The Four Types of Research Design — Everything You Need to Know
Updated: October 07, 2024
Published: December 23, 2022
When you conduct research, you need to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve and how to accomplish it. A good research design enables you to collect accurate and reliable data to draw valid conclusions.

In this blog post, we'll outline the key features of the four common types of research design with real-life examples from UnderArmor, Carmex, and more. Then, you can easily choose the right approach for your project.
Table of Contents

What is research design?
The four types of research design, research design examples.
Research design is the process of planning and executing a study to answer specific questions. This process allows you to test hypotheses in the business or scientific fields.
Research design involves choosing the right methodology, selecting the most appropriate data collection methods, and devising a plan (or framework) for analyzing the data. In short, a good research design helps us to structure our research.
Marketers use different types of research design when conducting research .
There are four common types of research design — descriptive, correlational, experimental, and diagnostic designs. Let’s take a look at each in more detail.
Researchers use different designs to accomplish different research objectives. Here, we'll discuss how to choose the right type, the benefits of each, and use cases.
Research can also be classified as quantitative or qualitative at a higher level. Some experiments exhibit both qualitative and quantitative characteristics.
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Experimental
An experimental design is used when the researcher wants to examine how variables interact with each other. The researcher manipulates one variable (the independent variable) and observes the effect on another variable (the dependent variable).
In other words, the researcher wants to test a causal relationship between two or more variables.
In marketing, an example of experimental research would be comparing the effects of a television commercial versus an online advertisement conducted in a controlled environment (e.g. a lab). The objective of the research is to test which advertisement gets more attention among people of different age groups, gender, etc.
Another example is a study of the effect of music on productivity. A researcher assigns participants to one of two groups — those who listen to music while working and those who don't — and measure their productivity.
The main benefit of an experimental design is that it allows the researcher to draw causal relationships between variables.
One limitation: This research requires a great deal of control over the environment and participants, making it difficult to replicate in the real world. In addition, it’s quite costly.
Best for: Testing a cause-and-effect relationship (i.e., the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable).
Correlational
A correlational design examines the relationship between two or more variables without intervening in the process.
Correlational design allows the analyst to observe natural relationships between variables. This results in data being more reflective of real-world situations.
For example, marketers can use correlational design to examine the relationship between brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. In particular, the researcher would look for patterns or trends in the data to see if there is a relationship between these two entities.
Similarly, you can study the relationship between physical activity and mental health. The analyst here would ask participants to complete surveys about their physical activity levels and mental health status. Data would show how the two variables are related.
Best for: Understanding the extent to which two or more variables are associated with each other in the real world.
Descriptive
Descriptive research refers to a systematic process of observing and describing what a subject does without influencing them.
Methods include surveys, interviews, case studies, and observations. Descriptive research aims to gather an in-depth understanding of a phenomenon and answers when/what/where.
SaaS companies use descriptive design to understand how customers interact with specific features. Findings can be used to spot patterns and roadblocks.
For instance, product managers can use screen recordings by Hotjar to observe in-app user behavior. This way, the team can precisely understand what is happening at a certain stage of the user journey and act accordingly.
Brand24, a social listening tool, tripled its sign-up conversion rate from 2.56% to 7.42%, thanks to locating friction points in the sign-up form through screen recordings.
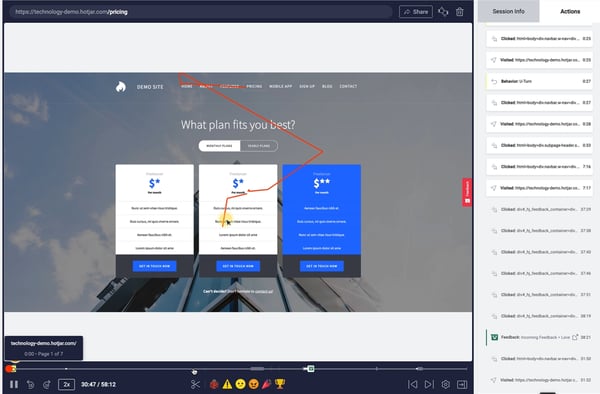
Carma Laboratories worked with research company MMR to measure customers’ reactions to the lip-care company’s packaging and product . The goal was to find the cause of low sales for a recently launched line extension in Europe.
The team moderated a live, online focus group. Participants were shown w product samples, while AI and NLP natural language processing identified key themes in customer feedback.
This helped uncover key reasons for poor performance and guided changes in packaging.
Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents
Research design is the framework or blueprint that guides the collection, measurement, and analysis of data in a study. It provides a structured approach to answering research questions, ensuring that the study’s goals are met in an organized, reliable, and valid manner. Research design is crucial as it directly impacts the study’s quality, credibility, and findings.

Research Design
Research design is a systematic plan outlining how a study is conducted, including methods of data collection, procedures, and tools for analysis. It aligns the research question with the appropriate methods, ensuring that the study remains focused, feasible, and ethically sound.
Purpose of Research Design :
- Provides a structured approach for data collection and analysis.
- Ensures consistency in the research process.
- Enhances the reliability and validity of findings.
- Minimizes bias by defining clear procedures and controls.
Types of Research Design
Research designs are typically classified into three main types: qualitative , quantitative , and mixed methods . Each type serves different purposes and is selected based on the nature of the research question, objectives, and resources.
1. Qualitative Research Design
- Definition : Qualitative research focuses on exploring complex phenomena, understanding individual experiences, and generating insights into social or human behavior. It often involves non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and textual analysis.
- Case Study : In-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or event.
- Ethnography : Study of cultural groups and practices within their natural setting.
- Grounded Theory : Development of a theory based on observed data.
- Phenomenology : Exploration of lived experiences and perceptions.
- Example : A case study on how remote work impacts employee well-being by conducting interviews with employees from various industries to gather personal insights and themes.
2. Quantitative Research Design
- Definition : Quantitative research is focused on quantifying variables and using statistical analysis to test hypotheses. It often involves large samples, standardized data collection tools, and numerical data.
- Descriptive : Provides a summary of characteristics or behaviors within a population (e.g., surveys, cross-sectional studies).
- Correlational : Examines relationships between two or more variables without manipulating them.
- Experimental : Involves manipulation of variables to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quasi-Experimental : Similar to experimental design but lacks random assignment.
- Example : An experimental study investigating the effect of a new teaching method on student test scores, with one group using the new method and a control group using traditional methods.
3. Mixed-Methods Research Design
- Definition : Mixed-methods design combines both qualitative and quantitative approaches in a single study, providing a more comprehensive analysis of the research question.
- Explanatory Sequential Design : Quantitative data is collected and analyzed first, followed by qualitative data to explain or expand on the quantitative findings.
- Exploratory Sequential Design : Qualitative data is collected first to explore a phenomenon, followed by quantitative data to confirm or generalize findings.
- Convergent Design : Both qualitative and quantitative data are collected simultaneously and compared to produce integrated insights.
- Example : A study on customer satisfaction, first surveying customers to get quantitative data and then conducting follow-up interviews to explore specific customer feedback in detail.
Methods in Research Design
Various methods are used within research designs to collect and analyze data. Each method is selected based on the research question, data type, and study objectives.
1. Survey and Questionnaire
- Definition : Surveys and questionnaires are tools for collecting standardized data from large samples. They are often used in descriptive and correlational studies.
- Develop questions related to the research objectives.
- Distribute to participants via online platforms, paper forms, or face-to-face interviews.
- Analyze results using statistical software for quantitative insights.
- Example : A survey assessing consumer satisfaction with a new product by collecting data on factors such as ease of use, design, and performance.
2. Interview
- Definition : Interviews are qualitative methods that gather in-depth information through direct questioning. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Design interview questions that align with the research goals.
- Conduct interviews in person, via phone, or virtually, recording responses for analysis.
- Use thematic or content analysis to interpret findings.
- Example : Conducting semi-structured interviews with educators to explore their experiences with online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic.
3. Observation
- Definition : Observation involves recording behaviors, actions, or events as they occur naturally. It is often used in ethnographic and case study designs.
- Choose between participant (researcher actively engages) or non-participant observation.
- Develop an observation checklist or guide for consistency.
- Record findings, often through field notes or video, and analyze for patterns.
- Example : Observing interactions in a classroom setting to study student engagement with different teaching methods.
4. Experiment
- Definition : Experiments involve manipulating variables to examine cause-and-effect relationships. They are commonly used in scientific and clinical research.
- Randomly assign participants to control and experimental groups.
- Manipulate the independent variable and measure changes in the dependent variable.
- Use statistical analysis to interpret results.
- Example : A laboratory experiment testing the effectiveness of a new drug on blood pressure by comparing outcomes in treated and untreated groups.
5. Case Study
- Definition : A case study is an in-depth investigation of an individual, group, organization, or event to explore underlying principles and patterns.
- Select a case that represents the phenomenon of interest.
- Use various data sources, including interviews, documents, and observations.
- Analyze for unique insights and apply findings to broader contexts.
- Example : A case study on the strategies a small business used to survive during an economic recession.
Examples of Research Design Applications
- Design : Quantitative, using a survey.
- Goal : To understand consumer preferences for eco-friendly packaging.
- Method : Survey distributed to a random sample of consumers asking about purchasing behaviors and attitudes toward sustainability.
- Design : Experimental, quantitative.
- Goal : To study the effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance.
- Method : Participants are randomly assigned to sleep-deprived and control groups, with cognitive performance measured using standardized tests.
- Design : Convergent mixed-methods.
- Goal : To evaluate the effectiveness of a new curriculum on student learning.
- Method : Collect quantitative data from student test scores and qualitative data from teacher interviews to provide a comprehensive evaluation.
- Design : Qualitative, ethnography.
- Goal : To study cultural practices in rural communities.
- Method : The researcher spends an extended period within the community, observing daily activities and conducting informal interviews.
Tips for Choosing the Right Research Design
- Align with Research Question : Choose a design that directly addresses the research question and allows for valid answers.
- Consider Data Type : Decide whether the research requires quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (textual or observational) data.
- Assess Feasibility : Take into account time, resources, and access to participants when selecting a design.
- Ensure Ethical Compliance : Make sure the design is ethically sound, with informed consent and confidentiality for participants.
- Anticipate Limitations : Be aware of potential limitations in each design type and how they might affect your findings.
Challenges in Research Design
- Sample Selection Bias : Choosing a non-representative sample can lead to biased results and impact the study’s validity.
- Data Collection Constraints : Limitations in resources or participant access may affect data quality.
- Ethical Concerns : Research involving vulnerable populations or sensitive topics requires careful ethical consideration.
- External Validity : Some designs, like case studies, may have limited generalizability beyond the studied context.
Research design is a critical component of the research process, as it determines how a study is structured, conducted, and analyzed. By choosing the appropriate design—whether qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods—researchers ensure that they answer their questions effectively, producing credible, reliable, and valid results. A solid research design aligns with the study’s objectives, considers resources and ethical issues, and anticipates limitations to provide meaningful contributions to knowledge.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . SAGE Publications.
- Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2008). The Research Methods Knowledge Base . Cengage Learning.
- Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research Methods for Business Students . Pearson Education.
- Yin, R. K. (2017). Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . SAGE Publications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...
- What is descriptive research?
Last updated
5 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Descriptive research is a common investigatory model used by researchers in various fields, including social sciences, linguistics, and academia.
Read on to understand the characteristics of descriptive research and explore its underlying techniques, processes, and procedures.
Analyze your descriptive research
Dovetail streamlines analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
Descriptive research is an exploratory research method. It enables researchers to precisely and methodically describe a population, circumstance, or phenomenon.
As the name suggests, descriptive research describes the characteristics of the group, situation, or phenomenon being studied without manipulating variables or testing hypotheses . This can be reported using surveys , observational studies, and case studies. You can use both quantitative and qualitative methods to compile the data.
Besides making observations and then comparing and analyzing them, descriptive studies often develop knowledge concepts and provide solutions to critical issues. It always aims to answer how the event occurred, when it occurred, where it occurred, and what the problem or phenomenon is.
- Characteristics of descriptive research
The following are some of the characteristics of descriptive research:
Quantitativeness
Descriptive research can be quantitative as it gathers quantifiable data to statistically analyze a population sample. These numbers can show patterns, connections, and trends over time and can be discovered using surveys, polls, and experiments.
Qualitativeness
Descriptive research can also be qualitative. It gives meaning and context to the numbers supplied by quantitative descriptive research .
Researchers can use tools like interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies to illustrate why things are what they are and help characterize the research problem. This is because it’s more explanatory than exploratory or experimental research.
Uncontrolled variables
Descriptive research differs from experimental research in that researchers cannot manipulate the variables. They are recognized, scrutinized, and quantified instead. This is one of its most prominent features.
Cross-sectional studies
Descriptive research is a cross-sectional study because it examines several areas of the same group. It involves obtaining data on multiple variables at the personal level during a certain period. It’s helpful when trying to understand a larger community’s habits or preferences.
Carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive studies are usually carried out in the participants’ everyday environment, which allows researchers to avoid influencing responders by collecting data in a natural setting. You can use online surveys or survey questions to collect data or observe.
Basis for further research
You can further dissect descriptive research’s outcomes and use them for different types of investigation. The outcomes also serve as a foundation for subsequent investigations and can guide future studies. For example, you can use the data obtained in descriptive research to help determine future research designs.
- Descriptive research methods
There are three basic approaches for gathering data in descriptive research: observational, case study, and survey.
You can use surveys to gather data in descriptive research. This involves gathering information from many people using a questionnaire and interview .
Surveys remain the dominant research tool for descriptive research design. Researchers can conduct various investigations and collect multiple types of data (quantitative and qualitative) using surveys with diverse designs.
You can conduct surveys over the phone, online, or in person. Your survey might be a brief interview or conversation with a set of prepared questions intended to obtain quick information from the primary source.
Observation
This descriptive research method involves observing and gathering data on a population or phenomena without manipulating variables. It is employed in psychology, market research , and other social science studies to track and understand human behavior.
Observation is an essential component of descriptive research. It entails gathering data and analyzing it to see whether there is a relationship between the two variables in the study. This strategy usually allows for both qualitative and quantitative data analysis.
Case studies
A case study can outline a specific topic’s traits. The topic might be a person, group, event, or organization.
It involves using a subset of a larger group as a sample to characterize the features of that larger group.
You can generalize knowledge gained from studying a case study to benefit a broader audience.
This approach entails carefully examining a particular group, person, or event over time. You can learn something new about the study topic by using a small group to better understand the dynamics of the entire group.
- Types of descriptive research
There are several types of descriptive study. The most well-known include cross-sectional studies, census surveys, sample surveys, case reports, and comparison studies.
Case reports and case series
In the healthcare and medical fields, a case report is used to explain a patient’s circumstances when suffering from an uncommon illness or displaying certain symptoms. Case reports and case series are both collections of related cases. They have aided the advancement of medical knowledge on countless occasions.
The normative component is an addition to the descriptive survey. In the descriptive–normative survey, you compare the study’s results to the norm.
Descriptive survey
This descriptive type of research employs surveys to collect information on various topics. This data aims to determine the degree to which certain conditions may be attained.
You can extrapolate or generalize the information you obtain from sample surveys to the larger group being researched.
Correlative survey
Correlative surveys help establish if there is a positive, negative, or neutral connection between two variables.
Performing census surveys involves gathering relevant data on several aspects of a given population. These units include individuals, families, organizations, objects, characteristics, and properties.
During descriptive research, you gather different degrees of interest over time from a specific population. Cross-sectional studies provide a glimpse of a phenomenon’s prevalence and features in a population. There are no ethical challenges with them and they are quite simple and inexpensive to carry out.
Comparative studies
These surveys compare the two subjects’ conditions or characteristics. The subjects may include research variables, organizations, plans, and people.
Comparison points, assumption of similarities, and criteria of comparison are three important variables that affect how well and accurately comparative studies are conducted.
For instance, descriptive research can help determine how many CEOs hold a bachelor’s degree and what proportion of low-income households receive government help.
- Pros and cons
The primary advantage of descriptive research designs is that researchers can create a reliable and beneficial database for additional study. To conduct any inquiry, you need access to reliable information sources that can give you a firm understanding of a situation.
Quantitative studies are time- and resource-intensive, so knowing the hypotheses viable for testing is crucial. The basic overview of descriptive research provides helpful hints as to which variables are worth quantitatively examining. This is why it’s employed as a precursor to quantitative research designs.
Some experts view this research as untrustworthy and unscientific. However, there is no way to assess the findings because you don’t manipulate any variables statistically.
Cause-and-effect correlations also can’t be established through descriptive investigations. Additionally, observational study findings cannot be replicated, which prevents a review of the findings and their replication.
The absence of statistical and in-depth analysis and the rather superficial character of the investigative procedure are drawbacks of this research approach.
- Descriptive research examples and applications
Several descriptive research examples are emphasized based on their types, purposes, and applications. Research questions often begin with “What is …” These studies help find solutions to practical issues in social science, physical science, and education.
Here are some examples and applications of descriptive research:
Determining consumer perception and behavior
Organizations use descriptive research designs to determine how various demographic groups react to a certain product or service.
For example, a business looking to sell to its target market should research the market’s behavior first. When researching human behavior in response to a cause or event, the researcher pays attention to the traits, actions, and responses before drawing a conclusion.
Scientific classification
Scientific descriptive research enables the classification of organisms and their traits and constituents.
Measuring data trends
A descriptive study design’s statistical capabilities allow researchers to track data trends over time. It’s frequently used to determine the study target’s current circumstances and underlying patterns.
Conduct comparison
Organizations can use a descriptive research approach to learn how various demographics react to a certain product or service. For example, you can study how the target market responds to a competitor’s product and use that information to infer their behavior.
- Bottom line
A descriptive research design is suitable for exploring certain topics and serving as a prelude to larger quantitative investigations. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the “what” of the group or thing you’re investigating.
This research type acts as the cornerstone of other research methodologies . It is distinctive because it can use quantitative and qualitative research approaches at the same time.
What is descriptive research design?
Descriptive research design aims to systematically obtain information to describe a phenomenon, situation, or population. More specifically, it helps answer the what, when, where, and how questions regarding the research problem rather than the why.
How does descriptive research compare to qualitative research?
Despite certain parallels, descriptive research concentrates on describing phenomena, while qualitative research aims to understand people better.
How do you analyze descriptive research data?
Data analysis involves using various methodologies, enabling the researcher to evaluate and provide results regarding validity and reliability.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 9 November 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, a whole new way to understand your customer is here, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Descriptive Research: Characteristics, Methods + Examples

Suppose an apparel brand wants to understand the fashion purchasing trends among New York’s buyers, then it must conduct a demographic survey of the specific region, gather population data, and then conduct descriptive research on this demographic segment.
The study will then uncover details on “what is the purchasing pattern of New York buyers,” but will not cover any investigative information about “ why ” the patterns exist. Understanding the nature of the market is the study’s main goal for the apparel brand trying to break into this market.
This type of research offers extensive advantages and applications, making it a potential game-changer for those who incorporate it into their business toolkit. Want to learn more? Keep reading to uncover everything you need to know to master and make the most of this valuable approach.
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a method describing the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This descriptive methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research subject than the “why” of the research subject.
The method primarily focuses on describing the nature of a demographic segment without focusing on “why” a particular phenomenon occurs. In other words, it “describes” the research subject without covering “why” it happens.
Descriptive Design
A widely used concept in this type of research is descriptive design. This methodology combines quantitative and qualitative approaches to gather information that allows for the description of specific cases under study. Popular methods include case studies, surveys, and observations, which we will explore later.
One of the main advantages of using this data type is that it enables manipulation through disciplines like statistics to predict and gain an in-depth understanding of specific phenomena.

Characteristics of Descriptive Research
The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, the design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity.
Some characteristics of descriptive research are:

- Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment’s nature.
- Uncontrolled variables: In it, none of the variables are influenced in any way. This uses observational methods to conduct the research. Hence, the nature of the variables or their behavior is not in the hands of the researcher.
- Cross-sectional studies: It is generally a cross-sectional study where different sections belonging to the same group are studied.
- The basis for further research: Researchers further research the data collected and analyzed from descriptive research using different research techniques. The data can also help point towards the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
Applications of Descriptive Research With Examples
A descriptive research method can be used in multiple ways and for various reasons. Before getting into any survey , though, the survey goals and survey design are crucial. Despite following these steps, there is no way to know if one will meet the research outcome. How to use descriptive research? To understand the end objective of research goals, below are some ways organizations currently use descriptive research today:
1. Define Respondent Characteristics
The aim of using close-ended questions is to draw concrete conclusions about the respondents . This could be the need to derive patterns, traits, and behaviors of the respondents. It could also be to understand from a respondent their attitude, or opinion about the phenomenon. For example, understand millennials and the hours per week they spend browsing the internet. All this information helps the organization researching to make informed business decisions.
2. Measure Data Trends
Researchers measure data trends over time with a descriptive research design’s statistical capabilities. Consider if an apparel company researches different demographics like age groups from 24-35 and 36-45 on a new range launch of autumn wear. If one of those groups doesn’t take too well to the new launch, it provides insight into what clothes are like and what is not. The brand drops the clothes and apparel that customers don’t like.
3. Conduct Comparisons
Organizations also use a descriptive research design to understand how different groups respond to a specific product or service. For example, an apparel brand creates a survey asking general questions that measure the brand’s image. The same study also asks demographic questions like age, income, gender, geographical location, geographic segmentation , etc. This consumer research helps the organization understand what aspects of the brand appeal to the population and what aspects do not. It also helps make product or marketing fixes or even create a new product line to cater to high-growth potential groups.
4. Validate Existing Conditions
Researchers widely use descriptive research to help ascertain the research object’s prevailing conditions and underlying patterns. Due to the non-invasive research method and the use of quantitative observation and some aspects of qualitative observation , researchers observe each variable and conduct an in-depth analysis . Researchers also use it to validate any existing conditions that may be prevalent in a population.
5. Conduct Research at Different Times
The analysis can be conducted at different periods to ascertain any similarities or differences. This also allows any number of variables to be evaluated. For verification, studies on prevailing conditions can also be repeated to draw trends.
Advantages of Descriptive Research
Some of the significant advantages of descriptive research are:

- Data collection: A researcher can conduct descriptive research using specific methods like observational method, case study method, and survey method. Between these three, all primary data collection methods are covered, which provides a lot of information. This can be used for future research or even for developing a hypothesis for your research object.
- Varied: Since the data collected is qualitative and quantitative, it gives a holistic understanding of a research topic. The information is varied, diverse, and thorough.
- Natural environment: Descriptive research allows for the research to be conducted in the respondent’s natural environment, which ensures that high-quality and honest data is collected.
- Quick to perform and cheap: As the sample size is generally large in descriptive research, the data collection is quick to conduct and is inexpensive.
Descriptive Research Methods
There are three distinctive methods to conduct descriptive research. They are:
01. Observational Method
The observational method is the most effective method to conduct this research, and researchers make use of both quantitative and qualitative observations.
A quantitative observation is the objective collection of data primarily focused on numbers and values. It suggests “associated with, of or depicted in terms of a quantity.” Results of quantitative observation are derived using statistical and numerical analysis methods. It implies observation of any entity associated with a numeric value such as age, shape, weight, volume, scale, etc. For example, the researcher can track if current customers will refer the brand using a simple Net Promoter Score question .
Qualitative observation doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead just monitoring characteristics. In this case, the researcher observes the respondents from a distance. Since the respondents are in a comfortable environment, the characteristics observed are natural and effective.
In a descriptive research design, the researcher can choose to be either a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or a full participant. For example, in a supermarket, a researcher can from afar monitor and track the customers’ selection and purchasing trends. This offers a more in-depth insight into the purchasing experience of the customer.
02. Case Study Method
Case studies involve in-depth research and study of individuals or groups. T hose studies lead to a hypothesis and widen a further scope of studying a phenomenon. However, case studies should not be used to determine cause and effect as they can’t make accurate predictions because there could be a bias on the researcher’s part.
The other reason why case studies are not a reliable way of conducting descriptive research is that there could be an atypical respondent in the survey. Describing them leads to weak generalizations and moving away from external validity.
03. Survey Research
In survey research, respondents answer through surveys or questionnaires or polls . They are a popular market research tool to collect feedback from respondents. A study to gather useful data should have the right survey questions. It should be a balanced mix of open-ended questions and close ended-questions . The survey method can be conducted online or offline, making it the go-to option for descriptive research where the sample size is enormous.
Examples of Descriptive Research
Some examples of descriptive research are:
- A specialty food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different people. To understand the preferred flavor palette, they conduct this type of research study using various methods like observational methods in supermarkets. By also surveying while collecting in-depth demographic information, offers insights about the preference of different markets. This can also help tailor make the rubs and spreads to various preferred meats in that demographic. Conducting this type of research helps the organization tweak their business model and amplify marketing in core markets.
- Another example of where this research can be used is if a school district wishes to evaluate teachers’ attitudes about using technology in the classroom. By conducting surveys and observing their comfortableness using technology through observational methods, the researcher can gauge what they can help understand if a full-fledged implementation can face an issue. This also helps in understanding if the students are impacted in any way with this change.
Some other research problems and research questions that can lead to descriptive research are:
- Market researchers want to observe the habits of consumers.
- A company wants to evaluate the morale of its staff.
- A school district wants to understand if students will access online lessons rather than textbooks.
- To understand if its wellness questionnaire programs enhance the overall health of the employees.
Use QuestionPro Research Suite for Descriptive Research
QuestionPro Research Suite is a versatile tool suitable for supporting exploratory research (which seeks to generate new ideas) and incredibly descriptive research that strives to describe features of populations or a phenomenon.
You can use descriptive research with this method as follows:
01. Survey Design
- Survey Design: With QuestionPro, online surveys can be highly customized. You have access to many different survey templates. This is great for a quick but descriptive study that you need up and running in hours rather than days. If you are still familiar with how surveys should be set up, this space will provide some structure.
- Data Collection: Surveys can be disseminated in various ways, such as via email, social media/website pop-ups, QR codes, or mobile devices, to target a large and diverse audience.
- Real-Time Analytics: QuestionPro is equipped with a set of tools to analyze data and responses after the survey has started. Visualizing trends and patterns is extremely important in descriptive research.
- Advanced Reporting: Reports can be automatically made and described in detail about your research findings. This will make your descriptive research data results easier by creating reports that can incorporate graphs, charts, and summaries.
- Panel Integration: You may need a measurement over research samples. In this case, you can take advantage of the integrated QuestionPro respondent panel to provide a more diverse set of participants so that your data will reflect the person about whom it was collected.
Using QuestionPro’s Research Suite, you can efficiently design and conduct descriptive research, gaining valuable insights into your research questions with robust data collection and analysis tools.
Descriptive research is a powerful method for understanding and summarizing a population’s or phenomenon’s characteristics. It provides a clear snapshot of “what is” without manipulating variables, making it invaluable for gathering factual data, identifying patterns, and informing decision-making.
While it doesn’t establish cause-and-effect relationships, it serves as a foundational tool in research, helping researchers and organizations gain insights into trends, behaviors, and conditions within a specific context.
Using tools like QuestionPro Research Suite significantly boosts the effectiveness of descriptive research by offering customizable survey designs, real-time analytics, and powerful data collection features. With QuestionPro, researchers can seamlessly gather in-depth insights and analyze data efficiently, ensuring accurate and actionable results.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs) about Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is a method for observing and describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon without manipulating variables. It focuses on providing a clear snapshot of “what is,” helping researchers gather factual information, identify patterns, and inform decision-making.
For Example: A survey measuring the average age, income level, and shopping habits of customers at a local grocery store.
The goal of descriptive research is to systematically define and summarize the characteristics of a population or phenomenon, providing a clear understanding of “what is” without establishing cause-and-effect relationships. It aims to gather factual data, identify patterns, and inform decision-making.
Descriptive research can be both qualitative and quantitative. It aims to describe characteristics or phenomena and may use numerical data (quantitative) or detailed observations and descriptions (qualitative) depending on the study’s goals.
MORE LIKE THIS

Qualtrics Employee Experience Alternatives: The 6 Best in 2024
Nov 19, 2024

Reputation Management: How to Protect Your Brand Reputation?

Reference Bias: Identifying and Reducing in Surveys and Research

Maximize Employee Feedback with QuestionPro Workforce’s Slack Integration
Nov 6, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Marketing91
Descriptive Research – Characteristics, Methods, Examples, Advantages
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Descriptive research is a type of research that provides an in-depth description of the phenomenon or population under study. Descriptive research is neither in the category of qualitative research nor in the class of quantitative research, but it uses the features of both types of research.
Descriptive research emphasizes what kind of question to be asked in the research study. The descriptive research provides the answer to the “what” part of a research and does not answer the questions why/when/how.
Descriptive research is a suitable choice if you want to learn about the trends of a particular field or the frequency of an event. This research is also an appropriate option when you do not have any information about the research problem, and primary information gathering is required to establish a hypothesis. In this article, you will learn about the characteristics, methods, examples, advantages, and disadvantages of descriptive research.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Descriptive Research

1. Statistical Outcome
Descriptive research answers the “what” questions in statistical form. As the output is in emphasizes form, it is easy for the researcher to deduce results and implement them. Because of this characteristic of descriptive research, it is popularly used in market researches.
2. The basis for secondary research
The results obtained from descriptive research is in statistical form. Therefore, it can also be used as secondary data for similar research problems. In addition to this, different research techniques can be applied to the data for the analysis of various factors of the research problem.
3. Unrestrained variable
Random variables are used in descriptive research. Therefore, it is not in the hands of researchers to control the variables of descriptive research. In descriptive research, the natural behavior of participants is observed to learn about them.
4. Natural setting
Descriptive researches are usually conducted in natural settings. For example, you can distribute questionnaires of surveys among random people, or in an observational method, you can observe the behavior of people in a particular environment. For example, if you want to learn about the buying behavior of people, then you can go to a supermarket and observe people.
5. Cross-sectional study
In descriptive research, different aspects of a single group are studied and compared to gain a different insight into the group.
Methods of Descriptive Research

There are three methods of descriptive research
1. Case study method
The case study method refers to the in-depth and detailed study of the subject, person or case, which is to be studied. A case study involves a formal research method to carry out the research. Using the outcomes obtained from the case study research hypothesis can be established, which can be used to expand the horizons of research.
However, case study research is not suitable to determine the relationship between cause and effect as it does not provide accurate results. Moreover, the outcome of the case study method is relevant to that particular case and similar cases and can’t be generalised. Case studies are focused on interesting and unusual cases that are complex and challenging and provide additional information about a particular case.
For example, in a medical case study, researchers study a rare medical case to get more knowledge about the medical case. Similarly, case study methods are used by scientists to learn about unusual phenomenon.
2. Observational Method
Observational research is a type of non-experimental research. Observational research can be defined as a type of research where the researcher observes the ongoing behaviors of the subject being studied. Observational research is majorly used in the marketing and social science fields. In observational research, the researcher finds the actions of subjects under study in their natural setting.
Observational methods are different from experimental research methods because, in experimental research methods, an artificial environment is created for the subjects under study. An observational study can be of two types, naturalistic observation or participant observation. A naturalistic observation study means the study of subjects when they are at their natural behavior.
In participant observation, people being observed in the research study are aware of the observation. They are asked to take part in the observation study. Observational research methods are suitable for studying the behavior of subjects under the study. However, this research is incapable of providing information about the actual cause of the behaviours of subjects under study.
3. Survey Research
Survey research is one of the most popular and easy forms of research to obtain information or to collect data. A questionnaire is prepared to contain questions related to the research problem either on paper or in any digital format. These questionnaires are distributed among random people in the hope of getting their accurate opinion.
The survey research method is popularly used in University researches and business researches. Survey research is also called primary research and can be used with other research methods to obtain accurate outcomes.
Moreover, data collected from survey research can be used as secondary research data by other researchers.
Examples of descriptive research

Let us take the case of a sports clothing brand. The sports brand wants to set up a business in selling gym gears. They want to know about in detail about the kind of clothes people want to wear while exercising in the gym. To get in-depth information about the preference of people, they adopted two descriptive methods one is naturalistic observation, and the other is a survey.
In naturalistic observation, they started observing people at different gyms and silently learn about the kind of clothes they prefer to wear. To know more about their choices, they conducted a survey and distributed questionnaire containing questions like How much would they like to spend on a sports track pant?
What color of gym gear do they prefer to wear while working out? Answer to these questions will provide them the knowledge that was difficult to obtain through observing.
A restaurant planned to start to serve continental food to its customers. Therefore, to learn about the choice of people in flavor and taste, they an observation method to learn about what kind of spreads, herbs, and meat preferred by people.
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Descriptive Research.
Advantages of descriptive research

- Data collected from descriptive research is helpful in important decision-making because the data is obtained from a large population. Because using the descriptive survey method, statistical information can be obtained, and analysis of that data can be made to deduce desired results.
- A variety of data can be obtained using different descriptive research methods like surveys, observation, and vase study. These three research methods provide different type of data which can be used to analysis for a research problem. For example, using the case study research method can be used to develop a hypothesis about a research problem.
- One advantage of descriptive research over other research methods is that it is cheap and quick to conduct descriptive research. You don’t require having a great place dedicated only to research. Descriptive research like observation research can be held in natural settings, and you can distribute surveys to people online or get them answered by random people at your business place or other public places.
- Descriptive research provides both quantitative and qualitative data. The variety of data provides a holistic understanding of the research problem.
- Descriptive research can be conducted in natural settings. There is no need to have a designated space to conduct research using any of the descriptive research methods.
Disadvantages of descriptive research
- Descriptive methods only provide the answers for “what” and do not answer the why and how. Therefore, descriptive research methods are not suitable for determining cause and effect relationships.
- Descriptive methods mainly depend on the responses of people. There are chances that people might not act their true selves if they know they are being observed. In the case of the survey method, there are chances that some people don’t answer the questions honestly, which makes the output of the descriptive research study invalid. Because the results derived from this type of data will not be accurate.
- Another problem associated with descriptive research is the halo effect. A researcher might get partial if he knows the participant personally. The observations made in this way would be considered invalid.
- In descriptive research methods, participants are picked randomly. The randomness of the sample can’t represent the whole population accurately.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- What is Behavioral research? Importance, Methods & Examples
- Field Research – Reasons And Methods
- Research Methodology – Overview, Types and Methods
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- What is Advertising? Advertising Methods and Advantages
- 11 Characteristics of Qualitative Research
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON:
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
We use cookies
This website uses cookies to provide better user experience and user's session management. By continuing visiting this website you consent the use of these cookies.
Descriptive research Design: What it is and How to use it
Imagine being able to carefully design studies that shed light on the who, what, where, and how of a particular phenomenon in your business.
With descriptive research design, you’ll learn how to gather and analyze data in a way that paints a vivid picture of the subject you’re investigating.

So, what exactly is descriptive research design?
It’s a powerful approach that allows you to observe and describe characteristics, behaviors, and trends without influencing or manipulating the variables.
Mastering descriptive research design is a game-changer if you’re a business professional looking to make informed decisions.
You’ll be equipped to gather reliable data, spot patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions.
In this blog, we’ll cover the following:
Table of Content:
What is descriptive research, understanding descriptive research analysis, why do we need a descriptive research design.
- Characteristics of Descriptive Research
Types of Descriptive Research Design
When to use a descriptive research design, descriptive research methods, top 10 descriptive research questions examples, how to conduct a descriptive research design, descriptive research design examples, how to analyze data for descriptive research design, descriptive research advantages and disadvantages, descriptive research design: faqs.
Before diving into the blog’s core, we’ll address the following question: What is descriptive research?
Definition: Descriptive research design allows you to observe and describe various aspects of a subject in your business without manipulating or influencing the variables involved.
It’s like taking a snapshot of the world as it is, providing you with a detailed picture of the who, what, where, and how.
In this type of research, the main goal is to capture accurate and reliable data for further analysis.
By collecting and analyzing data , you can identify patterns and uncover relationships that contribute to a deeper understanding of your business.
Use descriptive research design in various fields, such as psychology, sociology, business, and education.
Understanding and using descriptive research design is crucial if you’re a business owner or a professional seeking to make data-driven decisions .
By mastering this approach, you’ll have the tools to gather meaningful data and draw insightful conclusions.
Descriptive research analysis is the process of examining data to understand and summarize a phenomenon’s characteristics. By focusing on “what is” rather than “why,” it uses tools like averages, charts, and tables to identify patterns and trends.
This type of analysis provides a clear, factual basis that helps researchers and decision-makers understand the subject in depth and may guide future research or strategies.
Video Tutorial: Descriptive Research Design
We need a descriptive research design to accurately capture and document details about a phenomenon as it naturally occurs. This type of research provides a clear picture of the “what” by identifying patterns, behaviors, and characteristics within a population or situation.
By offering factual, detailed information, descriptive research serves as a foundation for further analysis, helping researchers and decision-makers understand trends, generate hypotheses, and inform policies without influencing or altering the studied environment.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research
When it comes to descriptive research design, several key characteristics set it apart.
Let’s dive into these distinctive features that shape the research method.
Descriptive research design is a quantitative approach.
It focuses on gathering quantifiable information that can be subjected to statistical analysis. By collecting numerical data, you can gain a deeper understanding of the characteristics and behaviors of your target market .
This makes it a valuable tool in market research , allowing you to describe and analyze different demographic segments.
Another important characteristic of descriptive research design is that it involves uncontrolled variables.
In other words, you don’t manipulate or influence any of the variables under study. Instead, you employ observational methods to observe and describe the subject of interest.
This ensures that the nature and behavior of the variables remain unaffected by external influences.
Descriptive research design often takes the form of cross-sectional studies.
This means that you examine different sections or groups within a population at a particular point in time.
By doing so, you can gain insights into the similarities, differences, and patterns among these sections.
Furthermore, the data collected through descriptive research design serves as a basis for further exploration. You can use the resulting insights to inform and guide subsequent research.
Let’s explore some of the common types of descriptive studies and how they contribute to our understanding of different phenomena.
Case reports and case series
In the healthcare and medical fields, case reports are instrumental in shedding light on uncommon illnesses. These reports provide detailed accounts of individual cases, while case series compile related cases. Together, they advance medical knowledge and diagnose and treat various conditions.
Normative surveys
Normative surveys complement descriptive surveys by comparing results to established norms. This allows you to gauge the degree to which certain conditions can be achieved and identify deviations from the norm.
Descriptive surveys
Descriptive surveys involve collecting information through questionnaires or interviews to gather data on a range of topics. The aim is to determine the prevalence and characteristics of specific conditions or behaviors.
Extrapolating the findings from sample surveys allows you to make inferences about the larger population being studied.
Correlative surveys
Correlative surveys examine the relationship between two variables to establish whether there’s a positive, negative, or neutral connection. These surveys provide insights into the associations between different factors and help identify patterns or trends.
Census surveys
Census surveys involve gathering comprehensive data on various aspects of a specific population. This can include individuals, families, you, objects, characteristics, and properties.
You gain a comprehensive understanding of the population under study by conducting thorough census surveys.
Cross-sectional studies
Conduct Cross-sectional studies during descriptive research to capture a snapshot of a particular behavior or attribute within a population at a given time.
These studies provide valuable insights into the prevalence and features of the phenomenon. They’re straightforward to carry out, cost-effective, and seldom pose ethical challenges.
Comparative studies
Comparative studies involve comparing the conditions or characteristics of two subjects, such as research variables, you, plans, or individuals.
Key factors in conducting effective comparative studies include identifying comparison points, assuming similarities, etc.
Let’s explore some of the practical applications that are widely used today.
Define respondent characteristics
One of the primary uses of descriptive research design is to understand and define the characteristics of your target respondents.
You can draw concrete conclusions about your target audience by employing close-ended questions.
Measure data trends
Descriptive research design enables you to measure data trends over time . Using this approach’s statistical capabilities, you can track changes and patterns in data and make informed decisions.
Conduct comparisons
Use descriptive research design to conduct comparisons among different groups. This helps you understand how various population segments respond to your brand offers.
By analyzing these differences, you can tailor their strategies to better cater to each group’s needs.
Validate existing conditions
Use descriptive marketing research to validate the prevailing conditions and underlying patterns related to your business.
By collecting and analyzing data, you gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of affairs, enabling you to identify strengths, weaknesses, etc.
Conduct research at different times
Descriptive research design offers the flexibility to conduct research at different periods. This allows you to explore changes or consistencies over time.
By comparing data collected at different time points, you can identify any similarities or differences, providing valuable insights for decision-making processes.
Descriptive research methods are approaches used to gather detailed information about a subject without manipulating it. Here are three main methods:
- Observational Method : Involves watching and recording behaviors or events as they naturally occur. It’s useful for studying real-life situations, such as customer interactions or classroom dynamics.
- Survey Method : Uses questionnaires, interviews, or polls to collect data directly from participants. It’s effective for gathering opinions, behaviors, and demographic information from a large audience.
- Case Study Method : In-depth examination of a single subject, group, or event. This method provides comprehensive insights into complex issues and is often used in fields like psychology, education, and business.
- What are the demographic characteristics of customers who prefer online shopping over in-store shopping?
- How do different age groups use social media platforms?
- What are the main reasons college students choose their specific fields of study?
- What types of activities are most popular among tourists visiting urban vs. rural areas?
- How frequently do people engage in physical exercise, and what types of activities do they prefer?
- What are the common challenges faced by remote workers in different industries?
- How do spending habits differ between single and married individuals?
- What are the key motivations for employees to participate in workplace training programs?
- What features do smartphone users consider most important when buying a new device?
- How do environmental awareness levels vary among people from different educational backgrounds?
Conducting a descriptive research design survey involves a series of important steps to ensure the success of your study. Let’s explore these steps.
Define the research objectives
Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of your research.
What specific information do you aim to gather?
What research questions or hypotheses are you trying to answer?
Defining your objectives will serve as a compass throughout the research process.
Determine the target population
Identify the specific population or group that you want to describe through your survey.
It could be your target market. Consider the characteristics and scope of the population to ensure it aligns with your research objectives.
Select the sampling method
Choose an appropriate sampling technique to select participants from your target market. Options include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, etc. Your choice will depend on factors like population size and available resources.
Develop data collection instruments
Select the appropriate methods and tools to gather data for your survey.
This can include surveys, interviews, observations, or the extraction of information from existing records.
Ensure your instruments are reliable, valid, and suitable for achieving your research objectives.
Pilot test the instruments
Conduct a pilot test with a small sample before launching your survey on a larger scale.
This will help you identify any issues, such as unclear survey questions. Make necessary adjustments based on feedback.
Collect the data
Implement your data collection plan by administering surveys, conducting interviews, or carrying out observations.
Ensure that you follow ethical guidelines and respect participant confidentiality throughout the process.
Analyze the data
Organize and visualize your data using charts like the Likert Scale Chart and CSAT Score Survey Chart.
Interpret and report the findings
Interpret your results and conclude. Describe the characteristics, patterns, and relationships identified. Present your findings clearly and concisely using visuals like tables, graphs or charts .
Validate the findings
Consider validating your findings through methods like peer review. This helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of your descriptive research.
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys : A business surveys to understand customer satisfaction levels and preferences for its products, using data to identify trends in customer opinions.
- Classroom Observation : An educational researcher observes a classroom to document student behaviors, engagement levels, and interactions with teachers, aiming to describe classroom dynamics without interference.
- Health and Lifestyle Studies : Researchers gather data on diet, exercise habits, and sleep patterns among different age groups to describe health-related behaviors in the population.
- Market Demographics Analysis : A company studies the demographic characteristics of its target market, such as age, income, and location, to better understand the audience it serves.
- Social Media Usage Study : A study explores how often people use various social media platforms, focusing on user demographics and patterns of engagement.
Congratulations on successfully learning the tested and proven tips on how to set up descriptive research design.
Now, it’s time to unlock the true potential of your descriptive design data by analyzing it.
While tools like Excel help organize data, they lack descriptive research design survey-specific charts, like the Likert Scale Chart.
Don’t worry.
There’s an exciting solution that can take your descriptive research design to a whole new level. It’s called ChartExpo.
ChartExpo is a powerful Excel add-in that will revolutionize how you analyze your best survey questions .
With its user-friendly interface and a wide range of descriptive research design survey-based charts, ChartExpo effortlessly transforms descriptive research design data into actionable insights.
You don’t need to be a programming genius to use ChartExpo’s features.
One of ChartExpo’s standout features is the Likert Scale Chart. This chart acts as a magnifying glass, allowing you to dive deep into your descriptive research design data for hidden insights.
Try ChartExpo’s free 7-day trial and experience its full potential
How to Install ChartExpo in Excel?
Let’s imagine you run an online business. You want to know whether your customers are satisfied with your brand offers.
You’ve organized a survey to gather feedback from your target customers using the sample questions below:
- Do you agree the price of our product is affordable?
- Do you agree the quality of the product is better than others?
- Do you agree our product is available in all stores in your city?
In the coming section, we’ll use ChartExpo, and sample data to demonstrate how you can leverage a Likert Scale Chart to visualize survey data for insights.
Before we dive into this, we’ll show you how to install ChartExpo in Excel.
To get started with ChartExpo in Excel, follow the steps below:
- Open your Microsoft Excel.
- Open the worksheet and click the Insert button to access the My Apps

- Click the Insert button to initiate the ChartExpo engine.

- Click the Search box and type “Likert Scale Chart.”

- Highlight your data and click the Create Chart From Selection button, as shown below.

- Use the multiple-choice responses you deployed in your survey to gather responses to map your Likert Scale Chart.
In our case we’ll use the following multiple-choice responses:
- Strongly Disagree=1
- Neither agree nor disagree=3
- Strongly Agree=5

- Click the Create Chart button, as shown above.

- To add the chart header, click the Edit Chart
- Once the Chart Header Properties window shows, fill in your header in Line 1, as shown.

- Toggle the small button below Line 2 to the right side to activate the header.
- Click the Apply button, as shown above.

- To edit the legend properties, click the pencil-like icon on the X-axis.
- Once the Legend Properties window shows, fill in your legend below the Text
- Click the Apply All button, as shown above.
- Click the Save Changes button to preserve all the changes.
- Check out the final Likert Scale chart below.

- Out of the surveyed customers, 60% agreed that our product is available in all stores, while 40% disagreed.
- When it comes to product quality, 45% of customers agreed and 35% disagreed. 20% chose not to answer.
- Regarding product price, 55% of customers agreed and 25% disagreed. 20% remained neutral.
- In terms of overall survey responses, 54% of customers provided positive feedback, 34% gave negative responses, and 13% did not provide a response.
Advantages of Descriptive Research
- Detailed Insights : Provides a thorough understanding of a phenomenon by capturing detailed information on specific characteristics and behaviors.
- Real-World Relevance : Studies subjects in their natural environments, offering data that reflects real-life settings without manipulation.
- Foundation for Further Research : Helps to identify trends, patterns, and relationships that can serve as a basis for hypothesis formulation and further studies.
- Cost-Effective : Often less expensive than experimental research, especially when using surveys or observational techniques.
Disadvantages of Descriptive Research
- Lacks Causality : It focuses on “what” rather than “why,” so it cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Prone to Bias : Observations and surveys may be influenced by researcher or participant biases, impacting data accuracy.
- Limited Control : Researchers cannot manipulate variables, which may result in findings affected by external factors.
- Data Interpretation Challenges : Large volumes of descriptive data can be difficult to analyze and may lead to subjective interpretations.
How is data collected in a descriptive research design?
Data in descriptive research design is collected through various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and existing records.
Surveys are commonly used, employing questionnaires to gather information.
Interviews involve direct conversations, while observations involve watching and recording behaviors. Existing records provide valuable data for analysis.
What are the key differences between descriptive and experimental research design?
The key differences between descriptive and experimental research designs lie in their objectives and methodologies.
Descriptive research aims to describe and analyze existing phenomena, while experimental research seeks to establish cause-and-effect relationships through the manipulation of variables.
Descriptive research observes, while experimental research controls and manipulates variables.
In conclusion, descriptive research design offers valuable insights into the characteristics, behaviors, and trends of a particular subject, such as your target market.
By employing methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations, you can gather comprehensive data to understand a phenomenon’s “what” and “how”.
ChartExpo, a user-friendly data visualization tool, can further enhance the power of descriptive research design.
Its intuitive charts and graphs allow you to present your findings in a visually appealing and easily understandable format.
By using ChartExpo, you can effectively communicate your research results and engage your audience.
The benefits of employing descriptive research design are numerous.
It enables you to describe and analyze real-world phenomena, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. More so, it provides a foundation for further research.
To leverage the benefits of descriptive research design and effectively present your findings, try ChartExpo today!
How much did you enjoy this article?
We will help your ad reach the right person, at the right time
Your Data. Your Insights.
Actionable insights discovered for you. Now you can do more in less time.
PPCexpo Keyword Planner
Find the perfect keyword. surprise yourself..
PPCexpo Keyword Planner will help you align your keywords with the customers’ intent.
Free Google Ads Audit Report.
Frequent audits will help you optimize your PPC campaign for success.
ChartExpo PPC Charts
Picture a thousand numbers. see the big picture..
Visualizations give you the ability to instantly grasp the insights hidden in your numbers.
PPCexpo PPC Reports
Simple and easy ppc reporting. for everyone..
Experience the new revolution in reporting … click your way to insights, don’t scroll.
Combinations Calculator
Do the math..
Calculate the number of combinations in your PPC campaign. It may surprise you.
Insightful pay-per-click tips and tricks, delivered to your inbox weekly.

Related articles
Google Sheets Tips and Tricks You Should Know
Explore Google Sheets tips and tricks to improve productivity. This guide offers techniques to streamline data, organize sheets, and boost your skills.
Confirmation Bias: Are You Only Seeing What You Want to See?
Confirmation bias in data visualization skews decisions by reinforcing existing beliefs. Learn how to recognize and avoid it to keep your insights objective. Read on!
What is Heteroskedasticity and How to Present it?
What is heteroskedasticity? Click here to learn how to detect, visualize, and correct heteroskedasticity for better, more reliable data analysis.
Table vs. Chart: Precision or Visual Impact – What's Right for You
Tables present detailed data with precision, while charts highlight trends at a glance. Need accuracy or quick insights? Learn the differences and choose the right one!
Descriptive Stats in Excel to Enhance Insights
Descriptive stats in Excel help summarize data with measures like mean and median. This guide helps you create reports, save time, and improve your analysis.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of Descriptive Research Design. 1. Healthcare Research. Study: Assessing patient satisfaction in a hospital. Method: Distributing surveys to patients. Outcome: Identified areas of improvement in hospital services, such as wait times and staff communication. 2. Marketing Research.
In short, a good research design helps us to structure our research. Marketers use different types of research design when conducting research. There are four common types of research design — descriptive, correlational, experimental, and diagnostic designs. Let’s take a look at each in more detail.
Descriptive research design. Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis. As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help ...
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what, where, when and how questions, but not why questions. A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables. Unlike in experimental research, the researcher does ...
Descriptive Research in Marketing. Design: Quantitative, using a survey. Goal: To understand consumer preferences for eco-friendly packaging. Method: Survey distributed to a random sample of consumers asking about purchasing behaviors and attitudes toward sustainability. Experimental Research in Psychology. Design: Experimental, quantitative.
This descriptive research method involves observing and gathering data on a population or phenomena without manipulating variables. It is employed in psychology, market research, and other social science studies to track and understand human behavior. Observation is an essential component of descriptive research.
Descriptive research is a method for observing and describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon without manipulating variables. It focuses on providing a clear snapshot of “what is,” helping researchers gather factual information, identify patterns, and inform decision-making. 2.
Descriptive research answers the “what” questions in statistical form. As the output is in emphasizes form, it is easy for the researcher to deduce results and implement them. Because of this characteristic of descriptive research, it is popularly used in market researches. 2. The basis for secondary research.
Definition: Descriptive research design allows you to observe and describe various aspects of a subject in your business without manipulating or influencing the variables involved. It’s like taking a snapshot of the world as it is, providing you with a detailed picture of the who, what, where, and how. In this type of research, the main goal ...
Some characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitativeness. Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences. Qualitativeness.