intervention, and assess its effectiveness and impact on future decision-making.
For example, you might want to see whether children learn times tables quicker through an educational game on their iPad versus a more teacher-led intervention. Here is an example: “An Investigation of the Impact of an iPad Multiplication Game for Primary School Children.”
- When do you use case studies?
Case studies are ideal when you want to gain a contextual, concrete, or in-depth understanding of a particular subject. It helps you understand the characteristics, implications, and meanings of the subject.
They are also an excellent choice for those writing a thesis or dissertation, as they help keep the project focused on a particular area when resources or time may be too limited to cover a wider one. You may have to conduct several case studies to explore different aspects of the subject in question and understand the problem.
- What are the steps to follow when conducting a case study?
1. Select a case
Once you identify the problem at hand and come up with questions, identify the case you will focus on. The study can provide insights into the subject at hand, challenge existing assumptions, propose a course of action, and/or open up new areas for further research.
2. Create a theoretical framework
While you will be focusing on a specific detail, the case study design you choose should be linked to existing knowledge on the topic. This prevents it from becoming an isolated description and allows for enhancing the existing information.
It may expand the current theory by bringing up new ideas or concepts, challenge established assumptions, or exemplify a theory by exploring how it answers the problem at hand. A theoretical framework starts with a literature review of the sources relevant to the topic in focus. This helps in identifying key concepts to guide analysis and interpretation.
3. Collect the data
Case studies are frequently supplemented with qualitative data such as observations, interviews, and a review of both primary and secondary sources such as official records, news articles, and photographs. There may also be quantitative data —this data assists in understanding the case thoroughly.
4. Analyze your case
The results of the research depend on the research design. Most case studies are structured with chapters or topic headings for easy explanation and presentation. Others may be written as narratives to allow researchers to explore various angles of the topic and analyze its meanings and implications.
In all areas, always give a detailed contextual understanding of the case and connect it to the existing theory and literature before discussing how it fits into your problem area.
- What are some case study examples?
What are the best approaches for introducing our product into the Kenyan market?
How does the change in marketing strategy aid in increasing the sales volumes of product Y?
How can teachers enhance student participation in classrooms?
How does poverty affect literacy levels in children?
Case study topics
Case study of product marketing strategies in the Kenyan market
Case study of the effects of a marketing strategy change on product Y sales volumes
Case study of X school teachers that encourage active student participation in the classroom
Case study of the effects of poverty on literacy levels in children
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Mixed Methods Research – Types & Analysis

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

- Writing well
How to write a case study response
- Starting well
- How to write an annotated bibliography
- How to write a critique
- How to write an empirical article
- How to write an essay
- How to write a literature review
- How to write a reflective task
- How to write a report
- Finishing well
Before you start writing, you need to carefully read the case study and make a note of the main issues and problems involved as well as the main stakeholders (persons or groups of persons who have an interest in the case).
Case study elements
A case study response would include the following elements:
Introduction
Introduce the main purpose of the case study and briefly outline the overall problem to be solved.
Description
Write a brief description of the case under discussion giving an outline of the main issues involved. Always assume that your reader knows nothing of the assignment task and provide enough information to give a context for your discussion of the issues.
Discuss the issues raised one by one, using information gained from your research of the academic literature.
Your discussion may include:
- an outline of the issue and its implications for or relationship to different stakeholders
- how that issue links to theories or research in the academic literature
- suggested solutions or ideas
- evaluation of the solutions or ideas for this particular case.
Conclusion / Recommendations
Finally, sum up the conclusions that you have come to and give recommendations to resolve the case. Give reasons for your recommendations.
- Carefully read the case and noted the main issues and stakeholders in the case?
- Written a brief description of the case to give your readers a context for the main issues?
- Discussed each issue with reference to the academic literature?
- Evaluated the solutions or ideas for each issue to find the ones most suitable?
- Made final recommendations of how to resolve the case?
- Used a well structured introduction, body and conclusion?
- Cited and referenced all of the work by other people?
- Used correct grammar, spelling and punctuation, clear presentation and appropriate reference style?
Further information
- Monash University: Writing a case study
- University of New South Wales: Writing a Case Study Report in Engineering
Global links and information
- Referencing and using sources
- Background and development
- Changes to QUT cite|write
- Need more help?
- Current students
- Current staff
- TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12079 (Australian University)
- CRICOS No. 00213J
- ABN 83 791 724 622
- Last modified: 28-May-2024
- Accessibility
- Right to Information
- Feedback and suggestions

Acknowledgement of Traditional Owners
QUT acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands where QUT now stands.
- All Categories
- Marketing Analytics Software
What Is a Case Study? How to Write, Examples, and Template

In this post
How to write a case study
Case study template, case study examples, types of case studies, what are the benefits of case studies , what are the limitations of case studies , case study vs. testimonial.
In today's marketplace, conveying your product's value through a compelling narrative is crucial to genuinely connecting with your customers.
Your business can use marketing analytics tools to understand what customers want to know about your product. Once you have this information, the next step is to showcase your product and its benefits to your target audience. This strategy involves a mix of data, analysis, and storytelling. Combining these elements allows you to create a narrative that engages your audience. So, how can you do this effectively?
What is a case study?
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing a business's success in helping clients achieve their goals. It's a form of storytelling that details real-world scenarios where a business implemented its solutions to deliver positive results for a client.
In this article, we explore the concept of a case study , including its writing process, benefits, various types, challenges, and more.
Understanding how to write a case study is an invaluable skill. You'll need to embrace decision-making – from deciding which customers to feature to designing the best format to make them as engaging as possible. This can feel overwhelming in a hurry, so let's break it down.
Step 1: Reach out to the target persona
If you've been in business for a while, you have no shortage of happy customers. But w ith limited time and resources, you can't choose everyone. So, take some time beforehand to flesh out your target buyer personas.
Once you know precisely who you're targeting, go through your stable of happy customers to find a buyer representative of the audience you're trying to reach. The closer their problems, goals, and industries align, the more your case study will resonate.
What if you have more than one buyer persona? No problem. This is a common situation for companies because buyers comprise an entire committee. You might be marketing to procurement experts, executives, engineers, etc. Try to develop a case study tailored to each key persona. This might be a long-term goal, and that's fine. The better you can personalize the experience for each stakeholder, the easier it is to keep their attention.
Here are a few considerations to think about before research:
- Products/services of yours the customer uses (and how familiar they are with them)
- The customer's brand recognition in the industry
- Whether the results they've achieved are specific and remarkable
- Whether they've switched from a competitor's product/service
- How closely aligned they are with your target audience
These items are just a jumping-off point as you develop your criteria. Once you have a list, run each customer through it to determine your top targets. Approach the ones on the top (your "dream" case study subjects) and work your way down as needed.
Who to interview
You should consider interviewing top-level managers or executives because those are high-profile positions. But consider how close they are to your product and its results.
Focusing on an office manager or engineer who uses your product daily would be better. Look for someone with a courtside view of the effects.
The ways to request customer participation in case studies can vary, but certain principles can improve your chances:
- Make it easy for customers to work with you, respecting their valuable time. Be well-prepared and minimize their involvement.
- Emphasize how customers will benefit through increased publicity, revenue opportunities, or recognition for their success.
- Acknowledge their contributions and showcase their achievements.
- Standardizing the request process with a script incorporating these principles can help your team consistently secure case study approvals and track performance.
Step 2: Prepare for the interview
Case study interviews are like school exams. The more prepared you are for them, the better they turn out. Preparing thoroughly also shows participants that you value their time. You don't waste precious minutes rehashing things you should have already known. You focus on getting the information you need as efficiently as possible.
You can conduct your case study interview in multiple formats, from exchanging emails to in-person interviews. This isn't a trivial decision. As you'll see in the chart below, each format has its unique advantages and disadvantages.
| Seeing each other's facial expressions puts everyone at ease and encourages case study participants to open up. It's a good format if you're simultaneously conferencing with several people from the customer's team. | Always be on guard for connection issues; not every customer knows the technology. Audio quality will probably be less good than on the phone. When multiple people are talking, pieces of conversation can be lost. | |
| It is a more personal than email because you can hear someone's tone. You can encourage them to continue if they get really excited about certain answers. Convenient and immediate. Dial a number and start interviewing without ever leaving the office. | It isn't as personal as a video chat or an in-person interview because you can't see the customer's face, and nonverbal cues might be missed. Don't get direct quotes like you would with email responses. The only way to preserve the interview is to remember to have it recorded. | |
| The most personal interview style. It feels like an informal conversation, making it easier to tell stories and switch seamlessly between topics. Humanizes the customer's experience and allows you to put a face to the incredible results. | Puts a lot of pressure on customers who are shy or introverted – especially if they're being recorded. Requires the most commitment for the participant – travel, dressing up, dealing with audiovisual equipment, etc. | |
| Gives customers the most flexibility with respect to scheduling. They can answer a few questions, see to their obligations, and return to them at their convenience. No coordination of schedules is needed. Each party can fulfill their obligations whenever they're able to. | There is less opportunity for customers to go “off script” and tell compelling anecdotes that your questions might have overlooked. Some of the study participant's personalities might be lost in their typed responses. It's harder to sense their enthusiasm or frustration. |
You'll also have to consider who will ask and answer the questions during your case study interview. It's wise to consider this while considering the case study format. The number of participants factors into which format will work best. Pulling off an in-person interview becomes much harder if you're trying to juggle four or five people's busy schedules. Try a video conference instead.
Before interviewing your case study participant, it is crucial to identify the specific questions that need to be asked. It's essential to thoroughly evaluate your collaboration with the client and understand how your product's contributions impact the company.
Remember that structuring your case study is akin to crafting a compelling narrative. To achieve this, follow a structured approach:
- Beginning of your story. Delve into the customer's challenge that ultimately led them to do business with you. What were their problems like? What drove them to make a decision finally? Why did they choose you?
- The middle of the case study. Your audience also wants to know about the experience of working with you. Your customer has taken action to address their problems. What happened once you got on board?
- An ending that makes you the hero. Describe the specific results your company produced for the customer. How has the customer's business (and life) changed once they implemented your solution?
Sample questions for the case study interview
If you're preparing for a case study interview, here are some sample case study research questions to help you get started:
- What challenges led you to seek a solution?
- When did you realize the need for immediate action? Was there a tipping point?
- How did you decide on the criteria for choosing a B2B solution, and who was involved?
- What set our product or service apart from others you considered?
- How was your experience working with us post-purchase?
- Were there any pleasant surprises or exceeded expectations during our collaboration?
- How smoothly did your team integrate our solution into their workflows?
- How long before you started seeing positive results?
- How have you benefited from our products or services?
- How do you measure the value our product or service provides?
Step 3: Conduct the interview
Preparing for case study interviews can be different from everyday conversations. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Create a comfortable atmosphere. Before diving into the discussion, talk about their business and personal interests. Ensure everyone is at ease, and address any questions or concerns.
- Prioritize key questions. Lead with your most crucial questions to respect your customer's time. Interview lengths can vary, so starting with the essentials ensures you get the vital information.
- Be flexible. Case study interviews don't have to be rigid. If your interviewee goes "off script," embrace it. Their spontaneous responses often provide valuable insights.
- Record the interview. If not conducted via email, ask for permission to record the interview. This lets you focus on the conversation and capture valuable quotes without distractions.
Step 4: Figure out who will create the case study
When creating written case studies for your business, deciding who should handle the writing depends on cost, perspective, and revisions.
Outsourcing might be pricier, but it ensures a professionally crafted outcome. On the other hand, in-house writing has its considerations, including understanding your customers and products.
Technical expertise and equipment are needed for video case studies, which often leads companies to consider outsourcing due to production and editing costs.
Tip: When outsourcing work, it's essential to clearly understand pricing details to avoid surprises and unexpected charges during payment.
Step 5: Utilize storytelling
Understanding and applying storytelling elements can make your case studies unforgettable, offering a competitive edge.

Source: The Framework Bank
Every great study follows a narrative arc (also called a "story arc"). This arc represents how a character faces challenges, struggles against raising stakes, and encounters a formidable obstacle before the tension resolves.
In a case study narrative, consider:
- Exposition. Provide background information about the company, revealing their "old life" before becoming your customer.
- Inciting incident. Highlight the problem that drove the customer to seek a solution, creating a sense of urgency.
- Obstacles (rising action). Describe the customer's journey in researching and evaluating solutions, building tension as they explore options.
- Midpoint. Explain what made the business choose your product or service and what set you apart.
- Climax. Showcase the success achieved with your product.
- Denouement. Describe the customer's transformed business and end with a call-to-action for the reader to take the next step.
Step 6: Design the case study
The adage "Don't judge a book by its cover" is familiar, but people tend to do just that quite often!
A poor layout can deter readers even if you have an outstanding case study. To create an engaging case study, follow these steps:
- Craft a compelling title. Just like you wouldn't read a newspaper article without an eye-catching headline, the same goes for case studies. Start with a title that grabs attention.
- Organize your content. Break down your content into different sections, such as challenges, results, etc. Each section can also include subsections. This case study approach divides the content into manageable portions, preventing readers from feeling overwhelmed by lengthy blocks of text.
- Conciseness is key. Keep your case study as concise as possible. The most compelling case studies are precisely long enough to introduce the customer's challenge, experience with your solution, and outstanding results. Prioritize clarity and omit any sections that may detract from the main storyline.
- Utilize visual elements. To break up text and maintain reader interest, incorporate visual elements like callout boxes, bulleted lists, and sidebars.
- Include charts and images. Summarize results and simplify complex topics by including pictures and charts. Visual aids enhance the overall appeal of your case study.
- Embrace white space. Avoid overwhelming walls of text to prevent reader fatigue. Opt for plenty of white space, use shorter paragraphs, and employ subsections to ensure easy readability and navigation.
- Enhance video case studies. In video case studies, elements like music, fonts, and color grading are pivotal in setting the right tone. Choose music that complements your message and use it strategically throughout your story. Carefully select fonts to convey the desired style, and consider how lighting and color grading can influence the mood. These elements collectively help create the desired tone for your video case study.
Step 7: Edits and revisions
Once you've finished the interview and created your case study, the hardest part is over. Now's the time for editing and revision. This might feel frustrating for impatient B2B marketers, but it can turn good stories into great ones.
Ideally, you'll want to submit your case study through two different rounds of editing and revisions:
- Internal review. Seek feedback from various team members to ensure your case study is captivating and error-free. Gather perspectives from marketing, sales, and those in close contact with customers for well-rounded insights. Use patterns from this feedback to guide revisions and apply lessons to future case studies.
- Customer feedback. Share the case study with customers to make them feel valued and ensure accuracy. Let them review quotes and data points, as they are the "heroes" of the story, and their logos will be prominently featured. This step maintains positive customer relationships.
Case study mistakes to avoid
- Ensure easy access to case studies on your website.
- Spotlight the customer, not just your business.
- Tailor each case study to a specific audience.
- Avoid excessive industry jargon in your content.
Step 8: Publishing
Take a moment to proofread your case study one more time carefully. Even if you're reasonably confident you've caught all the errors, it's always a good idea to check. Your case study will be a valuable marketing tool for years, so it's worth the investment to ensure it's flawless. Once done, your case study is all set to go!
Consider sharing a copy of the completed case study with your customer as a thoughtful gesture. They'll likely appreciate it; some may want to keep it for their records. After all, your case study wouldn't have been possible without their help, and they deserve to see the final product.
Where you publish your case study depends on its role in your overall marketing strategy. If you want to reach as many people as possible with your case study, consider publishing it on your website and social media platforms.
Tip: Some companies prefer to keep their case studies exclusive, making them available only to those who request them. This approach is often taken to control access to valuable information and to engage more deeply with potential customers who express specific interests. It can create a sense of exclusivity and encourage interested parties to engage directly with the company.
Step 9: Case study distribution
When sharing individual case studies, concentrate on reaching the audience with the most influence on purchasing decisions
Here are some common distribution channels to consider:
- Sales teams. Share case studies to enhance customer interactions, retention , and upselling among your sales and customer success teams. Keep them updated on new studies and offer easily accessible formats like PDFs or landing page links.
- Company website. Feature case studies on your website to establish authority and provide valuable information to potential buyers. Organize them by categories such as location, size, industry, challenges, and products or services used for effective presentation.
- Events. Use live events like conferences and webinars to distribute printed case study copies, showcase video case studies at trade show booths, and conclude webinars with links to your case study library. This creative approach blends personal interactions with compelling content.
- Industry journalists. Engage relevant industry journalists to gain media coverage by identifying suitable publications and journalists covering related topics. Building relationships is vital, and platforms like HARO (Help A Reporter Out) can facilitate connections, especially if your competitors have received coverage before.
Want to learn more about Marketing Analytics Software? Explore Marketing Analytics products.
It can seem daunting to transform the information you've gathered into a cohesive narrative. We’ve created a versatile case study template that can serve as a solid starting point for your case study.
With this template, your business can explore any solutions offered to satisfied customers, covering their background, the factors that led them to choose your services, and their outcomes.

The template boasts a straightforward design, featuring distinct sections that guide you in effectively narrating your and your customer's story. However, remember that limitless ways to showcase your business's accomplishments exist.
To assist you in this process, here's a breakdown of the recommended sections to include in a case study:
- Title. Keep it concise. Create a brief yet engaging project title summarizing your work with your subject. Consider your title like a newspaper headline; do it well, and readers will want to learn more.
- Subtitle . Use this section to elaborate on the achievement briefly. Make it creative and catchy to engage your audience.
- Executive summary. Use this as an overview of the story, followed by 2-3 bullet points highlighting key success metrics.
- Challenges and objectives. This section describes the customer's challenges before adopting your product or service, along with the goals or objectives they sought to achieve.
- How product/service helped. A paragraph explaining how your product or service addressed their problem.
- Testimonials. Incorporate short quotes or statements from the individuals involved in the case study, sharing their perspectives and experiences.
- Supporting visuals. Include one or two impactful visuals, such as graphs, infographics, or highlighted metrics, that reinforce the narrative.
- Call to action (CTA). If you do your job well, your audience will read (or watch) your case studies from beginning to end. They are interested in everything you've said. Now, what's the next step they should take to continue their relationship with you? Give people a simple action they can complete.
Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study:
- Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced using AWS.
- LinkedIn Marketing Solutions combines captivating visuals with measurable results in the case study created for BlackRock. This case study illustrates how LinkedIn has contributed to the growth of BlackRock's brand awareness over the years.
- Salesforce , a sales and marketing automation SaaS solutions provider, seamlessly integrates written and visual elements to convey its success stories with Pepe Jeans. This case study effectively demonstrates how Pepe Jeans is captivating online shoppers with immersive and context-driven e-commerce experiences through Salesforce.
- HubSpot offers a combination of sales and marketing tools. Their case study demonstrates the effectiveness of its all-in-one solutions. These typically focus on a particular client's journey and how HubSpot helped them achieve significant results.
There are two different types of case studies that businesses might utilize:
Written case studies
Written case studies offer readers a clear visual representation of data, which helps them quickly identify and focus on the information that matters most.
Printed versions of case studies find their place at events like trade shows, where they serve as valuable sales collateral to engage prospective clients. Even in the digital age, many businesses provide case studies in PDF format or as web-based landing pages, improving accessibility for their audience.
Note: Landing pages , in particular, offer the flexibility to incorporate rich multimedia content, including images, charts, and videos. This flexibility in design makes landing pages an attractive choice for presenting detailed content to the audience.
Written case study advantages
Here are several significant advantages to leveraging case studies for your company:
- Hyperlink accessibility. Whether in PDF or landing page format, written case studies allow for embedded hyperlinks, offering prospects easy access to additional information and contact forms.
- Flexible engagement. Unlike video case studies, which may demand in-person arrangements, written case studies can be conducted via phone or video streaming, reducing customer commitment and simplifying scheduling.
- Efficient scanning . Well-structured written case studies with a scannable format cater to time-strapped professionals. Charts and callout boxes with key statistics enhance the ease of information retrieval.
- Printable for offline use. Written case studies can be effortlessly printed and distributed at trade shows, sales meetings, and live events. This tangible format accommodates those who prefer physical materials and provides versatility in outreach, unlike video content, which is less portable.
Written case study disadvantages
Here are some drawbacks associated with the use of case studies:
- Reduced emotional impact. Written content lacks the emotional punch of live video testimonials, which engage more senses and emotions, making a stronger connection.
- Consider time investment. Creating a compelling case study involves editing, proofreading, and design collaboration, with multiple revisions commonly required before publication.
- Challenges in maintaining attention. Attention spans are short in today's ad-saturated world. Using graphics, infographics, and videos more often is more powerful to incite the right emotions in customers.

Video case studies
Video case studies are the latest marketing trend. Unlike in the past, when video production was costly, today's tools make it more accessible for users to create and edit their videos. However, specific technical requirements still apply.
Like written case studies, video case studies delve into a specific customer's challenges and how your business provides solutions. Yet, the video offers a more profound connection by showcasing the person who faced and conquered the problem.
Video case studies can boost brand exposure when shared on platforms like YouTube. For example, Slack's engaging case study video with Sandwich Video illustrates how Slack transformed its workflow and adds humor, which can be challenging in written case studies focused on factual evidence.
Source : YouTube
This video case study has garnered nearly a million views on YouTube.
Video case study advantages
Here are some of the top advantages of video case studies. While video testimonials take more time, the payoff can be worth it.
- Humanization and authenticity. Video case studies connect viewers with real people, adding authenticity and fostering a stronger emotional connection.
- Engaging multiple senses. They engage both auditory and visual senses, enhancing credibility and emotional impact. Charts, statistics, and images can also be incorporated.
- Broad distribution. Videos can be shared on websites, YouTube, social media, and more, reaching diverse audiences and boosting engagement, especially on social platforms.
Video case study disadvantages
Before fully committing to video testimonials, consider the following:
- Technical expertise and equipment. Video production requires technical know-how and equipment, which can be costly. Skilled video editing is essential to maintain a professional image. While technology advances, producing amateurish videos may harm your brand's perception.
- Viewer convenience. Some prospects prefer written formats due to faster reading and ease of navigation. Video typically requires sound, which can be inconvenient for viewers in specific settings. Many people may not have headphones readily available to watch your content.
- Demand on case study participants. On-camera interviews can be time-consuming and location-dependent, making scheduling challenging for case study participants. Additionally, being on screen for a global audience may create insecurities and performance pressure.
- Comfort on camera. Not everyone feels at ease on camera. Nervousness or a different on-screen persona can impact the effectiveness of the testimonial, and discovering this late in the process can be problematic.
Written or video case studies: Which is right for you?
Now that you know the pros and cons of each, how do you choose which is right for you?
One of the most significant factors in doing video case studies can be the technical expertise and equipment required for a high level of production quality. Whether you have the budget to do this in-house or hire a production company can be one of the major deciding factors.
Still, written or video doesn't have to be an either-or decision. Some B2B companies are using both formats. They can complement each other nicely, minimizing the downsides mentioned above and reaching your potential customers where they prefer.
Let's say you're selling IT network security. What you offer is invaluable but complicated. You could create a short (three- or four-minute) video case study to get attention and touch on the significant benefits of your services. This whets the viewer's appetite for more information, which they could find in a written case study that supplements the video.
Should you decide to test the water in video case studies, test their effectiveness among your target audience. See how well they work for your company and sales team. And, just like a written case study, you can always find ways to improve your process as you continue exploring video case studies.
Case studies offer several distinctive advantages, making them an ideal tool for businesses to market their products to customers. However, their benefits extend beyond these qualities.
Here's an overview of all the advantages of case studies:
Valuable sales support
Case studies serve as a valuable resource for your sales endeavors. Buyers frequently require additional information before finalizing a purchase decision. These studies provide concrete evidence of your product or service's effectiveness, assisting your sales representatives in closing deals more efficiently, especially with customers with lingering uncertainties.
Validating your value
Case studies serve as evidence of your product or service's worth or value proposition , playing a role in building trust with potential customers. By showcasing successful partnerships, you make it easier for prospects to place trust in your offerings. This effect is particularly notable when the featured customer holds a reputable status.
Unique and engaging content
By working closely with your customer success teams, you can uncover various customer stories that resonate with different prospects. Case studies allow marketers to shape product features and benefits into compelling narratives.
Each case study's distinctiveness, mirroring the uniqueness of every customer's journey, makes them a valuable source of relatable and engaging content. Storytelling possesses the unique ability to connect with audiences on an emotional level, a dimension that statistics alone often cannot achieve.
Spotlighting valuable customers
Case studies provide a valuable platform for showcasing your esteemed customers. Featuring them in these studies offers a chance to give them visibility and express your gratitude for the partnership, which can enhance customer loyalty . Depending on the company you are writing about, it can also demonstrate the caliber of your business.
Now is the time to get SaaS-y news and entertainment with our 5-minute newsletter, G2 Tea , featuring inspiring leaders, hot takes, and bold predictions. Subscribe below!

It's important to consider limitations when designing and interpreting the results of case studies. Here's an overview of the limitations of case studies:
Challenges in replication
Case studies often focus on specific individuals, organizations, or situations, making generalizing their findings to broader populations or contexts challenging.
Time-intensive process
Case studies require a significant time investment. The extensive data collection process and the need for comprehensive analysis can be demanding, especially for researchers who are new to this method.
Potential for errors
Case studies can be influenced by memory and judgment, potentially leading to inaccuracies. Depending on human memory to reconstruct a case's history may result in variations and potential inconsistencies in how individuals recall past events. Additionally, bias may emerge, as individuals tend to prioritize what they consider most significant, which could limit their consideration of alternative perspectives.
Challenges in verification
Confirming results through additional research can present difficulties. This complexity arises from the need for detailed and extensive data in the initial creation of a case study. Consequently, this process requires significant effort and a substantial amount of time.
While looking at case studies, you may have noticed a quote. This type of quote is considered a testimonial, a key element of case studies.
If a customer's quote proves that your brand does what it says it will or performs as expected, you may wonder: 'Aren't customer testimonials and case studies the same thing?' Not exactly.

Testimonials are brief endorsements designed to establish trust on a broad scale. In contrast, case studies are detailed narratives that offer a comprehensive understanding of how a product or service addresses a specific problem, targeting a more focused audience.
Crafting case studies requires more resources and a structured approach than testimonials. Your selection between the two depends on your marketing objectives and the complexity of your product or service.
Case in point!
Case studies are among a company's most effective tools. You're well on your way to mastering them.
Today's buyers are tackling much of the case study research methodology independently. Many are understandably skeptical before making a buying decision. By connecting them with multiple case studies, you can prove you've gotten the results you say you can. There's hardly a better way to boost your credibility and persuade them to consider your solution.
Case study formats and distribution methods might change as technology evolves. However, the fundamentals that make them effective—knowing how to choose subjects, conduct interviews, and structure everything to get attention—will serve you for as long as you're in business.
We covered a ton of concepts and resources, so go ahead and bookmark this page. You can refer to it whenever you have questions or need a refresher.
Dive into market research to uncover customer preferences and spending habits.
Kristen McCabe
Kristen’s is a former senior content marketing specialist at G2. Her global marketing experience extends from Australia to Chicago, with expertise in B2B and B2C industries. Specializing in content, conversions, and events, Kristen spends her time outside of work time acting, learning nature photography, and joining in the #instadog fun with her Pug/Jack Russell, Bella. (she/her/hers)
Explore More G2 Articles

Key Study Skills
- Assignment Calculator
- Managing nervousness
- Group Work and Collaboration
- Allocating time and using the marking system
- Using the reading time effectively
- Answering multi-choice and short answer questions
- Answering essay and case study questions in exams
- Managing exam stress
- Academic Skills for Success
Answering essay questions in exams
Writing an essay in an exam is similar in many ways to writing an essay for an assignment: It needs to be clearly structured, and your ideas need to be linked and supported by evidence.
Essay questions in exams
- Read the question through carefully to make sure you are answering what has been asked. Missing one part of a question can cost you a lot of marks.
- Make a quick plan of the points you want to include in your answer.
- Use essay structure: introduction, points, conclusion. But if you run out of time, it can be a good idea to write notes.
- Get right to the point from the beginning. Use the words from the question to write your first sentence. For example:
Question: What do you think is the most important intercultural communication issue in New Zealand? First sentence: At present in New Zealand the most important intercultural communication issue is...
- Remember to include one idea per paragraph, and to begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence.
- Make sure your writing is legible.
- Grammar, punctuation and spelling are not as important as in an assignment but should still be of a good standard.
Answering case study questions
Exam questions that ask you to anlayse case studies (also called scenarios) are usually designed to test your ability to relate theories and concepts to real-world situations.
Preparing for case studies before the exam:
- Start by identifying the theories and concepts covered in your course. Organise and review the information you have on these theories/concepts so you understand them.
- Practice reading case studies and identifying relevant information. It's probably useful to practice doing this with a time limit as you will have one in your exam.
- Practice relating concepts and theories to real-world situations: ask lecturers and check textbooks for practice examples. It is also worth checking past exams for your course to see if there are examples of case study questions.
During the exam
- Take time to plan: Have a clear idea of how much time you have to answer the question. Then plan to spend some time reading the exam question, the case study and planning your answer. Take time to make sure you have understood the case study and know what the exam question is asking you to do:
- Read the exam question(s)
- Then skim read the case study to get the general idea. Highlight or underline key points
- Reread the question to make sure you understand it and to focus your attention when you reread the case study.
- Reread the case study carefully. Make a note of any ideas that you think of.
- Answer the question linking relevant theories and concepts to specific information from the case study. Usually you will need to write your answers in clearly formed paragraphs which have a clear topic that is well-supported with evidence and examples.
- Instead of simply describing or restating information from the case itself, use specific details or examples to support the points you are trying to make. This is where you link theory to the facts from the case study.
- << Previous: Answering multi-choice and short answer questions
- Next: Managing exam stress >>
Unitec Private Bag 92025 Victoria Street West Auckland 1142 Unitec website
- Last Updated: Aug 14, 2024 3:45 PM
- URL: https://guides.unitec.ac.nz/studyskills
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Harvard Case Study Solution
- Case Study Report Writing Service
- Case Study Presentation Help
- Finance Case Study Help
- Accounting Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Management Case Study Help
- Economics Case Study Help
- MBA Case Study Help
- Assignment Help
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Finance Assignment Help
- Marketing Assignment Help
- HR Assignment Help
- Economics Assignment Help
- Law Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Biology Assignment Help
- Chemistry Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Homework Help
- Thesis Help
- Dissertation Help
- How it Works
How To Answer A Case Study
We totally understand the dire need of students to find credible help with their case studies. Whether they are the students of a college or a university, time and again, you will be asked to make your case studies effectively. This brings to the question as to who will answer a case study impressively? Students can find several online companies that guarantee some great tips for answering your case studies nicely, but not all of them are to rely on.
We bet we have the best step to step guide with us that can easily get you to the end of your case study solutions . The following tips will promise to help you efficiently with your case, irrespective of how difficult they are. Precisely, when it comes to the question of how to answer a case study, it’s all about words. So, do not hesitate in using the correct and researched words to leave a lasting impact.
How To Answer A Consulting Case Study On Three Major Types
Case studies are not an easy task to fulfill in your academic life. If students dare to take it lightly, chances are you will not be able to impress your teachers. However, case studies do not come as easy as they sound. There are three significant types of case studies that are popular among students.
- Legal Case Study
- Nursing Case Study
- Management Case Study
These are the common subjects that will lead to stress in your college or university life. With so much other stuff to do, students don’t feel happy about the pressure of finding a fruitful answer to the case study. There is no doubt it’s quite a challenging situation for any student who has to make a flawless case study. That’s why we usually advise our students to get online help for their case study writing. Because of it, they can have fewer chances of flunking in these exams.
The Helpful 15 Tips On How To Answer A Case Study
When students have no option but to write a persuasive case study, it is preferable to set out on a journey to get external help for it. You can get easy help online. You will be pleased to know that our writing help has some best case study assignment writers who can distress you in a matter of a few hours. But, the most vital thing to know is that a student should know the basic formulas to find good answers to your case studies on their own.
We have collected some fabulous notable tips for our students can help them for years with their case studies:
- Use Conventional Tone: The foremost thing while writing case studies is to use a professional tone to have a lasting impact on your papers.
- Use Your Words Only: It is equally important for a student to use simple and their wording while writing case studies.
- Don’t Be Too Precise: Sometimes, providing proper sentences gives an understandable image to your case studies. Hence, soon use shorter or confusing sentences.
- Use Examples: The students should support their case studies with relevant examples. The examples can be given through a video, statements which should prove your opinions as well.
- Accurate Grammar: Your writing is the crucial thing, Don’t engage in poorly written content. Use proper English without any grammatical errors or spelling mistakes.
- No Acronyms: Students should avoid using acronyms while writing their case studies.
- Use Life Experiences: Your practical life experiences are important to make a compelling case study. Try to use live examples to give a more impactful expression to your case studies.
- Justified Statements Are Necessary: The best way to answer a case study is to agree or disagree with the justified statements.
- Make Complete Sentences: It is also an important point to make a flawless case study paper. While writing, try to make complete sentences.
- No Spelling Flaws: Bad grammar or wrong spellings are not tolerable. Hence, students should do keen writing with no spelling mistakes.
- Proper Answers: Try to give proper answers to the questions.
- Adequate Justifications: Justifications are crucial. Make adequate justifications to avoid any confusion.
- Sufficient Reasoning: The reasoning should be enough while writing a case study.
- No indefinite Answers: Indefinite answers cause a hell of a lot of confusion and complexity in a case study. That’s why the students should avoid making indefinite answers.
- Provide Proper Conversations: It is also vital to contribute as much as possible in conversations.
Related: How To Buy A Case Study
How To Properly Answer A Case Study
Precisely, a good case study is a scenario that students will analyze out of a professional concept. However, it is blended with useful questions that demand definite answers. There can be a sample case study assignment online that can always help a student while writing one but, it is equally important to know the proper way of answering a case study.
- Reading a case study is the foremost important thing. Later analyze the question carefully too.
- It is mandatory to identify the issue of the case study thoroughly
- A bridge is vital to link the theory to practice
- Planning of the answers comes next.
- Start making your case study answers
- Proofread and edit it carefully to avoid mistakes
- Submit the case studies to your tutors.
How To Answer A Case Study Interview
This aspect is a bit tricky. In a case study interview, you will be given a case and will be asked to analyze the situation with possible solutions.
Here are some common and most useful tips about answering the interview questions:
- Listening carefully to the questions is the key
- Asl the proper questions
- Highlight your approach
- do brainstorming
- Don’t lose focus
- Be attentive to feedback
- Prove your quantitative skills
- Summarize in detail
To write a productive case study is hard, but if you choose online help for it, this task becomes really easy. Be a smarter version of yourself and find great ways of handling the answers to your case study problems. We have a proficient team that can make this hectic task to answer your case study a piece of cake. Don’t be late to avail of our quality help.
Suggested Articles
Importance OF Case Study
How To Write A Case Study For Assignment
How To Write Case Study In MBA
How To Solve A Case Study

How to Write a Case Study: A Complete Guide with Templates

Writing compelling and insightful case studies is a marketer’s biggest job, yet most get frustrated with this content. The challenge? Figuring out how to write a case study that not only highlights the company’s strongest suit but engages new clients with strategic information. If you often struggle with making case studies as more than just dry facts and figures, you’re leading your efforts to missed opportunities.
How to Write a Case Study Step-by-Step
- Craft a Compelling Headline: Highlight the main success with a clear, direct title.
- Start with a Strong Introduction: Provide a broad overview and hook the reader.
- Discuss Unique Client Challenges: Highlight specific industry-related challenges.
- Highlight the Solution: Showcase your strategies and key results.
- Present Quantifiable Results: Use data and visuals to demonstrate impact.
- Be Clear and Concise: Stick to the point and support claims with data.
- Treat Your Case Study Like a Story: Focus on the customer’s journey and success.
- Use Direct Quotes from the Client: Add authenticity with client testimonials.
- Make the Key Takeaway Clear: Reinforce your expertise and the solution’s value.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): Guide the reader on what to do next.
- Make It Readable: Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points.
- Finalize and Proofread: Review for errors and ensure a smooth flow.
In this blog, you’ll discover a step-by-step guide that simplifies the process, making it easier to create interesting case studies. From planning to writing, I’ve got you covered. So, let’s start with some basics.
Table of Contents
What is the format of a case study.
- How to Plan a Case Study
How to Write a Case Study
How to summarize a case study, how to cite a case study.
A well-structured case study isn’t just a collection of facts—it’s a powerful marketing tool that tells a compelling story. Using the right format for a case study ensures that your message is clear, engaging, and impactful.
The proper format guides readers through the narrative with hierarchy and scannability, helping them connect with your brand on a deeper level. Most importantly, it empowers you as a marketer to set clear goals for presenting your case studies and ensures you deliver the correct information effectively!

Case studies format helps you to plan and write the case study for your clients. With this outline in mind, you can create steps to complete the process of writing and publishing your case study research. There are eight components of a case study that are essential for building a layout of information in the correct order that makes sense to the viewers.
Start with a catchy “Title” that grabs attention and an “Overview” that sets the stage. Clearly define the “Problem” your client faced, and then showcase your “Solution” in detail. Highlight the success with “Results” that are measurable and impactful. Add authenticity with “Testimonials and Quotes” from satisfied clients. Wrap it up with a firm “Conclusion” and a compelling “Call to Action” in the “About Us” section that guides the reader on what to do next.
By following this format, you create a case study design that resonates with your audience and effectively showcases your brand’s value.
Check out the marketing case study template I’ve included below—it has a clear outline that makes it easy to see how sticking to a format can help you plan and write the entire thing.

How to Plan a Case Study
Now comes the big part! Understanding what to include in a case study outline is just the starting point for beginners. The real challenge lies in creating a step-by-step plan to craft that outline and filling it in with the right information!

1. Set Clear Goals for Your Case Study
Before diving into how to write a case study, defining your ultimate objective is essential. Think about it—what do you want your audience to take away from this case study? For example, your goal is to showcase how your SEO strategies boosted a client’s organic traffic by 150% in just six months. This clear goal will shape your entire narrative and ensure that your case study is laser-focused on demonstrating your expertise and the value you bring.
2. Select a Client that Highlights Your Strongest Suit
Choosing the right client or subject is vital while creating case studies. Imagine you’ve worked with a small e-commerce brand struggling to rank for competitive keywords. Your strategies helped them rank on the first page and increase conversions. This is the perfect client for your case study because their success story directly showcases your SEO prowess.
By picking a client whose experience aligns with your goals, you’ll create a case study that resonates with your target audience.
3. Reach Out to Your Client for Collaboration
Now that you’ve identified the ideal client, it’s time to reach out. Let’s say you contact your client and explain how a case study can highlight their remarkable success story. It’s a great way to spotlight a mutual collaboration based on credibility. Their buy-in is crucial; their insights and data will authenticate your case study.
4. Gather Comprehensive Data and Insights
Data is the lifeblood of any compelling case study. For instance, in your SEO case study, you’ll need to gather data on key metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, and conversion rates before and after implementing your strategies. Let’s say your client saw a 50% increase in organic traffic within three months of optimizing their website. Collecting this data will help you build a robust, evidence-based narrative highlighting your impact.
It’s essential to monitor the before-and-after data to track the effectiveness of implementing your strategies.
5. Prepare Insightful Questions and Conduct Interviews
It would be best to ask the right questions to get the most out of your client interviews. Imagine asking your client, “What specific challenges were you facing with your organic search rankings before we started working together?” or “How did our SEO strategies help you achieve your business goals?” These questions will lead to detailed responses that add depth to your case study, making it more than just numbers on a page.
Always ask questions that uncover the key challenges your clients face. This way, your prospects will know when to turn to you to navigate or overcome similar obstacles in their business.
Since I’m giving an example of an SEO case study in marketing, you can try these questions to interview your existing client. Obviously, you can modify the sentences according to your industry basics, but these types of questions are fundamental for collecting structured data from your clients.
- What were your business’s main SEO challenges before we started working together?
- Can you describe your initial expectations for implementing our SEO strategies?
- What specific SEO tactics did we implement that you found most effective?
- How did you monitor and measure the impact of these strategies on your organic traffic?
- What were the key metrics or results that stood out to you after the first three months?
6. Ask Questions That Drive the Story Forward
Impactful questions are the backbone of a strong case study. They allow you to highlight the unique value you delivered to your clients. You can effortlessly showcase your USPs within the case study by asking the right questions.
Focus on inquiring about the effectiveness of your services and strategies, their impact, and which aspects of the solution were most beneficial. This insight will be your key to demonstrating the tangible benefits you offer your clients.
Consider asking questions like:
- Can you share a moment when you first noticed a significant improvement in your website’s organic traffic?
- How did the increase in organic traffic impact other business areas, such as lead generation or sales?
- What feedback did your team or customers receive regarding the changes in your site’s performance?
- Looking back, what do you believe was the most critical factor in achieving these results?
- How has this success with SEO influenced your overall marketing strategy moving forward?
These types of questions encourage clients to share their experiences in a way that paints a vivid picture for your readers, making the case study more relatable and engaging.
7. Draft a Clear and Organized Outline
With all the data and insights gathered, it’s time to create a well-structured case study outline. Let’s say you start with a brief overview of your client’s business and its challenges, followed by a detailed account of the SEO strategies you implemented. Then, you showcase the results with hard data and close with client testimonials and a solid call to action.
As mentioned above, organizing your content in a logical, easy-to-follow format will help you write a case study that not only informs but also captivates your audience.
These steps are the cornerstones of designing a case study. Once you complete this checklist, you can proceed to the next step, which is writing a case study. Since I discussed planning an SEO case study extensively, here is a case study template that perfectly illustrates the process.

You want to create an informative case study for your prospects. But how do you make sure it’s done right? Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a case study that drives results.
1. Craft a Compelling Headline
Your headline is the first thing readers see, so make it count! It should grab attention and hint at the success story you’re about to share.
How to Write a Case Study Title:
1. Highlight the Result: Showcase the critical success, like “Increased Sales by 200%.”
2. Be Clear and Direct: Make sure the headline is straightforward to grasp.
3. Use Action Words: Start with strong verbs like “How We” or “Achieved.”
4. Mention Client or Industry: Include relevant details for specificity.
5. Keep It Short: Make it concise and attention-grabbing.
2. Start with a Strong Introduction
Kick off your case study with a broad overview that sets the stage. Provide the big picture and construct a clear narrative that draws readers in, making them eager to learn more about how you solved a significant challenge.
Look at the consulting case study template , which includes a stunning overview description and precise instructions for writing a short and compelling introduction. You can add every little detail to hook the reader.

Get This Template and More
3. Discuss Specific Challenges of Your Client
This is where your prospect can truly connect. By highlighting unique yet specific challenges to their industry, you give them insight into issues they might not have encountered yet—or ones they’ve already faced. This way, they’ll know exactly who to turn to when similar challenges arise.
The following financial case study template provides a brief flow of the company’s common challenges in the financial analysis process. The template is almost ready to use with this domain-specific content, requiring minimal adjustments to design your case study.

4. Highlight the Solution
Now, dive into the heart of the story. Highlight the solution you provided, and make sure to include a notable achievement or key result. This is your chance to shine!
Check out the format for presenting the implications of your service on your client’s business. The benefits should be well-written and data-driven to convince your upcoming clients. This graphic design case study format helps you understand the specific impacts a company seeks from a reputable graphic design firm.

5. Present Quantifiable Results
When sharing the outcome, numbers speak louder than words. Present quantifiable results that clearly demonstrate the impact of your solution. Use graphs or charts to make the data easy to digest and visually appealing.
6. Be Clear and Concise
Less is more. Stick to the point and offer just the right amount of detail to keep your readers engaged. Include data that supports your claims, but avoid overwhelming them with too much information.
Here’s a stunning sales consulting case study that uses a simple case study layout and details written in readable, plain language to gauge more utility.

7. Treat Your Case Study Like a Story
Focus on your customer’s journey. Think of your case study as a story in which your client is the hero, and your solution is the tool that helped them succeed. This approach will make your case study relatable and compelling.
8. Be as Specific as Possible
Don’t be vague—details matter. Mention the specific company and its industry to let your audience know that the challenge and solution are relevant to them. The more precise you are, the more credible and trustworthy your case study will be.
Check out the sample case study below for payroll accounting. The details are clearly organized and grouped to emphasize the type of case study.

Also, the next case study template displays very specific problems that a company faces when it lacks digital marketing expertise.

These templates make it a breeze to craft a case study that’s perfect for your niche.
9. Use Direct Quotes from the Client
Quotes from your client add authenticity and credibility. They give readers insight into the client’s perspective and make your case study more relatable. Plus, a glowing testimonial is always a nice touch!
The following inbound marketing case study has a prominent client testimonial. With the brief instructions on this template, it’s easier for you to understand how to capture the golden words of your client and use them as a word-of-mouth strategy within the case study.

10. Pick an Interesting Angle
Find a unique angle that makes your case study stand out. Maybe it’s an unexpected challenge you overcame, or perhaps it’s a particularly innovative solution. Whatever it is, make it intriguing.
11. Make the Key Takeaway Crystal Clear
Your readers should walk away with a clear understanding of the main point of your case study. This takeaway should reinforce your expertise and the value of your solution.
12. Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Don’t leave your readers hanging—tell them what to do next! Include a compelling summary about your company, showcase your happy client base, and conclude the journey with a strong CTA, whether to contact you for a consultation, download a related resource, or learn more about your services on social media, like the following case study template design.

12. Format Professionally
The design of the case study is just as important as the content. A well-formatted, visually appealing document makes a great impression and enhances readability. With ready-to-use niche-oriented templates, you can easily create a professional-looking case study that impresses and converts. Here is an eye-catching template for an AI assistant software case study that displays a sleek and well-navigated format.

13. Make It Readable
Easy readability is key. Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points where appropriate. Your case study should be easy to scan and digest. Follow the thirteen design principles to create a standout piece that enhances your marketing efforts.
To understand this, take a look at the following consulting case study template.

14. Finalize and Proofread Your Case Study
In order to excel in how to write case studies, give your case study a final review before you hit publish. Proofread carefully to catch any typos or errors, and make sure everything flows smoothly. A polished case study reflects your attention to detail and professionalism.
To effectively summarize a case study, start by completing all sections, including the introduction, challenges, solutions, and results. This approach helps marketers identify key points to highlight, making it easier to craft a succinct and engaging summary.
One tricky thing is the length of the case study summary. So, how long should a case study summary be?
The length of a case study summary can vary depending on the details you’re covering. Generally, it should be kept concise, usually spanning a couple of lines or up to a single page with several paragraphs. If you’re crafting a customer case study and want to flex your storytelling muscles, it’s perfectly fine for the summary to stretch to a full page.
If summarizing a case study seems daunting, try DocHipo’s advanced AI Writer tool, which effortlessly creates a crisp and concise summary.
Watch this short video to use it.
This is the last step in writing a case study analysis. Citation in a case study is the practice of giving proper credit to the sources you reference or use in your research. It helps validate your work, shows the depth of your research, and avoids plagiarism. Follow the below steps to cite a case study:
- Identify the Source: Gather details like the author, title, publication year, and where the case study was published.
- Choose a Citation Style: Follow the specific formatting style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) required for your work.
- Format the Citation: Arrange the details according to the chosen citation style.
- Include In-Text Citations: Place citations within the text or paragraphs for the case study.
- Create a References List: At the end of your case study, compile all your sources in a bibliography or reference list.
For case studies, citations in APA and MLA styles are very common. If you are just beginning, then you might be confused about these case study citation formats.
Hence, take a look at the picture below, which easily comprehends the APA vs MLA citation features.
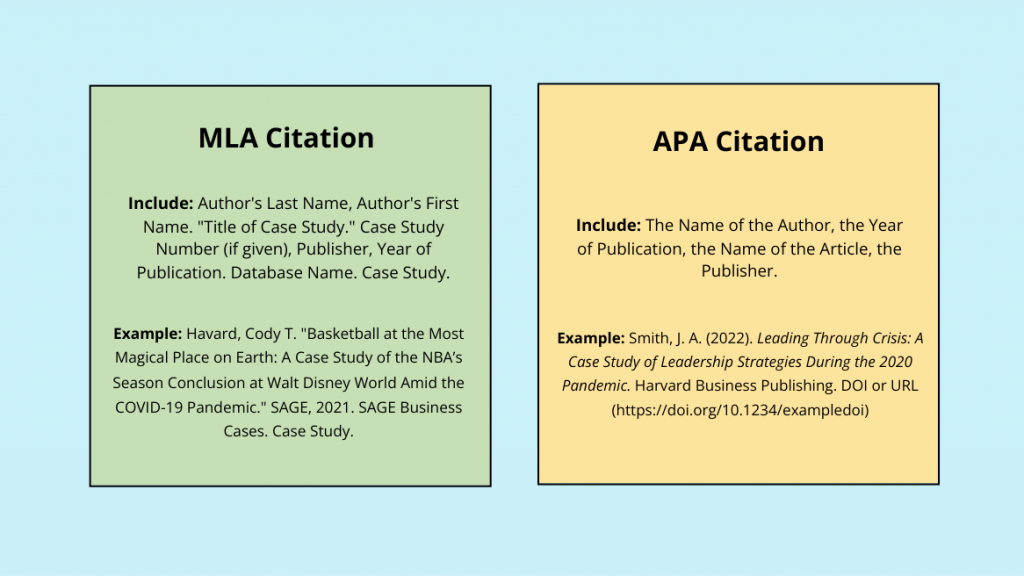
Still feeling overwhelmed about case studies? Be stress-free with the most convenient case study maker, which saves time and allows you to present data in the most attention-grabbing way.
Watch the video to create case studies in minutes with DocHipo’s case study maker.
Conclusion
To summarize, if you want to write a case study, start with a proper case study format, plan the case study, and finally write it with all the information in hand. Then, write a summary to provide an overview of your case study, and finally, add citations for reference.
Meanwhile, if you want to design a case study, Try DocHipo templates. Sign up to explore all the case study templates.
What is the structure of a case study?
A case study typically includes the following sections: Title, Introduction, Background, Problem Statement, Solutions, Results, and Conclusion. Each section serves to tell a comprehensive story of the business, from the issue at hand to the resolution and outcomes.
What are the 5 essential elements of a great case study?
The 5 essential elements are: 1) Clear Objective, 2) Detailed Background, 3) Specific Challenges, 4) Effective Solutions, and 5) Measurable Results. These components provide a compelling narrative that highlights the value delivered.
How to begin a case study?
Start a case study by defining the purpose and scope of the study. Introduce the subject, outline the problem, and provide background information to give readers context. This sets the stage for the detailed analysis that follows.
How to make an introduction in case study?
To craft a compelling introduction, briefly describe the subject, outline the problem they faced, and explain why the study is relevant. This section should grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in the rest of the study.
How to make a business case study?
A business case study should begin with a clear objective and background information. Identify the problem, explain the solutions implemented, and conclude with the results achieved. Use real data and quotes from stakeholders to enhance credibility.
How to write a case study step by step?
To write a case study step by step, start by identifying the case you want to explore and gathering relevant data on the subject. Outline the structure of your case study, then craft an engaging Introduction to set the context. Next, detail the Background and Challenges faced, followed by the Solutions applied. Share the Results and Conclusion to highlight the impact. Finally, edit and proofread your case study to ensure clarity and accuracy.

Turn your ideas into beautiful design
No prior design skill required

Talk to Sales
Wherever you are on your Dochipo journey, you can always get in touch.

Talk to Support
Online Case Study Answer Generator for Students
Here Is Your Case Study Analysis
If you want to quickly and effectively carry out case study analyses, you’ve come to the right place. Just for you, we’ve created a free AI-powered tool that can analyze case studies on any subject!
Our app will be the perfect solution for those who don’t want to spend a ton of time structuring their texts and looking for examples. Use it to save time and nerves!
- ️🎉 Benefits of Our Generator
- ️🤖 How to Use
- ️✨ Case Study Definition
- ️🔎 Structure of a Case Study
- ️✍️ Writing Steps
- ️🔝 Top 12 Topics & Examples
- ️🔗 References
🎉 Benefits of Our Case Study Analysis Generator
Our generator is one of the best, and there are many reasons for us to say so:
| 💸 100% free | Don’t pay a penny for it! |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Cutting-edge | Our tool has advanced AI. |
| 🤩 User-friendly | Using this app is a cinch. |
| ⏳ Time-saving | Save time for more urgent things. |
| 🌐 No download | Use it right in your browser. |
🤖 How to Use Our Case Study Answer Generator
Getting a case study analysis has never been simpler—see for yourself!
- Paste your case study into the field.
- Add questions or issues you need to resolve in your analysis.
- Press “Analyze now.”
- Receive the results!
Keep in mind that the answers given by the tool are to be used for reference purposes only.
✨ Case Study Analysis Definition
A case study analysis aims to examine a problem and find a solution. It is traditionally used in business and other spheres, like education, healthcare, and social sciences. The main feature of such research is that it’s rooted in a real-world context.

Researchers use direct observations, interviews, tests, and samples to gather data for their case studies. This information is then applied to develop solutions and recommendations backed with evidence.
🔎 Structure of a Case Study Analysis
Usually, a case study analysis comprises 6 parts. Each one is dedicated to a certain aspect and serves its respective aim. Let’s go through them and see how they differ.
Introduction
An introduction defines the context of the examined topic and provides substantial background on the case study’s subject. When you write it, keep in mind the following questions:
- What is your case study about?
- What is the primary reason for your research?
- Why is it essential to conduct it?
Problem Statement
The next part introduces the central problem the study will be concentrating on. Typically, it’s concerned with a challenge faced by a person or organization in question. The problem statement provides a clear focus for the whole research.
Now, it’s time for the most gripping part—the analysis itself. When it comes to business problems, students can employ various approaches:
- SWOT analysis "> SWOT analysis evaluates the firm’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Descriptive statistics recaps the main characteristics of the collected data using various measures.
- Identification of causes approach looks for the underlying reasons behind the issue.
- Stakeholder researches the perspectives of different stakeholders involved in the case.

This part proposes several ways to settle the issue in question. The solutions must be pragmatic and achievable. It’s also worth to mention their pros and cons and thus identify the most potent ones.
Recommendations
This part revolves around the best potential solution to the problem determined in the previous section. It explains how to execute it practically and how it will help eliminate the issue. It may also propose ways to deal with other minor dilemmas involved in the case.
Conclusions
Now, it’s time for the final section of the analysis: your conclusions . Here is what to do:
- Restate the results of your case study analysis and elucidate how they relate to the research’s main problem.
- Be sure to underline how vital your study is and how it helps make the issue more controllable.
- Make further proposals based on your findings.
✍️ How to Write a Case Study
Now you know what to include in your case study. But how do you write one that is truly outstanding? Just follow our step-by-step guide:
1. Pick a Case to Explore
Choosing the right topic is essential. You need to do it early on to ensure that the research subject is sufficiently explored.
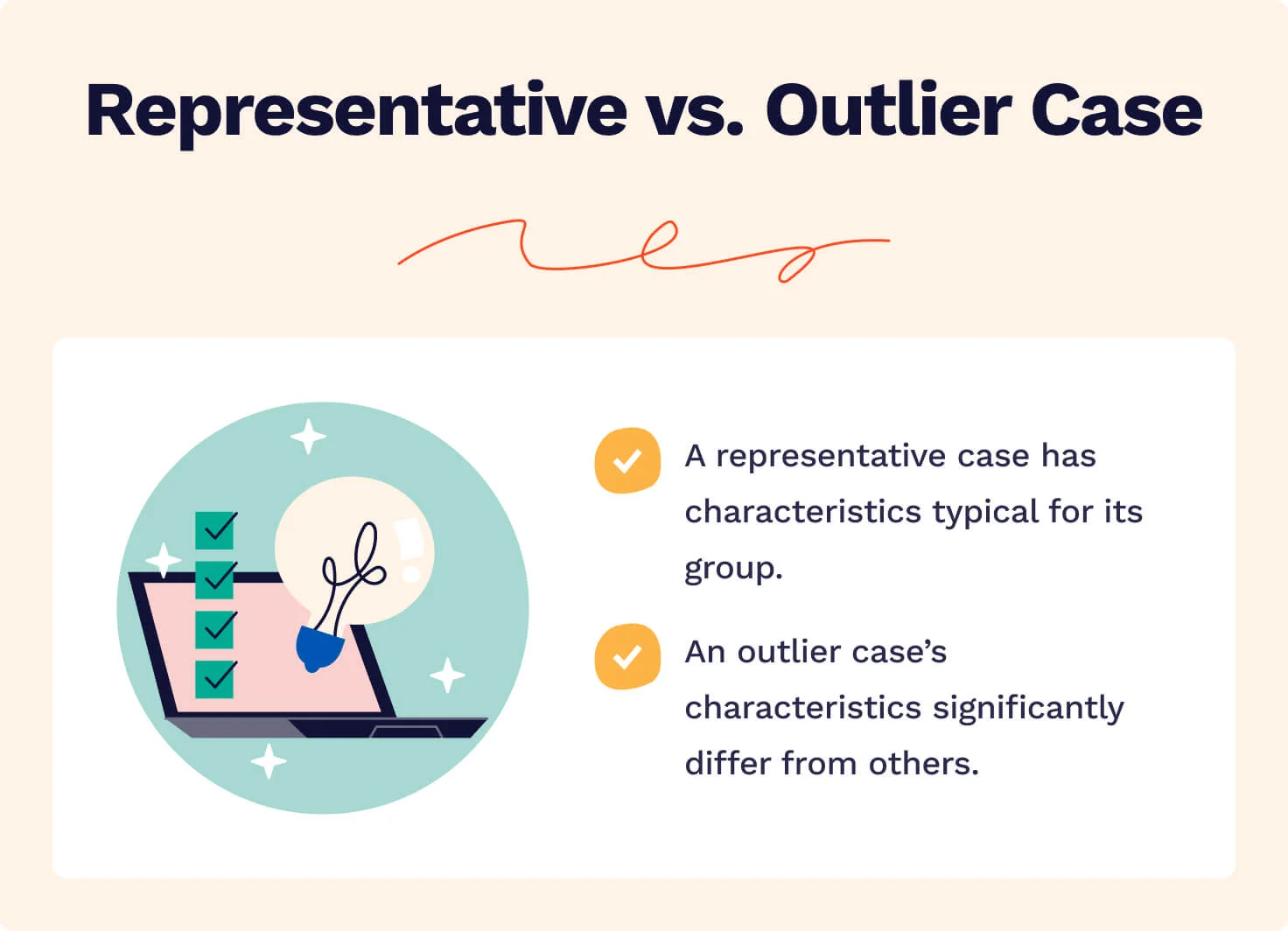
For example, suppose you want to examine how COVID-19 has affected the hospitality sector. In that case, you can choose either a representative case, such as a large hotel chain, or an outlier case, such as a small Bed and Breakfast that has managed to survive the pandemic. The latter case may sound more interesting, but if there’s not enough information available on it, it’s best to choose the former.
2. Formulate a Problem Statement
Now, you should clearly and concisely formulate the central problem you will be focusing on. To do it, answer the 5 Ws:
- What is the problem you’re researching?
- Who is affected by it?
- Where does it occur?
- When did the problem arise?
- Why is this issue significant?
If you need help with this part of your analysis, you can always use our research problem generator .
3. Gather Evidence & Collect Data
Data gathering can be done through both primary and secondary sources of information . You can use a range of research techniques, such as observations, surveys, and interviews. It is crucial to make sure the data you’ve collected is pertinent to the case study.
4. Describe Your Findings & Analyze Them
Next, you analyze trends and themes in your data. This analysis must be supported by facts and evidence. Use various analysis methods to make your study more in-depth.
5. Provide Solutions & Recommendations
Develop several possible solutions using the information you’ve gathered. Once you’ve done it, answer the following questions:
- What are the pros and cons of these solutions?
- Which one can be the most beneficial?
- How can the entity you’re analyzing implement it in practice?
The more detailed your recommendations are, the better. If possible, try to include aspects such as timeline, resource allocation, and KPIs for monitoring.
🔝 Top 12 Case Study Topics & Examples
Want inspiration for your analysis? Or maybe you need help picking a case to explore? Check out this list of topics with examples!
- Operations and Information Management: A Case Study of CC Music
- Netflix and Blockbuster: Case Study
- Strategic Planning Case Study: Process Management
- HRM Incident: Case Study Analysis
- Case Study Summary: Hiring a Sustainable Development Specialist
- Organizational Change: Qatargas Case Study
- Childhood Development Case Study
- Case Study of Engstrom Auto Mirror Plant and Workplace
- Strategic Marketing: Amazon Go Case Study
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Case Study
- Social Determinants of Health: Case Study
- Recovering Supply Chain Operations: A Case Study of Nissan
Now you know how to complete a case study! Remember that the tiring process of analyzing can be effectively streamlined if you use our free case study answer generator. Try it out—you won’t regret it!
We also recommend using our transition words maker and personal statement generator to enhance your writing.
❓ Case Study Analysis Generator: FAQ
❓ what questions to answer in a case study.
A case study must either prove or disprove an existing theory. It also aims to find a solution to the research’s central question. This question can vary depending on your topic and subject. You present the answer in your research findings and conclusions.
❓ How Do You Write a Case Study Analysis?
First, you introduce your case and provide its background. Then, you gather information and analyze it to develop several solutions. Finally, you propose the best solution and give recommendations on how to implement it. Also, remember to explain how your case study will deepen the existing knowledge.
❓ What Are the 4 Most Important Parts of Case Study?
Every case study begins with the introduction of a topic and its background. Then, you present an analysis of sources that can provide knowledge on the case. The third part is the analysis of collected data. Your case study ends with conclusions based on your findings.
❓ What Are Some Examples of Case Studies?
Case studies are frequently used in psychology to shed light on peculiar circumstances. Famous case study examples include Sigmund Freud’s Little Hans as well as John Martin Marlow’s study of Phineas Gage, the man who had a railroad spike driven through his brain.
Updated: Aug 21st, 2024
🔗 References
- Case Study: Definition, Examples, Types, and How to Write: Verywell Mind
- What Is a Case Study?: Evidence Based Nursing
- What the Case Study Method Really Teaches: Harvard Business Review
- Using Case Studies to Teach: Boston University
- What Is a Case Study? Definition, Elements and 15 Examples: Indeed
- Writing a Case Study: University of Southern California
- Writing a Case Study – Student Academic Success: Monash University

- Free Case Studies
- Business Essays
Write My Case Study
Buy Case Study
Case Study Help
- Case Study For Sale
- Case Study Services
- Hire Writer
How to Answer Case Study: few tips
Here are a few tips on how to answer questions relating to case studies;
1)Read the case-study carefully: Case-studies will run up to many lines. So, do not think twice about spending time on reading the question. Read it the second time if [o haven’t understood clearly.
We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically For You For Only $13.90/page!
2)Read the questions relating to the case: After a first time reading of the case study, reading the questions pertaining to it, will help you know what to look out for in the case. Underline these instances in the case study for later reference.
3)Make notes of key points: While reading through your case study, make notes of key points (in bullet format).
This will help you to assess and analyses the facts for arriving at the right solution.
4)Look for cues: Sometimes, the answer may be hidden in the question itself. Certain Norms, or conjunctions in the sentence will give away the answer, if you read between them. Remember to look for these cues.
5)Background preparation: attempting case studies questions will be easier if you have enough exposure to solving these question types earlier.
Browse through detent portals or your university online interface to get better insights about case studies, and the mode to solve them.
Case studies are a vital part of testing management expertise and are woven into the distance learning MBA programs, which follow industry-standards. With the above tips, you can practice such type of questions with a new approach and get the expected results. Identification of issues ; problems There are three steps involved in the identification and analysis of issues and problems.
What are The Steps of Writing Content Analysis Case Study ?
Step 1 – overview of the case study (background context)
Understanding the background issues helps to understand the context of the case study. Read the case study to gain an overview and ask and answer the following questions as you read.
* What background facts influence the current problems? * What are the constraints or obstacles of the situation?
Step 2 – identifying the problems Identifying the major problems and their causes at this stage is vital to identify appropriate solutions later. Re-read the case study and summaries or list the issues and / or problems in your own words.
Make sure you: * sort he major problems from the minor problems * identify evidence from the case study which relates to each of the problems * identify underlying causes of the problems. A setup strategy is to represent the problems and their relationships as a mind.
Step 3 – linking theory to problems and case evidence Relating the identified issues / or problems to theory is vital when answering case studies.
This is where you demonstrate your knowledge of the theory in your course and your ability to relate it to practical situations.
If you are afraid to be expelled or think that you will not pass the plagiarism of your work, then it is better to ask for help in writing the case study with us.
Use your readings to select appropriate theories to match the identified problems. * Home * Identifying issues * Solutions * Recommendations I Antispasmodics can be a useful strategy to summaries / organism problems and to show their relationships to each other. The example below is a representation of the problems of the management case study.
Example I * Home * Identifying issues * Solutions * Recommendations I Integrating theory in a case strangulating relevant theory into your case study answer is vital. His allows you to demonstrate how theory relates to the actual issues / problems mound in the case study, as well as demonstrate your understanding of your course content. The following example shows how the theory and issues have been woven together. Example I * Home * Identifying issues * Solutions * Recommendations I Solution’s section evaluates potential solutions for the identified key problems. Often there is more than one solution, so it is useful to evaluate each solution in terms of its advantages and disadvantages.
This will also assist in determining your recommendations.
Things that may need to be considered are: * costs * time * sources * expertise. Structures section should be clear and concise. Recommended structure: * use headings and subheadings where possible * bullet points or numbered lists can also be used to list the advantages and disadvantages. Example I Recommendation’s section should outline your recommendations based upon the given solutions for each of the identified problems.
It may also need to include an action plan, egg what should be done by whom and the associated timeliness, but check with your teacher / lecturer for specific requirements.
Each recommendation would be realistic, ‘e practical and achievable, and be linked back to relevant and supporting theory. Structuralizes and subheadings should be used in this section. For example:communication * Staff constitutionalism the recommendations based on the identified solutions and supported by relevant theory. * Staff meetinghouse the recommendations based on the identified solutions and supported by relevant theory.
Leadership * Team bloodletting the theory. * Participative leadership storyline the recommendations based on the Identified solutions and supported by relevant theory. I
Related posts:
- Business Law Case Study Writing Tips
- Tips on Writing College Level Case Studies
- Tips on Writing a One Page Case Study
- Tips on Writing a Case Study for Publication
- Answer for case study
- Brose Case Study Answer
- Case Study and Its Answer of Nestle
Quick Links
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Testimonials
Our Services
Case Study Writing Services
Case Studies For Sale
Our Company
Welcome to the world of case studies that can bring you high grades! Here, at ACaseStudy.com, we deliver professionally written papers, and the best grades for you from your professors are guaranteed!
[email protected] 804-506-0782 350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118, USA
Acasestudy.com © 2007-2019 All rights reserved.

Hi! I'm Anna
Would you like to get a custom case study? How about receiving a customized one?
Haven't Found The Case Study You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
How to Make Case Study Videos in 10 Steps [Examples Included]
Confidence in your brand is important, but it’s only the beginning. To make a real impact, you need to back up your claims with solid proof. That’s where case study videos come in. Let your satisfied customers do the talking giving new leads an authentic view into your products and services. Let’s look at how to create case study videos easily.
Article Last Updated: August 23, 2024
![how to answer case study How to Make Case Study Videos in 10 Steps [Examples Included]](https://zight.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/case-study-video-examples.png)
What is a Case Study Video?
Types of case study videos, why are case study videos important, how and where to use your case study video, how to create an impactful case study video.
Who doesn’t enjoy a captivating story? That’s likely why case study videos have become so popular. They’re more than just stories as they offer a deep dive into real-world scenarios, featuring genuine people and authentic businesses. Through these videos, companies showcase the real impact of their products and services, whether it’s through documenting product development , cultural shifts, or community impact.
To bring these stories to life, tools like Zight can be incredibly useful. With Zight’s features like screen recording , GIF creation , and easy file sharing , you can capture every moment and detail seamlessly. Imagine using Zight to record a customer’s success journey or create engaging visuals to complement your narrative. It’s all about making your case study videos as compelling and impactful as possible.
The question is, what does a good case study video look like? Our guide below will cover every aspect of case study videos, from their purpose, creating compelling videos, exploring what makes them successful, and sharing practical case study video examples and tips to help you craft impactful case study videos that resonate and drive results. Let’s get into it.
A case study video is a type of video content that demonstrates how other people are successfully using and benefiting from a product. It focuses on real customer success stories to show the value of a company’s products or services. In a crowded market of claims and promises, these videos serve as credible proof that your business delivers on its promises.
The strength of a case study video comes from its relatability. When potential customers see themselves in your stories, it fosters a true connection. Seeing real people handle challenges makes your business appear more trustworthy and your solutions more appealing. After all, who could offer a more credible opinion to potential customers than someone who’s experienced your services firsthand?
How is a Video Case Study Different From a Written Case Study?
Both written and video case studies aim to convert customers, but video case studies have several specific advantages:
- More Persuasive : While written case studies require readers to interpret the message, video case studies present it directly from the customer, making the impact more immediate and convincing.
- More Engaging : Videos captivate with dynamic visuals, vibrant colors, and sound, making them far more engaging than dense blocks of text. Who wouldn’t prefer a lively video over a long read?
- Higher Conversion Rates : Video marketing campaigns are very effective. It’s not surprising, given how seamlessly videos can be optimized for mobile devices—something text-heavy content struggles with.
Like in any film or video genre, you’ll notice certain styles and tones that recur frequently. This is also true for case study videos, where you’ll come across several common types as you explore case study videos.
That said, there are different types of case study videos that your business can produce, with different levels of complexity. Each type of case study video has a specific customer problem and appeals to different aspects of your audience’s decision-making process. Depending on your objectives and the topic, choosing the right style of case study video can effectively communicate the message you want to share.
1. Customer Testimonials
This type of video is quite simple to make and is one of the easiest case study videos to make. In customer testimonial videos, you interview your happy customers about their experience with your business and its impact on their lives. Since it involves just a straightforward interview with the customer, you only need one filming location and minimal editing to create the video.
Product or service review case study videos provide a thorough look at your offering’s features, functionality, and benefits. They offer an objective assessment and serve as valuable resources for new customers.
Target Audience : These videos target potential customers who are researching your product or service and need detailed information to make an informed decision.
Testimonial Video Example:

This video is a standout example of customer testimonials. Instead of simply listing features, the interviews highlight the challenges the company faced and how Zoom provided effective solutions . The video’s concise length keeps viewers engaged while still delivering a complete and compelling story in one location.
2. Customer Reviews
Customer reviews are authentic insights that highlight a product’s real-world performance. Much like a customer testimonial video, a customer review video features a happy customer discussing your product or service. However, there’s a key difference: in a customer review video, the customer focuses more on the specific features of the product or service, rather than just the value it provided them.
Depending on your approach, such videos may include footage of the customer using your product on camera. Generally, most case study video testimonials follow a Q&A style of storytelling .
Creating a customer review video is straightforward. The interview portion requires just one shoot location and minimal editing. If you decide to add footage of the product in action, the shoot and editing process will be more complex.
Target Audience : These videos are aimed at potential customers who are actively researching your product or service. They provide detailed information to help them make an informed purchase decision.
Customer Reviews Case Study Video Example:

This customer review case study video features Lana Blakely who explains how Notion has transformed her personal and professional life. She breaks down specific features like databases, templates, and task management tools, showing real-life examples of how she uses the app to stay organized. The video includes screen recordings of how she navigates the Notion workspace, providing viewers with a visual understanding of how the platform functions. Any potential customer actively looking for Notion will find information about the tool and can be able to make an informed decision.
3. Case Study Narrative
This is the most complex type of case study video. A case study narrative video involves on-camera interviews with customers and B-roll visuals, such as footage of the customer using your product or your team engaging with the customer. Additionally, these videos often incorporate graphics and text overlays. Due to its complexity, creating this type of video content demands more shoot time, strategic planning, and extensive editing .
Narrative case study videos focus on storytelling , aiming to engage viewers emotionally by presenting a compelling narrative highlighting a customer’s journey from problem to solution, often emphasizing the transformative aspects.
Target Audience : Narrative case study videos are particularly effective for creating an emotional connection with viewers, engaging a wide range of audiences, including those in the awareness and consideration stages.
Case Study Narrative Video Example:

This video by LLLLITL is a case study of Dove’s “Turn Your Back” campaign, which was designed to raise awareness about the issue of body image. The video uses powerful storytelling to connect with viewers on an emotional level.

Case study videos can significantly enhance your video marketing strategy , particularly for B2B companies . They provide a rich, multi-faceted way to showcase a product or service and offer benefits beyond financial gains. Here is why they are important:
- Credibility and Trust : Case study videos provide authentic success stories that show how your products or services have made a real difference for customers. This helps build trust and credibility with potential clients.
- Engagement : Videos naturally draw people in more effectively than text or static images. With a case study video, you can tell a compelling story that keeps your audience engaged and interested.
- Demonstration of Expertise : These videos allow you to highlight your industry knowledge and position yourself as an expert. By showcasing real-world results, you establish your business as a reliable solution provider.
- Problem-Solution Narrative : Case study videos often follow a clear problem-solving structure, helping potential customers relate to the challenges and see how your product or service can address their needs.
- Personal Connection : Featuring customer interviews or testimonials adds a personal touch. Prospective clients can connect with real people who have benefited from your offerings, making your brand more relatable.
- Versatility : Case study videos are highly versatile and can be used across various platforms , including your website, social media channels, email marketing , and presentations . This ensures your success stories reach a broad audience.
- Measurable Impact : Including data and metrics in your videos demonstrates the tangible results achieved by your clients. This evidence of ROI can be very persuasive for potential customers.
- Lead Generation : Well-crafted case study videos can generate leads by addressing problems similar to those your potential customers face, making them valuable assets in your video marketing strategy.
- Storytelling : Effective visual storytelling in case study videos helps forge an emotional connection with your audience, making your brand memorable and engaging.
After perfecting your case study video, it’s time to share it with your target audience. But where should you promote it?
- Your Website – Embed the video prominently on your website’s homepag e or a dedicated landing page to make it easily accessible. Consider having a section just for case studies, giving prospects a convenient reference point.
- Social Media – Share the video on your company’s social media platforms like Facebook , Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube . Optimize it for each platform and actively engage with your audience through comments, likes, and shares to boost its visibility.
- Email Marketing – Include the video in your email marketing campaigns , especially targeting those interested in the topic. Adding the video to your email signature can also create a dynamic touchpoint.
- Sales and Marketing Presentations – Integrate the video into your sales pitches and marketing presentations . Real-world examples of success can be highly persuasive during client interactions.
- Content Marketing – Use the video in blog posts, articles, or other written content related to the case study’s topic. Create videos as teaser content from snippets to pique interest and direct viewers to the full video for more details.
Now that you have seen some examples of case study videos, you can now create your case study video. Case studies don’t always stick to a strict timeline or template, but some key steps are usually involved in creating a case study video. Follow these steps to create an engaging case study video that will resonate with your audience.
1. Identify the Right Story
The first step in crafting an attention-grabbing case study video is selecting the right story. You need a story that resonates with your target audience and showcases clear results.
For instance, if you run a software company like Zight, don’t just feature any client who used your software. Highlight businesses that experienced a boost in efficiency with your platform . Numbers like these provide concrete proof of your product’s effectiveness.
Your audience is looking for solutions, so your story should present a compelling example of how you’ve delivered just that. A thoughtfully chosen story sets the stage for a truly engaging case study video.
2. Ask Important Questions
The next key step is to craft the right questions. These will be the basis of your case study video.
- Start by setting the scene for your viewers : Ask about the customer’s initial problem. For example, “What issues were you dealing with before using our product?”
- Then, dive into the specifics : Analyze the customer’s decision-making process with questions like, “What pulled you to our product instead of others?”
- Finally, highlight the results : Ask questions such as, “How has our product made a difference in your operations?” or “Would you recommend our service to others?”
This thoughtful questioning will help create a well-rounded story, listing the problem, the solution, and the impact of your product or service.
3. Choose the Right Audience
You might have a great customer success story and perfectly crafted questions, but they won’t make an impact if they don’t resonate with your target audience’s needs and interests.
Imagine you’re showcasing Zight. Your audience could range from tech-savvy professionals to small business owners who aren’t as familiar with advanced tools. If your case study highlights a large corporation using Zight’s advanced features , it might not connect with a small business owner looking for simple and effective screen recording solutions .
Before diving in, do some audience research. What challenges are they facing? What solutions are they after? Tailor your case study video to address these, using language and examples that speak directly to their needs.
4. Plan Out the Storyline
To craft an engaging storyline for your case study video, you need to guide the viewer through a story that resonates. Start with a compelling introduction that highlights a common problem your audience faces, making it instantly relatable.
For instance, if you’re showcasing Zight, an issue could be the struggle businesses face with lengthy communication chains that slow down decision-making. Many teams feel this pain, making it an effective hook. Then, introduce Zight as the solution. This is where you spotlight its unique features—like screen recording and sharing capabilities—that streamline communication and boost productivity .
Support your claims with testimonials or expert opinions to add credibility. Hearing from satisfied users can make a significant impact.
Finally, wrap up by showcasing measurable results . Use statistics or before-and-after comparisons to emphasize how Zight made a difference. Conclude with a clear call-to-action, guiding the viewer on what steps to take next.
5. Conduct Background Interviews
Conducting background interviews is essential before you start filming. These pre-shoot conversations offer valuable insights that can enhance your storyline. They help you understand the full scope of the customer’s experience , adding richness and depth to your case study video.
These interviews also help you identify key talking points and decide who should be featured in the video. Whether it’s the CEO providing strategic insights or a front-line employee sharing day-to-day benefits, understanding this in advance ensures you capture the most relevant content, saving you time and effort during production.
6. Develop Your Script
The video script is the backbone to create engaging video content, pulling together visuals, dialogue, and pacing to create a cohesive story. Here’s how to craft one that leaves an impact:
- Start by outlining the key points you’ve gathered from background interviews and your storyline.
- Be clear and specific—rather than saying, “Our product is great,” highlight its strengths with something like, “Our software boosts productivity by 40%.”
- Keep the tone conversational yet professional to ensure your message resonates.
- Make sure the script flows smoothly, making complex ideas easy to understand.
- Consider using bullet points or numbered lists to emphasize key features or benefits.
Wrap up with a compelling call-to-action , guiding viewers on what to do next, whether that’s visiting your website or reaching out to your sales team.
7. Back it up with Data
Including data and statistics adds credibility to your case study video. While a compelling story captures attention, solid data reinforces your claims and makes your video campaigns more convincing.
Incorporate charts, graphs, or other visuals to present the data. Visual elements help make complex information more digestible and memorable. Ensure the data aligns with your storyline and addresses the needs or concerns of your audience.
8. Select the Right Location
The location you choose for your case study video adds depth and context to your story. Opt for a setting that complements the narrative and enhances its authenticity. For instance, if your case study involves educational software, filming in a classroom or school can make the story feel more genuine.
Your location should also resonate with your audience. Remember to consider practical aspects like lighting , sound, and permissions. The perfect location can fall flat if it has poor acoustics or requires difficult-to-obtain permits.
9. Create a Shot List
A carefully planned shot list is essential for a smooth filming experience. It details every shot you need, acting as a guide for your production team.
For example, if you’re capturing a customer testimonial, your shot list might include:
- Close-ups of the customer speaking
- Cutaways of the product in action
- Wide-angle shots to set the scene
Your shot list should specify the type of shots—wide, medium, or close-up—and any particular camera movements like pans or zooms. This ensures you capture all the crucial elements of your video marketing campaign from product details to emotional moments.
A shot list also helps you manage time and resources efficiently, allowing you to anticipate special equipment or lighting needs ahead of time, and preventing last-minute scrambling.
10. Shoot and Edit
This is where all your planning comes to life. Stick to your shot list and script during the shoot, but be open to capturing spontaneous moments that could enhance the story. High-quality equipment is necessary for clear audio and well-lit scenes —these technical details can elevate your final product.
Editing is where you shape the story , choosing the best shots to create a compelling narrative. Use cutaways, transitions, and background music to keep the pacing dynamic and the viewer engaged.
Pay attention to color grading, sound mixing, and special effects, ensuring they match the tone and message of your video. Avoid overdoing effects, as they can easily overshadow the content.
Now that you’ve seen how major brands craft their case study videos, let these examples spark ideas for your own. Use them to motivate your sales team , improve your video marketing strategy, and captivate your audience.
In addition, incorporating tools like Zight offers practical solutions such as screen recording and GIF creation, these videos not only tell a compelling story but also demonstrate how your product can deliver tangible results. What are you waiting for? Sign up and get started .
Create & share screenshots, screen recordings, and GIFs with Zight
Get Zight for iOS.
Queensland Nickel – Digging for Answers Down Under
October 09, 2020
FTI Consulting was appointed as Administrators and subsequently as Liquidators of Queensland Nickel. Once on the job, various anomalies were discovered, which required an investigation jointly led by FTI Consulting’s corporate finance, forensic and e-discovery experts. With the situation quickly deemed one of Australia’s largest corporate failures and Clive Palmer, a larger than life character, at the helm, the Administrators with guidance from Strategic Communications professionals launched a proactive communications approach. This addressed the political landscape and various agendas with key stakeholders, including employees and clients of Queensland Nickel, government authorities, creditors and the media.
- Corporate Finance & Restructuring: As administrator, FTI Consulting assumed control of Queensland Nickel’s assets and business operations while working to identify key risks, stabilize operations and implement controls over expenditures. Concurrently, the team surfaced opportunities to implement operational improvements, cost savings and rationalization to determine the true financial position of the enterprise.
- Forensic & Litigation Consulting and Technology: In our role as Administrator and subsequently as Liquidator, various anomalies were discovered. Issues were investigated in full by our forensic and e-discovery experts, and the recovery of assets was pursued determinedly. These covered statutory investigations, the ownership of Queensland Nickel joint venture and Palmer Aviation assets, loans and transactions with related parties, and material donations and gifts, among other items.
- Strategic Communications: We played a critical role in ensuring that a proactive rather than defensive communications approach to addressing the political landscape and outside agendas was employed with key stakeholders, including employees and clients of Queensland Nickel, government authorities, creditors and the media.
- FTI Consulting provided unmatched expertise from acting in the role of Administrators to bringing forensic and e-discovery capabilities to the investigation and providing end to end communications support.
- FTI Consulting coordinated the assessment and distribution of payments of approximately AU$70 million to nearly all 787 Queensland Nickel employees.
- The actions of our experts led to recouping approximately AU$200 million owed to more than 1,500 creditors.
WATCH VIDEO
Key contacts.
Senior Managing Director, Head of Australia Corporate Finance & Restructuring
Kelly Trenfield
Senior Managing Director
Stuart Carson
Managing Director
- Download Case Study
Sign up to get access to FTI Consulting Insights
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 29 | 31 | |||
Comments and moderation policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find answers to common case study questions with helpful insights and advice. Explore real-life examples and sharpen your problem-solving skills.
Considering this, case studies often involve: Isolating Key Issues: Identifying the most critical challenges or problems in the case. Evaluating Strategies: Weighing the pros and cons of various remedial options or strategies. Making Recommendations: Presenting a well-reasoned solution that addresses the key issues effectively. 10 steps to ...
Dive into our comprehensive guide on case study presentation. Learn proven techniques and see real-world examples to master this art.
What is a case study? A case study presents either a real-life situation or a simulation of a real-life situation. A case study mirrors the complexity that you would experience in the business world. Cases often contain enough information to support multiple viable solutions, so part of your role in analyzing a case study is to recognize what information supports certain solutions.
Find comprehensive case study questions and answers to enhance your problem-solving skills. Explore real-life scenarios, analyze data, and develop insightful solutions to common business challenges.
Case studies are used in many professional education programs, primarily in business school, to present real-world situations to students and to assess their ability to parse out the important aspects of a given dilemma. In general, a case study should include, in order: background on the business environment, description of the given business, identification of a key problem or issue, steps ...
Learn how to prepare, draft, and finalize a case study analysis for your business course. Follow the guidelines to identify key problems, propose solutions, and support your arguments with evidence.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Learn how to choose a case, build a theoretical framework, collect data, and analyze the case in this guide.
Case study methodology can entail the study of one or more "cases," that could be described as instances, examples, or settings where the problem or phenomenon can be examined. The researcher is tasked with defining the parameters of the case, that is, what is included and excluded. This process is called bounding the case, or setting boundaries.
A case study deeply dives into a particular subject, such as a person, event, or group. Case studies are used in multiple areas of research. See examples of how to use case studies in your research.
Find the best case study samples (with answers) on the web. Learn from others as they solve case studies on video and get expert feedback!
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
Learn how to prepare for a case study interview, including how to practice different use cases and answer potential questions with effective answers.
Abstract Qualitative case study methodology enables researchers to conduct an in-depth exploration of intricate phenomena within some specific context. By keeping in mind research students, this article presents a systematic step-by-step guide to conduct a case study in the business discipline.
Case studies are marketing tools that showcase your customers' success and highlight your brand value. Learn how to write them with examples and templates.
How to write a case study response Before you start writing, you need to carefully read the case study and make a note of the main issues and problems involved as well as the main stakeholders (persons or groups of persons who have an interest in the case).
Learn how to write a case study that showcases your success. Use our template and proven techniques to create a compelling case study for your clients.
Answering case study questions Exam questions that ask you to anlayse case studies (also called scenarios) are usually designed to test your ability to relate theories and concepts to real-world situations. Preparing for case studies before the exam:
A case study is an in-depth analysis of one individual or group. Learn more about how to write a case study, including tips and examples, and its importance in psychology.
How to Analyze a Case Study Adapted from Ellet, W. (2007). The case study handbook. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School. A business case simulates a real situation and has three characteristics: 1. a significant issue, 2. enough information to reach a reasonable conclusion, 3. no stated conclusion.
Learn more about case study interview examples, review a few sample responses and discover tips to help you succeed during your next case study interview.
Get to know the powerful tips about how to answer a case study effectively. Read on to find help with your case studies from our words.
How to Write a Case Study Step-by-Step . Craft a Compelling Headline: Highlight the main success with a clear, direct title. Start with a Strong Introduction: Provide a broad overview and hook the reader. Discuss Unique Client Challenges: Highlight specific industry-related challenges. Highlight the Solution: Showcase your strategies and key results. ...
A case study analysis aims to examine a problem and find a solution. It is traditionally used in business and other spheres, like education, healthcare, and social sciences. The main feature of such research is that it's rooted in a real-world context. Researchers use direct observations, interviews, tests, and samples to gather data for ...
How to Answer Case Study: few tips Here are a few tips on how to answer questions relating to case studies; 1)Read the case-study carefully: Case-studies will run up to many lines. So, do not think twice about spending time on reading the question. Read it the second time if [o haven't understood clearly.
Case studies don't always stick to a strict timeline or template, but some key steps are usually involved in creating a case study video. Follow these steps to create an engaging case study video that will resonate with your audience. 1. Identify the Right Story.
It included 1,135 U.S. adults who were randomly selected from the Understanding America Study, conducted by the USC Dornsife's Center for Economic and Social Research, between August and October 2023.
/ Queensland Nickel Digging Answers Down Under; Queensland Nickel - Digging for Answers Down Under. October 09, 2020. Downloads. Download Case Study Share. Situation. FTI Consulting was appointed as Administrators and subsequently as Liquidators of Queensland Nickel. Once on the job, various anomalies were discovered, which required an ...
You'll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more. Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media ...