Pete’s PowerPoint Station
- Science Index
- Math/Maths Index
- Language Arts/Literature Index
- Social Studies Index
- Holidays Index
- Art, Music, and Many More, A-Z
- Meteorology
- Four Seasons
- Pre-Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Pre-Calculus & Calculus
- Language Arts
- Punctuation
- Social Studies
- World Religions
- US Government
- Criminal Justice
- Famous People
- American History
- World History
- Ancient History
- The Middle Ages
- Architecture
- All Topics, A–Z
- Privacy & Cookie Policy
- Presentations

Free Science PowerPoints for Kids & Teachers – Black Holes
Did You Know?
A black hole is a region of space where the gravitational force is so strong that nothing can escape from it, including light. Gravity of this strength may be produced by matter which has been squeezed into a very tiny space.
Free Presentations in PowerPoint format
Understanding Black Holes
Black Holes in a Different Light
Dark Matter and Black Holes
What Makes Up a Black Hole?
What Do Black Holes Look Like? This!
Can We Detect Black Holes with Atlas?
Black Hole Gravity Wells
Black Hole PowerPoints at FreeClubWeb
Black Holes
Hubble Site – Black Holes
See Also: Astronomy , Space Index
Free Black Holes Games & Activities for Kids
For Teachers
Lots of Lessons – Black Holes
What Is a Black Hole?
Free Astronomy Video Clips
Free Clipart
Free Templates

- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
Black Holes: Facts, Theory, and Definition
Published by Melvin McCormick Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Black Holes: Facts, Theory, and Definition"— Presentation transcript:

Black Holes Devouring Monsters of the Universe. How are they made? Only the very largest stars, beginning with at least 50 solar masses, are able to form.

Notes 30.2 Stellar Evolution

Special Stars Neutron Stars Black Holes. Massive Star Evolution 4 Massive stars burn hot and bright while on the main sequence, usually as a blue or whitish-blue.
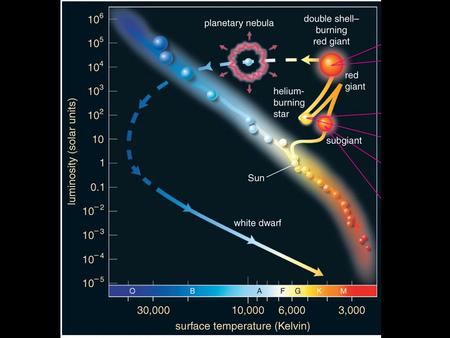
Supernovae and nucleosynthesis of elements > Fe Death of low-mass star: White Dwarf White dwarfs are the remaining cores once fusion stops Electron degeneracy.

Stellar Evolution Describe how a protostar becomes a star.

Chapter 12 Space Exploration.

Caty Pilachowski IU Astronomy Mini-University 2014.

Chandrasekar Limit--white dwarfs form with remnant under 1.3 M sun.

Black Holes. Outline Escape velocity Definition of a black hole Sizes of black holes Effects on space and time Tidal forces Making black holes Evaporation.
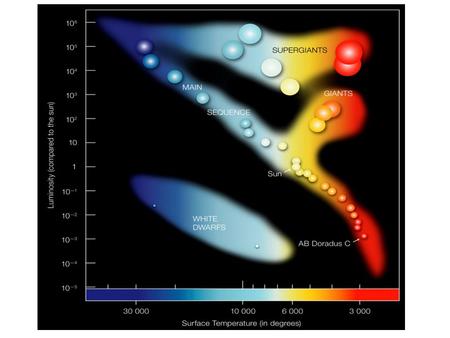
The last days of massive stars Outer layers expand as helium core contracts Helium fuses to form carbon, carbon fuses with helium to make oxygen, and.
Earth Science 25.2B : Stellar Evolution

Black Holes by Dalton, Connor, and Bryan. What is a black hole? The idea of black holes comes from the escape velocity. The escape velocity basically.

Black Holes Dennis O’Malley. How is a Black Hole Created? A giant star (more than 25x the size of the sun) runs out of fuel –The outward pressure of the.

Astronomy for beginners Black Holes Aashman Vyas.

Black Holes By Irina Plaks. What is a black hole? A black hole is a region in spacetime where the gravitational field is so strong that nothing, not even.

13.3 Black Holes: Gravity’s Ultimate Victory Our Goals for Learning What is a black hole? What would it be like to visit a black hole? Do black holes really.

Black Holes.

Astrophysics and Cosmology Some of the biggest ideas of the last 100 years Of the Stars, the Universe and Everything!!! (the answer is )

Unit 06 “Circular Motion, Gravitation and Black Holes” “Gravitation and Black Holes”

Black Holes By: Mikenzie Hammel.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
